Endocrinol Metab.
2010 Jun;25(2):142-146. 10.3803/EnM.2010.25.2.142.
A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome with Frontal Lobe Atrophy and Mental Retardation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. okdom@medmail.co.kr
- 2Department of Family Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2169021
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.2.142
Abstract
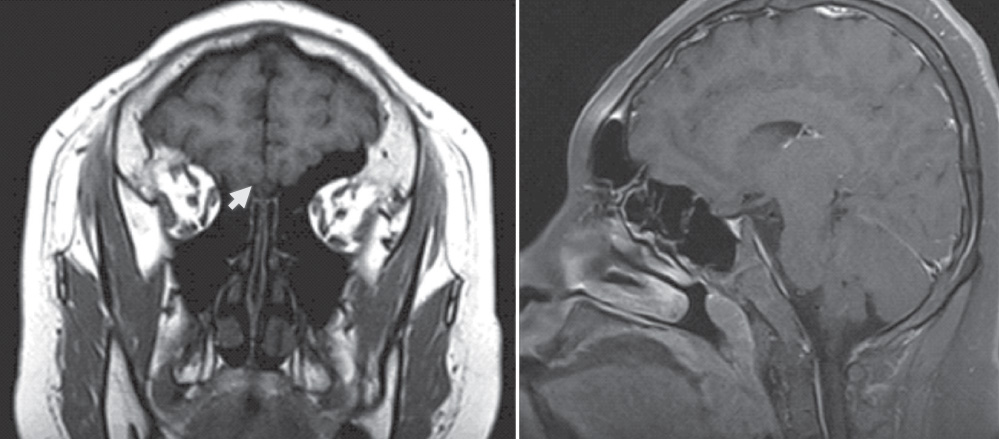
- Kallmann's syndrome is a rare condition, and this is defined as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia or hyposmia. The syndrome may be associated with cleft lip, cleft palate, color blindness, skeletal abnormalities, renal agenesis, sensory neural hearing loss, obesity, etc. About 10 cases of Kallmann's syndrome have been reported in Korea, but there are no reports on cases of Kallmann's syndrome with atrophy of the frontal lobe, severe mental retardation and unilateral renal agenesis. We experienced a case of 17-year-old boy with abnormalities of the olfactory system, as was noted on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). He had an atrophy of the frontal lobe, mental retardation, a micropenis and unilateral renal agenesis. Hormonal assay documented low levels of luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), testosterone and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). So, we report here on an unusual case of Kallmann's syndrome along with briefly reviewing the relevant medical literature.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Atrophy
Cleft Lip
Cleft Palate
Color Vision Defects
Congenital Abnormalities
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Frontal Lobe
Genital Diseases, Male
Hearing Loss
Humans
Hypogonadism
Intellectual Disability
Kallmann Syndrome
Kidney
Kidney Diseases
Korea
Luteinizing Hormone
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Obesity
Olfaction Disorders
Penis
Testosterone
Thyrotropin
Congenital Abnormalities
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Genital Diseases, Male
Kidney
Kidney Diseases
Luteinizing Hormone
Penis
Testosterone
Thyrotropin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Merriam GR, Beitins IZ, Bode HH. Father-to-son transmission of hypogonadism with anosmia: Kallmann's syndrome. Am J Dis Child. 1977. 131:1216–1219.2. Yoshimoto Y, Moridera K, Imura H. Restoration of normal pituitary gonadotropin reserve by administration of luteinizing-hormone-releasing hormone in patients with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. N Engl J Med. 1975. 292:242–245.3. Naftolin F, Harris GW, Bobrow M. Effect of purified luteinizing hormone releasing factor on normal and hypogonadotrophic anosmic men. Nature. 1971. 232:496–497.4. Lieblich JM, Rogol AD, White BJ, Rosen SW. Syndrome of anosmia with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (Kallmann syndrome): clinical and laboratory studies in 23 cases. Am J Med. 1982. 73:506–519.5. Jones JR, Kemmann E. Olfacto-genital dysplasia in the female. Obstet Gynecol Annu. 1976. 5:443–466.6. Santen RJ, Paulsen CA. Hypogonadotropic eunuchoidism. I. Clinical study of the mode of inheritance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973. 36:47–54.7. Valk TW, Corley KP, Kelch RP, Marshall JC. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: hormonal responses to low dose pulsatile administration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980. 51:730–738.8. Moorman JR, Crain B, Osborne D. Kallmann's syndrome with associated cardiovascular and intracranial anomalies. Am J Med. 1984. 77:369–372.9. Itoh M, Houdou S, Mizushima M, Tokita Y, Kawahara H, Ishii S, Ohama E. Two autopsied cases of Kallmann's syndrome with dysplasia of the hippocampus. J Child Neurol. 1997. 12:510–513.10. Martul P, Pineda J, Levilliers J, Vazquez JA, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Loridan L, Diaz-Perez JL. Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism with hyposmia, X-linked ichthyosis, and renal malformation syndrome. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1995. 42:121–128.11. O'Neill MJ, Tridjaja B, Smith MJ, Bell KM, Warne GL, Sinclair AH. Familial Kallmann syndrome: a novel splice acceptor mutation in the KAL gene. Hum Mutat. 1998. 11:340–342.12. Levy CM, Knudtzon J. Kallmann syndrome in two sisters with other developmental anomalies also affecting their father. Clin Genet. 1993. 43:51–53.13. Colle ML, Asch RH, Greenblatt RB. Kallmann's syndrome: effect of repeated stimulation of pituitary-gonadal axis with LH-RH. J Reprod Med. 1977. 18:31–34.14. Crowley WF Jr, McArthur JW. Simulation of the normal menstrual cycle in Kallmanns syndrome by pulsatile administration of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980. 51:173–175.15. Whitcomb RW, Crowley WF Jr. Clinical review 4: Diagnosis and treatment of isolated gonadotropin-releasing hormone deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. 70:3–7.16. Choi YK, Kim YS, Yoo JH, Jung NJ, Lee JI, Kim SW. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia (Kallmann's syndrome) and response to luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH). Korean J Intern Med. 1980. 23:253–258.17. Hong SC, Yoo YS, Kim ES, Kim SC, Park SH, Kim JK, Kang SH. Development of KVSS test (Korean version of Sniffin' sticks test). Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1999. 42:855–860.18. Lee EJ, Hong SW, Hong YK, Yoon JS, Mok JO, Kim YJ, Park HK, Kim CH, Kim SJ, Byun DW, Bae WK, Sub KI, Yoo MH. A case of Kallmann's syndrome with unilateral renal aplasia and diabetes mellitus. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 2005. 20:96–102.19. Cho YW, Han SW, Oh DY, Whang SG, Kim SJ, Lee HC, Huh KB. Two cases of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia (Kallmann's syndrome). J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1990. 5:308–313.20. Nam YS, Kim NK, Jeong CJ, Cha SH, Cha KY. A case of Kallmann syndrome conceived by administration of gonadotropin. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2002. 45:714–717.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of atrophy of bilateral frontal lobe which showed negative symptoms of schizophrenia
- A Case of Kallmann Syndrome and A Case of Successful Pregnancy of Kallmann Syndrome Patient
- Significance of frontal cortical atrophy in Parkinson's disease: computed tomographic study
- Two Cases of Kallmann Syndrome
- Update on Mental Retardation