Ewha Med J.
2014 Sep;37(2):116-120. 10.12771/emj.2014.37.2.116.
Portal and Splenic Vein Thrombosis Successfully Treated with Anticoagulants in Acute Pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Red Cross Hospital, Seoul, Korea. love1226@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2171294
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2014.37.2.116
Abstract
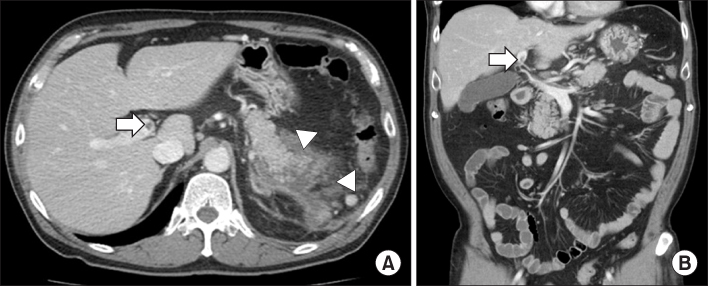
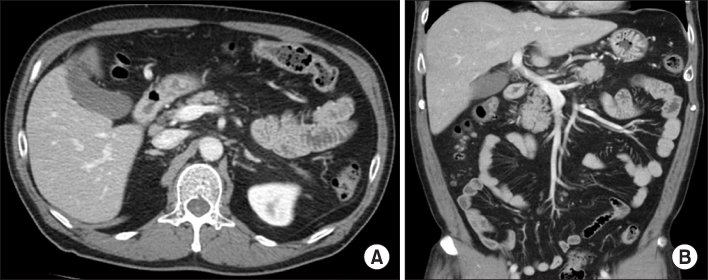
- Splanchnic vein thrombosis arising from complications of acute pancreatitis is very rare. It usually occurs as a form of portal, splenic and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, either in combination or separately. It could develop portal hypertension, bowel ischemia and gastrointestinal variceal bleeding. Treatment of splanchnic vein thrombosis includes anticoagulants, thrombolysis, insertion of shunts, bypass surgery and liver transplantation. In some cases, anticoagulation therapy may be considered to prevent complications. However, the standard protocol for anticoagulation in splanchnic vein thrombosis has not been determined yet. We report a case of 43-year-old man who had portal and splenic vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. The patient was successfully treated with oral anticoagulants following low molecular weight heparin therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mallick I, Winslect M. Vascular complications of pancreatitis. JOP. 2004; 5:328–337.2. Gonzelez HJ, Sahay SJ, Samadi B, Davidson BR, Rahman SH. Splanchnic vein thrombosis in severe acute pancreatitis: a 2-year, single-institution experience. HPB (Oxford). 2011; 13:860–864.3. Bang SM. Management of venous thrombosis in atypical location. Korean J Med. 2014; 86:20–25.4. Chung KY. Portal vein thrombosis. Korean J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; 27:97–102.5. Kim HS, Hong SH, Park HS, Lee ES, Kang IW. Hepatic infarction complicating acute pancreatitis: a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000; 43:73–76.6. Kim WS, Lee JW, Lee ES, Yang MH, Park SW, Kim SY, et al. A case of isolated superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2002; 40:68–71.7. Chai JY, Yun SI, Bae SS, Chae HB, Park SM, Youn SJ, et al. A case of jejunal infarction and perforation due to acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:120–124.8. Ko H, Jung SH, Yoon SJ, Kim AN, John BM, Choi GY, et al. Portal vein thrombosis that successfully treated with low molecular weight heparin in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Med. 2005; 69:541–544.9. Cheun JY, Lee TH, Kim YS, Lim DS, Kim SM, Im EH, et al. Portal and splenic vein thrombosis successfully treated with low molecular weight heparin in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Med. 2008; 74:S37–S41.10. Song HS, Yang NR, Jin SH, Choi KD, Jang YT. Isolated splenic vein thrombosis associated with acute pancreatitis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009; 12:221–225.11. Na BS, John BM, Kim KB, Lee JS, Jo HW, Seock CH, et al. Spontaneous dissolution of isolated superior mesenteric vein thrombosis in acute pancreatitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011; 57:38–41.12. Kim JH, Lee DG, Park SB, Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Lee SH, et al. A case of portal vein thrombosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis treated with low-molecular-weight heparin. Korean J Med. 2013; 84:76–80.13. Sobhonslidsuk A, Reddy KR. Portal vein thrombosis: a concise review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002; 97:535–541.14. Heider TR, Azeem S, Galanko JA, Behrns KE. The natural history of pancreatitis-induced splenic vein thrombosis. Ann Surg. 2004; 239:876–880.15. Riva N, Ageno W, Schulman S, Bang SM, Sartori MT, Grandone E, et al. In : Reitsma P, Rosendaal F, Levi M, editors. Antithrombotic threatment of splanchnic vein thrombosis in the ISTH international registry: results of 6-month follow-up. XXIV Congress of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis and 59th Annual SSC Meeting; Amsterdam: Wiley-Blackwell;2013. p. 104.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolated Splenic Vein Thrombosis Associated with Acute Pancreatitis
- Portal vein thrombosis that successfully treated with low molecular weight heparin in acute pancreatitis
- A Case of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Acute Necrotizing Pancreatitis Treated with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
- Portal Vein Thrombosis during Pregnancy
- Acute Appendicitis with Superior Mesenteric Vein Thrombosis and Portal Vein Thrombosis