Patterns of Recurrence after Breast-Conserving Treatment for Early Stage Breast Cancer by Molecular Subtype
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. doho.choi@samsung.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2175642
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2011.14.1.46
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To study clinical features and patterns of recurrence after breast-conserving treatment (BCT) for three molecular subtypes of early stage breast cancer.
METHODS
The sample studied included 596 patients with T1-2N0-1 breast cancer who received BCT. Three groups were defined by receptor status. Luminal: estrogen receptor (ER) or progesterone receptor (PR) positive; triple negative (TN): ER, PR, and epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) receptor negative; and HER2 overexpressing: ER and PR negative but HER2 receptor positive.
RESULTS
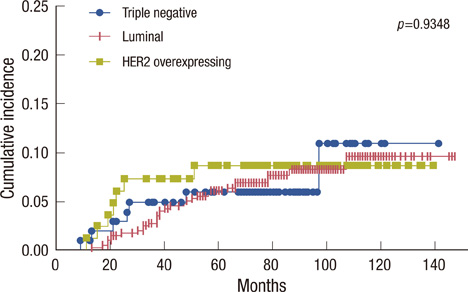
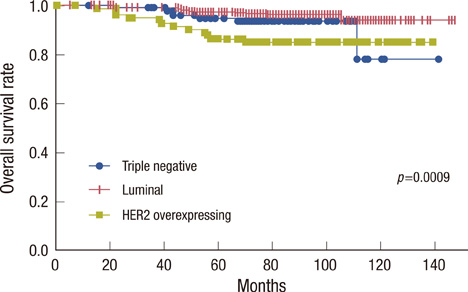
The number of patients in each group was 408 (68.5%), 105 (17.6%), and 83 (13.9%), respectively. The median follow-up period was 79 months. The TN and HER2 subtypes occurred in younger patients (p=0.0007) and had higher nuclear grade and poorer histologic grade (p<0.0001 and 0.0071, respectively). During the follow-up period, locoregional recurrence was detected as the first site of recurrence in 26 (6.4%), 11 (10.5%), and 9 (10.8%) patients in the luminal, TN, and HER2 subtypes, respectively (p=0.1924). Thirty-one (7.6%), 7 (6.7%), and 7 (8.4%) patients in each group had distant metastases as the first sign of recurrence (p=0.8996). Median time to locoregional and distant recurrence was shorter in the HER2 subtype (p=0.0889 and 0.0780, respectively), and the HER2 subtype was significantly associated with poor overall survival (p=0.0009).
CONCLUSION
After BCT in Korean women with early stage breast cancer, the patterns of recurrence were not different among the molecular subtypes, although the TN and HER2 subtypes were associated with younger age, higher nuclear grade, and poorer histologic grade.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Breast
Breast Neoplasms
Epidermal Growth Factor
Estrogens
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Mastectomy, Segmental
Neoplasm Metastasis
Phenobarbital
Receptor, erbB-2
Receptors, Estrogen
Receptors, Progesterone
Recurrence
Epidermal Growth Factor
Estrogens
Phenobarbital
Receptor, erbB-2
Receptors, Estrogen
Receptors, Progesterone
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Risk Factors for Distant Metastasis as a Primary Site of Treatment Failure in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
Hyeli Park, Sei Kyung Chang, Ja Young Kim, Bo Mi Lee, Hyun Soo Shin
Chonnam Med J. 2014;50(3):96-101. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2014.50.3.96.Impact of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Phenotype on Prognosis in Patients with Stage I Breast Cancer
Jeong Eun Kim, Heui June Ahn, Jin-Hee Ahn, Dok Hyun Yoon, Sung-Bae Kim, Kyung Hae Jung, Gyung-Yub Gong, Mi-Jung Kim, Byung Ho Son, Sei Hyun Ahn
J Breast Cancer. 2012;15(2):197-202. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.2.197.Analysis of factors related systemic recurrence after breast conserving surgery in stage I breast cancer
Yoon-Seok Kim, Dong-Won Ryu, Chung-Han Lee
Kosin Med J. 2018;33(3):289-296. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.3.289.
Reference
-
1. Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000. 406:747–752.
Article2. Sørlie T. Molecular portraits of breast cancer: tumour subtypes as distinct disease entities. Eur J Cancer. 2004. 40:2667–2675.
Article3. Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. 98:10869–10874.
Article4. Brenton JD, Carey LA, Ahmed AA, Caldas C. Molecular classification and molecular forecasting of breast cancer: ready for clinical application? J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:7350–7360.
Article5. Sørlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, et al. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:8418–8423.
Article6. Sotiriou C, Neo SY, McShane LM, Korn EL, Long PM, Jazaeri A, et al. Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population-based study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. 100:10393–10398.
Article7. Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006. 295:2492–2502.
Article8. Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:5367–5374.
Article9. Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO. Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:2568–2581.
Article10. van Dongen JA, Voogd AC, Fentiman IS, Legrand C, Sylvester RJ, Tong D, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. 92:1143–1150.
Article11. Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:1227–1232.
Article12. Poggi MM, Danforth DN, Sciuto LC, Smith SL, Steinberg SM, Liewehr DJ, et al. Eighteen-year results in the treatment of early breast carcinoma with mastectomy versus breast conservation therapy: the National Cancer Institute Randomized Trial. Cancer. 2003. 98:697–702.
Article13. Lazovich D, Solomon CC, Thomas DB, Moe RE, White E. Breast conservation therapy in the United States following the 1990 National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference on the treatment of patients with early stage invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1999. 86:628–637.
Article14. Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, et al. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:5652–5657.
Article15. Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, et al. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008. 26:2373–2378.
Article16. Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. 13(15 Pt 1):4429–4434.
Article17. Freedman GM, Anderson PR, Li T, Nicolaou N. Locoregional recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery and radiation. Cancer. 2009. 115:946–951.
Article18. Korean Breast Cancer Society. Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients in Korea in year 2000. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2002. 5:217–224.19. Yoo KY, Shin A. Epidemiological characteristics of breast cancer in Korea. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2002. 5:209–211.
Article20. Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M, Leyland-Jones B, Goldhirsch A, Untch M, Smith I, et al. Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1659–1672.21. Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, Suman VJ, Geyer CE Jr, Davidson NE, et al. Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:1673–1684.
Article22. Matos I, Dufloth R, Alvarenga M, Zeferino LC, Schmitt F. p63, cytokeratin 5, and P-cadherin: three molecular markers to distinguish basal phenotype in breast carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2005. 447:688–694.
Article23. Siziopikou KP, Cobleigh M. The basal subtype of breast carcinomas may represent the group of breast tumors that could benefit from EGFR-targeted therapies. Breast. 2007. 16:104–107.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast-Conserving Surgery With or Without Radiation Therapy for Early Breast Cancer
- Radiation Therapy for Patiens with Early-Stage Breast Carcinoma Treated with Breast-Conserving Surgery
- Analysis of factors related systemic recurrence after breast conserving surgery in stage I breast cancer
- Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer
- Comparison of Psychiatric Symptoms between Total Mastectomy and Breast Conserving Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients