J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2010 Feb;45(1):78-82. 10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.1.78.
Intramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis (ISCM) Arising from Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Haeundae Hospital, Busan, Korea. sirjeon@kyuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2185598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2010.45.1.78
Abstract
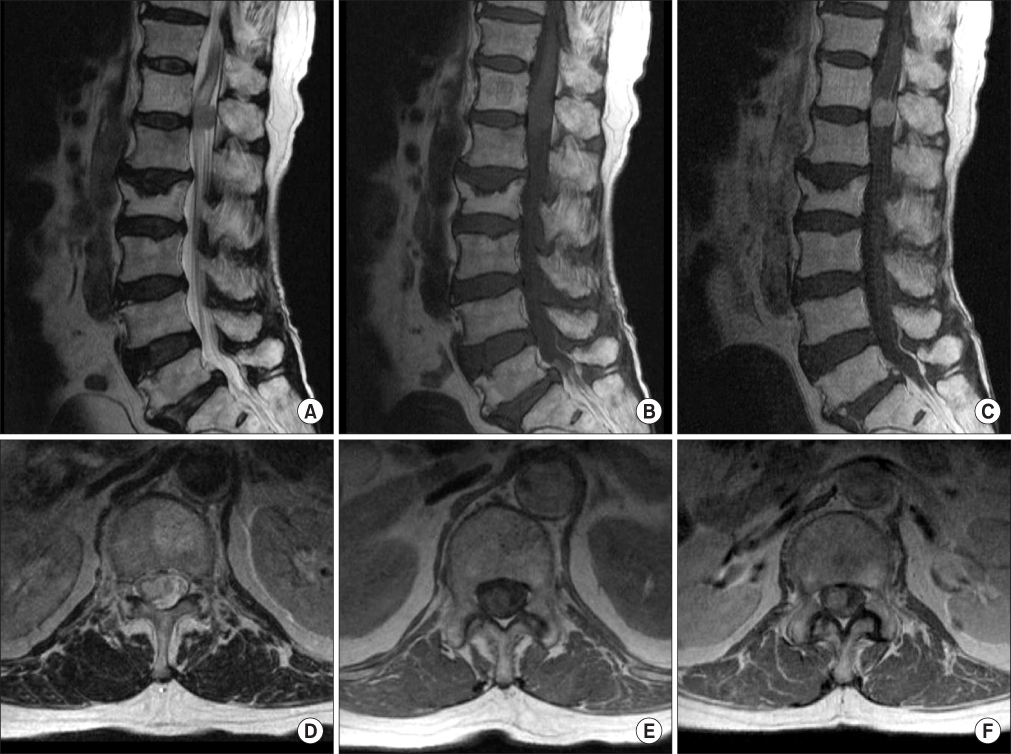
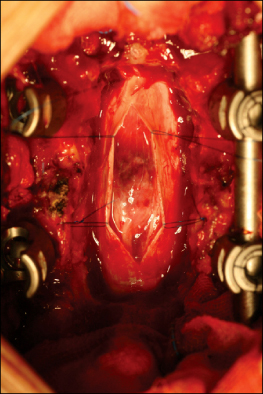
- Intramedullary spinal cord metastases occurring from any malignant tumor are usually accompanied by frequent metastases in the intracranium. The clinical features of this disease have been described as the rapid progression of neurologic deficit that can lead to complete paraplegia. In this case, the authors treated a 76-year-old woman, who was diagnosed with an intramedullary spinal cord metastasis arising from a small cell lung cancer without an invasion of the brain, with decompressive surgery and posterior instrumentation. The patient suffered from weakness of her legs, walking difficulties, and urinary and fecal incontinence. Her preoperative neurologic symptoms were improved significantly after surgery. The patient did not want to have further treatment for the primary cancer, and she died from pneumonia caused by aggravation of the underlying disease 3 months after surgery. We report this rare case, which was diagnosed as a metastasis of a small cell lung cancer postoperatively, with a review of the relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Conill C, Marruecos J, Verger E, et al. Clinical outcome in patients with intramedullary spinal cord metastases from lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2007. 9:172–176.
Article2. Costigan DA, Winkelman MD. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. A clinicopathological study of 13 cases. J Neurosurg. 1985. 62:227–233.3. Dam-Hieu P, Seizeur R, Mineo JF, Metges JP, Meriot P, Simon H. Retrospective study of 19 patients with intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2009. 111:10–17.
Article4. Endo S, Hida K, Yano S, et al. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis treated with radiation therapy: report of 3 cases. No Shinkei Geka. 2008. 36:345–349.5. Gasser T, Sandalcioglu IE, El Hamalawi B, van de Nes JA, Stolke D, Wiedemayer H. Surgical treatment of intramedullary spinal cord metastases of systemic cancer: functional outcome and prognosis. J Neurooncol. 2005. 73:163–168.
Article6. Kalayci M, Cağavi F, Gül S, Yenidünya S, Açikgőz B. Intramedullary spinal cord metastases: diagnosis and treatment - an illustrated review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2004. 146:1347–1354.7. Kim TG, Yoon DH, Kim YS. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2002. 31:501–504.8. Oh YK, Park HC. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis: a report of two cases and a review of the literature. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2001. 19:353–358.9. Sutter B, Arthur A, Laurent J, et al. Treatment options and time course for intramedullary spinal cord metastasis. Report of three cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 1998. 4:e3.
Article10. Yang JW, Lee JI. Intramedullary spinal cord metastasis: case report. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003. 33:422–424.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Intramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis From Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis: A Report of Two Cases and a Review of the Literature
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis From Rectal Cancer
- Newly Developed Weakness of Lower Extremities Despite Improved Brain Metastasis of Lung Cancer after Radiotherapy
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis