Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Jun;86(6):295-301. 10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.295.
Causes and outcomes of revisional bariatric surgery: initial experience at a single center
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjgs1997@gmail.com
- KMID: 2167106
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.295
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Bariatric surgery has become more prevalent owing to the worldwide obesity epidemic. With the growing number of bariatric procedures performed annually, the requirement for revisional and secondary operations is increasing accordingly. This study aimed to evaluate the initial experience of revisional bariatric surgery at a single specialized center.
METHODS
A retrospective review of the prospectively established database identified all patients who underwent revisional bariatric surgery between January 2008 and August 2013. The causes, surgical outcomes, and efficacy of the revisional surgeries were analyzed.
RESULTS
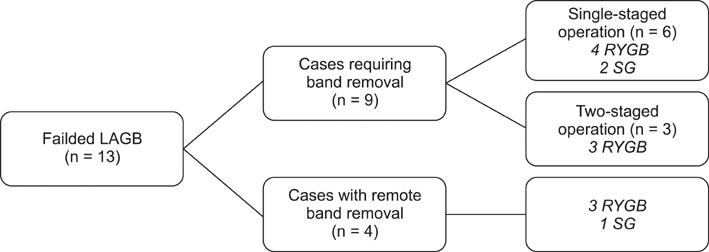
Twenty-two revisional surgeries were performed laparoscopically during the study period (13 laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, 9 laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy). The most common indication for revision was weight regain or insufficient weight loss (12/23, 52.2%), and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) was the most commonly performed secondary procedure (17/23, 73.9%, including four resectional RYGB procedures). Gastric pouch leak occurred in one patient following revisional RYGB, which required reoperation on the first postoperative day. The mean body mass index decreased from 35.9 to 28.8 kg/m2 at a mean follow-up period of 10 months after revision. The percent excess weight losses at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively were 18.8%, 41.1%, 40.1%, and 47.4%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
Revisional bariatric surgery can be successfully performed via a laparoscopic approach with acceptable risk. Deliberate selection for the proper revisional procedure can efficiently manage undesirable results from the primary surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Asymptomatic Gastric Band Erosion Detected during Routine Gastroduodenoscopy
Gee Young Yun, Woo Sub Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Sun Hyung Kang, Hee Seok Moon, Jae Kyu Sung, Hyun Yong Jeong
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(3):294-297. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.001.
Reference
-
1. Heo YS, Park JM, Kim YJ, Kim SM, Park DJ, Lee SK, et al. Bariatric surgery versus conventional therapy in obese Korea patients: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 83:335–342.2. Deitel M, Gawdat K, Melissas J. Reporting weight loss 2007. Obes Surg. 2007; 17:565–568.3. Behrns KE, Smith CD, Kelly KA, Sarr MG. Reoperative bariatric surgery. Lessons learned to improve patient selection and results. Ann Surg. 1993; 218:646–653.4. Radtka JF 3rd, Puleo FJ, Wang L, Cooney RN. Revisional bariatric surgery: who, what, where, and when? Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2010; 6:635–642.5. Spyropoulos C, Kehagias I, Panagiotopoulos S, Mead N, Kalfarentzos F. Revisional bariatric surgery: 13-year experience from a tertiary institution. Arch Surg. 2010; 145:173–177.6. Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H, et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:741–752.7. Boza C, Gamboa C, Perez G, Crovari F, Escalona A, Pimentel F, et al. Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB): surgical results and 5-year follow-up. Surg Endosc. 2011; 25:292–297.8. Van Nieuwenhove Y, Ceelen W, Stockman A, Vanommeslaeghe H, Snoeck E, Van Renterghem K, et al. Long-term results of a prospective study on laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2011; 21:582–587.9. Himpens J, Cadiere GB, Bazi M, Vouche M, Cadiere B, Dapri G. Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Arch Surg. 2011; 146:802–807.10. Romy S, Donadini A, Giusti V, Suter M. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs gastric banding for morbid obesity: a case-matched study of 442 patients. Arch Surg. 2012; 147:460–466.11. O'Brien PE, MacDonald L, Anderson M, Brennan L, Brown WA. Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: fifteen-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg. 2013; 257:87–94.12. Higa K, Ho T, Tercero F, Yunus T, Boone KB. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: 10-year follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011; 7:516–525.13. Himpens J, Coromina L, Verbrugghe A, Cadiere GB. Outcomes of revisional procedures for insufficient weight loss or weight regain after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2012; 22:1746–1754.14. Weiner RA, Theodoridou S, Weiner S. Failure of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: further procedure? Obes Facts. 2011; 4:Suppl 1. 42–46.15. van Rutte PW, Smulders JF, de Zoete JP, Nienhuijs SW. Indications and short-term outcomes of revisional surgery after failed or complicated sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2012; 22:1903–1908.16. Acholonu E, McBean E, Court I, Bellorin O, Szomstein S, Rosenthal RJ. Safety and short-term outcomes of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy as a revisional approach for failed laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in the treatment of morbid obesity. Obes Surg. 2009; 19:1612–1616.17. Victorzon M. Revisional bariatric surgery by conversion to gastric bypass or sleeve: good short-term outcomes at higher risks. Obes Surg. 2012; 22:29–33.18. Jennings NA, Boyle M, Mahawar K, Balupuri S, Small PK. Revisional laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass following failed laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2013; 23:947–952.19. Weber M, Muller MK, Michel JM, Belal R, Horber F, Hauser R, et al. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, but not rebanding, should be proposed as rescue procedure for patients with failed laparoscopic gastric banding. Ann Surg. 2003; 238:827–833.20. Gagner M, Gumbs AA. Gastric banding: conversion to sleeve, bypass, or DS. Surg Endosc. 2007; 21:1931–1935.21. Zundel N, Hernandez JD. Revisional surgery after restrictive procedures for morbid obesity. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010; 20:338–343.22. Schwartz RW, Strodel WE, Simpson WS, Griffen WO Jr. Gastric bypass revision: lessons learned from 920 cases. Surgery. 1988; 104:806–812.23. Owens BM, Owens ML, Hill CW. Effect of Revisional bariatric surgery on weight loss and frequency of complications. Obes Surg. 1996; 6:479–484.24. Sugerman HJ, Kellum JM Jr, DeMaria EJ, Reines HD. Conversion of failed or complicated vertical banded gastroplasty to gastric bypass in morbid obesity. Am J Surg. 1996; 171:263–269.25. Gagner M, Gentileschi P, de Csepel J, Kini S, Patterson E, Inabnet WB, et al. Laparoscopic reoperative bariatric surgery: experience from 27 consecutive patients. Obes Surg. 2002; 12:254–260.26. Mognol P, Chosidow D, Marmuse JP. Laparoscopic conversion of laparoscopic gastric banding to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a review of 70 patients. Obes Surg. 2004; 14:1349–1353.27. Van Dessel E, Hubens G, Ruppert M, Balliu L, Weyler J, Vaneerdeweg W. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass as a re-do procedure for failed restricive gastric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:1014–1018.28. Hii MW, Lake AC, Kenfield C, Hopkins GH. Laparoscopic conversion of failed gastric banding to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: short-term follow-up and technical considerations. Obes Surg. 2012; 22:1022–1028.29. Tran TT, Pauli E, Lyn-Sue JR, Haluck R, Rogers AM. Revisional weight loss surgery after failed laparoscopic gastric banding: an institutional experience. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:4087–4093.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Revisional Bariatric Surgery: Focus on Quality of Life
- Revisional Surgery After Adjustable Gastric Banding: Sleeve Gastrectomy or Gastric Bypass?
- Bariatric endoscopy: from managing complications to primary metabolic procedures
- Current Status of Robotic Bariatric Surgery
- Conversion of One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is Effective in Dealing with Late Complications of OAGB: Experience from a Tertiary Bariatric Center and Literature Review