J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2012 Mar;20(1):30-36. 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.30.
Early Cardiac Valvular Changes in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Transesophageal Echocardiography Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology, School of Medicine Kyung Hee University, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea. issohn@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Rheumatology, School of Medicine Kyung Hee University, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2177338
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.30
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
This study was conducted to determine the early cardiac valvular changes in young male ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients.
METHODS
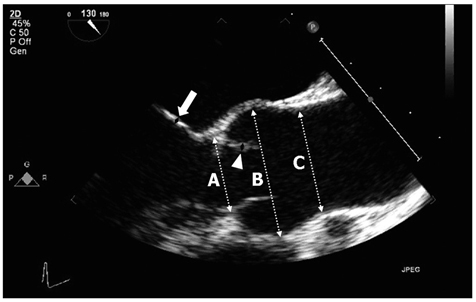
A total of 70 AS patients on treatment without clinical cardiac symptoms were divided into group I (< 10 years, n = 50) and group II (> or = 10 years, n = 20) depending on their disease duration after first diagnosis. Twenty-five healthy volunteers were selected as control subjects. All the subjects underwent transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography, electrocardiography, and rheumatologic evaluation for AS patients.
RESULTS
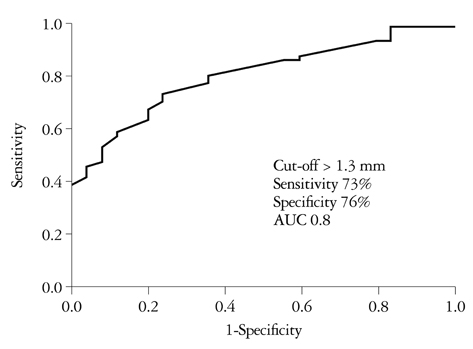
The thickness of both the aortic and mitral valve was more increased in AS patients than in controls. Aortic valve thickness over 1.3 mm could predict AS with a sensitivity of 73% and specificity of 76%. The prevalence of aortic valve thickening was higher in the AS group compared to the controls. The prevalence of aortic and mitral regurgitation was very low and there was no difference between the controls and the patients. The aortic valve thickening was related to longer disease duration, high blood pressure, disease activity and inflammatory markers.
CONCLUSION
Thickening of the aortic and mitral valve was observed without regurgitation in male AS patients early in the course of their disease without clinical cardiac manifestations. This subclinical change of aorto-mitral valve in early AS should be considered and followed up to determine its prognostic implication and evolution.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis and Cardiac Abnormalities
Dong Heon Yang
J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2012;20(1):23-24. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2012.20.1.23.
Reference
-
1. Braun J, Sieper J. Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet. 2007. 369:1379–1390.
Article2. Bulkley BH, Roberts WC. Ankylosing spondylitis and aortic regurgitation. Description of the characteristic cardiovascular lesion from study of eight necropsy patients. Circulation. 1973. 48:1014–1027.3. Lautermann D, Braun J. Ankylosing spondylitis--cardiac manifestations. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002. 20:S11–S15.4. O'Neill TW, Bresnihan B. The heart in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992. 51:705–706.5. Roldan CA, Chavez J, Wiest PW, Qualls CR, Crawford MH. Aortic root disease and valve disease associated with ankylosing spondylitis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998. 32:1397–1404.
Article6. Palazzi C, D'Angelo S, Lubrano E, Olivieri I. Aortic involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008. 26:S131–S134.7. Tucker CR, Fowles RE, Calin A, Popp RL. Aortitis in ankylosing spondylitis: early detection of aortic root abnormalities with two dimensional echocardiography. Am J Cardiol. 1982. 49:680–686.
Article8. Arnason JA, Patel AK, Rahko PS, Sundstrom WR. Transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of the aortic root and subvalvular structures in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1996. 23:120–123.9. Flachskampf FA, Badano L, Daniel WG, Feneck RO, Fox KF, Fraser AG, Pasquet A, Pepi M, Perez de Isla L, Zamorano JL, Roelandt JR, Piérard L. European Association of Echocardiography. Echo Committee of the European Association of Cardiothoracic Anaesthesiologists. Recommendations for transoesophageal echocardiography: update 2010. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010. 11:557–576.
Article10. van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984. 27:361–368.11. Pearson AC, Guo R, Orsinelli DA, Binkley PF, Pasierski TJ. Transesophageal echocardiographic assessment of the effects of age, gender, and hypertension on thoracic aortic wall size, thickness, and stiffness. Am Heart J. 1994. 128:344–351.
Article12. Winker MA. Age and the cardiovascular system. N Engl J Med. 1993. 328:1279–1280.
Article13. Cowling P, Ebringer R, Ebringer A. Association of inflammation with raised serum IgA in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1980. 39:545–549.
Article14. Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994. 21:2286–2291.15. Jones SD, Calin A, Steiner A. An update on the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity and Functional Indices (BASDAI, BASFI): excellent Cronbach's alpha scores. J Rheumatol. 1996. 23:407.16. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005. 18:1440–1463.
Article17. Douglas PS, Khandheria B, Stainback RF, Weissman NJ, Brindis RG, Patel MR, Alpert JS, Fitzgerald D, Heidenreich P, Martin ET, Messer JV, Miller AB, Picard MH, Raggi P, Reed KD, Rumsfeld JS, Steimle AE, Tonkovic R, Vijayaraghavan K, Yeon SB, Hendel RC, Peterson E, Wolk MJ, Allen JM. TTE/TEE Appropriateness Criteria Writing Group. TTE/TEE Appropriateness Criteria Technical Panel. ACCF Appropriateness Criteria Working Group. American College of Cardiology Foundation Quality Strategic Directions Committee Appropriateness Criteria Working Group. American Society of Echocardiography. American College of Emergency Physicians. American Society of Nuclear Cardiology. Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. ACCF/ASE/ACEP/ASNC/SCAI/SCCT/SCMR 2007 appropriateness criteria for transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiography: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Quality Strategic Directions Committee Appropriateness Criteria Working Group, American Society of Echocardiography, American College of Emergency Physicians, American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, and the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Endorsed by the American College of Chest Physicians and the Society of Critical Care Medicine. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007. 20:787–805.
Article18. Nagueh SF, Middleton KJ, Kopelen HA, Zoghbi WA, Quiñones MA. Doppler tissue imaging: a noninvasive technique for evaluation of left ventricular relaxation and estimation of filling pressures. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997. 30:1527–1533.
Article19. Sohn DW, Chai IH, Lee DJ, Kim HC, Kim HS, Oh BH, Lee MM, Park YB, Choi YS, Seo JD, Lee YW. Assessment of mitral annulus velocity by Doppler tissue imaging in the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997. 30:474–480.
Article20. Lacombe F, Dart A, Dewar E, Jennings G, Cameron J, Laufer E. Arterial elastic properties in man: a comparison of echo-Doppler indices of aortic stiffness. Eur Heart J. 1992. 13:1040–1045.
Article21. Stefanadis C, Stratos C, Boudoulas H, Kourouklis C, Toutouzas P. Distensibility of the ascending aorta: comparison of invasive and non-invasive techniques in healthy men and in men with coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 1990. 11:990–996.
Article22. Brunner F, Kunz A, Weber U, Kissling R. Ankylosing spondylitis and heart abnormalities: do cardiac conduction disorders, valve regurgitation and diastolic dysfunction occur more often in male patients with diagnosed ankylosing spondylitis for over 15 years than in the normal population? Clin Rheumatol. 2006. 25:24–29.
Article23. Demiralp E, Kardesoglu E, Kiralp MZ, Cebeci BS, Keskin I, Ozmen N, Dursun H. Aortic elasticity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Cardiol. 2004. 59:630–634.
Article24. Nishino M, Tanouchi J. Transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of atherosclerosis. Korean Circ J. 2008. 38:573–582.
Article25. Sugawara J, Hayashi K, Yokoi T, Tanaka H. Age-associated elongation of the ascending aorta in adults. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008. 1:739–748.
Article26. Peters MJ, van Eijk IC, Smulders YM, Serne E, Dijkmans BA, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Nurmohamed MT. Signs of accelerated preclinical atherosclerosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2010. 37:161–166.
Article27. Caliskan M, Erdogan D, Gullu H, Yilmaz S, Gursoy Y, Yildirir A, Yucel E, Muderrisoglu H. Impaired coronary microvascular and left ventricular diastolic functions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Atherosclerosis. 2008. 196:306–312.
Article28. Heeneman S, Daemen MJ. Cardiovascular risks in spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. 19:358–362.
Article29. Han C, Robinson DW Jr, Hackett MV, Paramore LC, Fraeman KH, Bala MV. Cardiovascular disease and risk factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 2006. 33:2167–2172.30. Crowley JJ, Donnelly SM, Tobin M, FitzGerald O, Bresnihan B, Maurer BJ, Quigley PJ. Doppler echocardiographic evidence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in ankylosing spondylitis. Am J Cardiol. 1993. 71:1337–1340.
Article31. Yildirir A, Aksoyek S, Calguneri M, Oto A, Kes S. Echocardiographic evidence of cardiac involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol. 2002. 21:129–134.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinieal Values of Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography ( SPECT ) in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- A Study on Cardiac Abnormalities in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis and Undifferentiated Spondyloarthropathy
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Prevention And Surgical Correction Of Deformity
- Ankylosing Spondylitis and Cardiac Abnormalities
- Progressive Pulmonary Fibrocystic Changes of Both Upper Lungs in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis