Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2015 Jun;19(2):122-126. 10.13104/imri.2015.19.2.122.
Imaging Features of Madelung's Disease: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Pusan National University Hospital, Biomedical Research Institute, Busan, Korea. lis@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2175593
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.2.122
Abstract
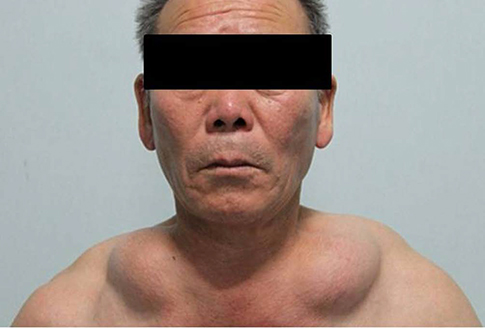
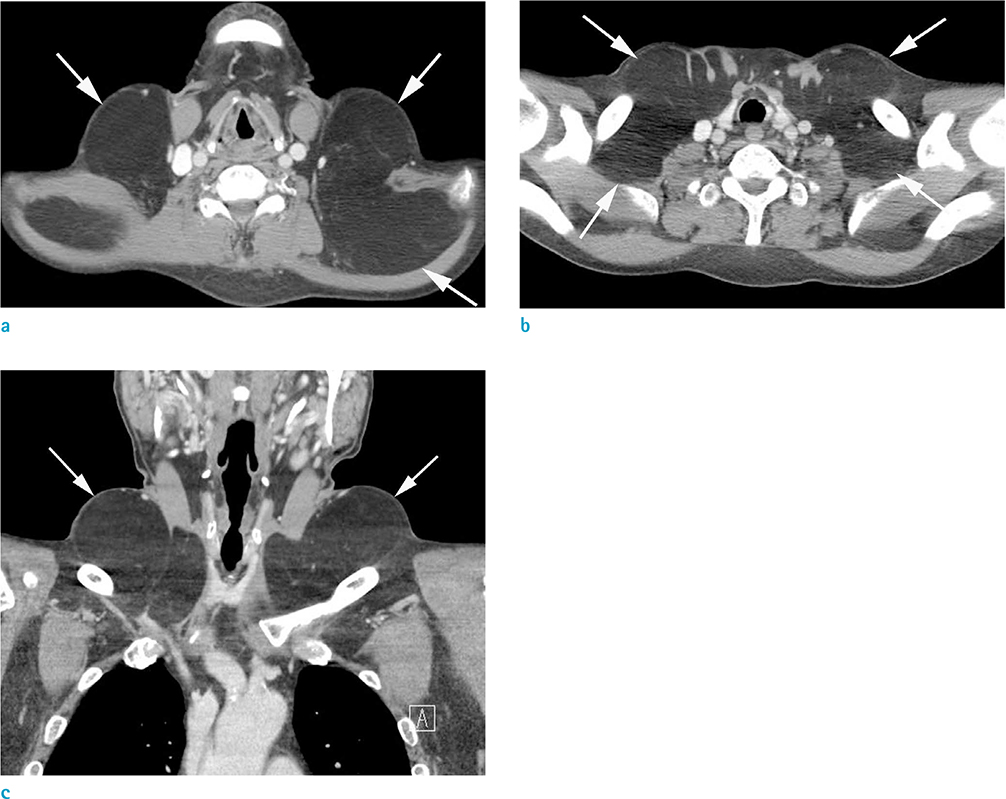
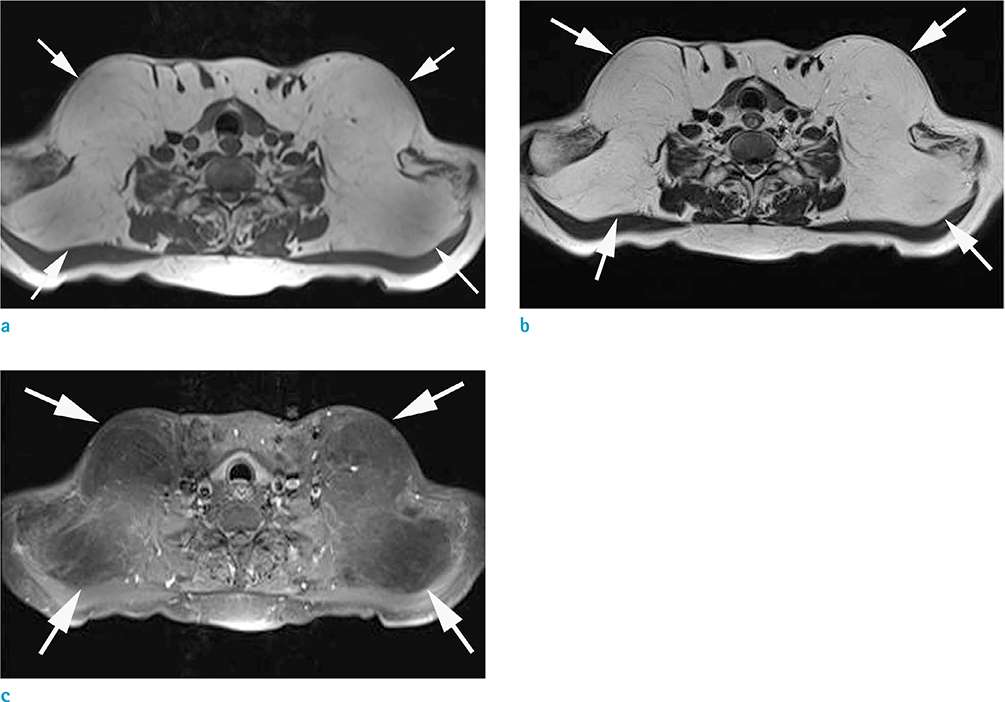
- Madelung's disease, or benign symmetric lipomatosis, is an uncommon disorder that is characterized by massive symmetrical deposits of adipose tissue in the upper trunk, neck and head, and is usually associated with alcohol abuse; as such, patients usually complain of cosmetic issues. Historically, Madelung's disease is usually encountered in men between 30 and 60 years of age, and is more prevalent in the Mediterranean population. In this case study, we describe a rare case of Madelung's disease, in an Asian patient who presented with symmetrically located bilateral masses in the anterior neck, which grew progressively larger over a period of seven years.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bulum T, Duvnjak L, Car N, Metelko Z. Madelung's disease: case report and review of the literature. Diabetologia Croatica. 2007; 36:25–30.2. Milisavljevic D, Zivic M, Radovanovic Z, Stankovic P. Severe dyspnea as atypical presenting symptom of Madelung's disease. Hippokratia. 2010; 14:133–135.3. Brea-Garcia B, Cameselle-Teijeiro J, Couto-Gonzalez I, Taboada-Suarez A, Gonzalez-Alvarez E. Madelung's disease: comorbidities, fatty mass distribution, and response to treatment of 22 patients. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2013; 37:409–416.4. Landis MS, Etemad-Rezai R, Shetty K, Goldszmidt M. Case 143: Madelung disease. Radiology. 2009; 250:951–954.5. Ruzicka T, Vieluf D, Landthaler M, Braun-Falco O. Benign symmetric lipomatosis Launois-Bensaude. Report of ten cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987; 17:663–674.6. Becker-Wegerich P, Steuber M, Olbrisch R, Ruzicka T, Auburger G, Hofhaus G. Defects of mitochondrial respiratory chain in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Arch Dermatol Res. 1998; 290:652–655.7. Yeh NC, Yang CY, Chou CW, Yen FC, Lee SY, Tien KJ. Madelung's disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 97:3012–3013.8. Klopstock T, Naumann M, Schalke B, et al. Multiple symmetric lipomatosis: abnormalities in complex IV and multiple deletions in mitochondrial DNA. Neurology. 1994; 44:862–866.9. Berkovic SF, Andermann F, Shoubridge EA, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in multiple symmetrical lipomatosis. Ann Neurol. 1991; 29:566–569.10. Zhang XY, Li NY, Xiao WL. Madelung disease: manifestations of CT and MR imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008; 105:e57–e64.11. Smith PD, Stadelmann WK, Wassermann RJ, Kearney RE. Benign symmetric lipomatosis (Madelung's disease). Ann Plast Surg. 1998; 41:671–673.12. Gologorsky Y, Gologorsky D, Yarygina AS, Surti U, Zirwas MJ. Familial multiple lipomatosis: report of a new family. Cutis. 2007; 79:227–232.