Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Dec;87(6):319-324. 10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.319.
The advantages of early trauma team activation in the management of major trauma patients who underwent exploratory laparotomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. spmun@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2167088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.87.6.319
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Trauma team activation (TTA) has been shown to have fundamental impact on trauma patients' outcomes. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the short-term outcomes of use of a new TTA protocol in the management of major trauma patients who underwent exploratory laparotomy.
METHODS
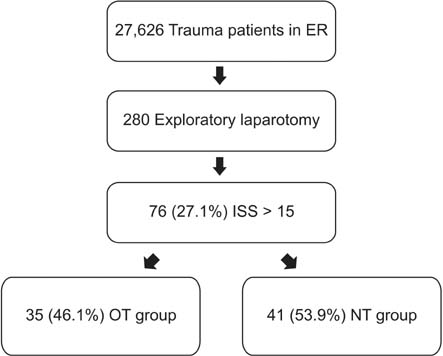
The medical records of trauma patients who had been treated by the new TTA protocol (NT) over 18 months were compared with those of trauma patients treated by the old TTA protocol (OT) over 18 months. Comparisons between the two groups in terms of the time interval between accident and emergency room (ER) arrival, between ER arrival and CT scanning, between ER arrival and operating room (OR) presentation, between accident and OR presentation, mean intensive care unit (ICU) stay, mean hospital stay, mortality within 24 hours, mean mortality within one month, and overall mortality were performed using the Pearson chi-squared test and Student t-test.
RESULTS
The time interval between accident and ER arrival, between ER arrival and CT scanning, between ER arrival and OR presentation, and between accident and OR presentation was found to have decreased significantly with the use of NT compared to OT. However, the mean ICU stay, mean hospital stay, mortality within 24 hours, mortality within one month, and overall mortality were found not to have improved.
CONCLUSION
While initiation of early TTA can shorten the time interval in the management of trauma patients, it may not improve patient outcomes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rivara FP, Grossman DC, Cummings P. Injury prevention. First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 1997; 337:543–548.2. Demetriades D, Martin M, Salim A, Rhee P, Brown C, Chan L. The effect of trauma center designation and trauma volume on outcome in specific severe injuries. Ann Surg. 2005; 242:512–517.3. MacKenzie EJ, Rivara FP, Jurkovich GJ, Nathens AB, Frey KP, Egleston BL, et al. A national evaluation of the effect of trauma-center care on mortality. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:366–378.4. Lehmann RK, Arthurs ZM, Cuadrado DG, Casey LE, Beekley AC, Martin MJ. Trauma team activation: simplified criteria safely reduces overtriage. Am J Surg. 2007; 193:630–634.5. Kouzminova N, Shatney C, Palm E, McCullough M, Sherck J. The efficacy of a two-tiered trauma activation system at a level I trauma center. J Trauma. 2009; 67:829–833.6. Williams D, Foglia R, Megison S, Garcia N, Foglia M, Vinson L. Trauma activation: are we making the right call? A 3-year experience at a Level I pediatric trauma center. J Pediatr Surg. 2011; 46:1985–1991.7. Cherry RA, King TS, Carney DE, Bryant P, Cooney RN. Trauma team activation and the impact on mortality. J Trauma. 2007; 63:326–330.8. American College of Surgeons. Committee on Trauma. Resources for optimal care of the injured patient. Chicago, IL: ACS;2006.9. Celso B, Tepas J, Langland-Orban B, Pracht E, Papa L, Lottenberg L, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing outcome of severely injured patients treated in trauma centers following the establishment of trauma systems. J Trauma. 2006; 60:371–378.10. Krieger AR, Wills HE, Green MC, Gleisner AL, Vane DW. Efficacy of anatomic and physiologic indicators versus mechanism of injury criteria for trauma activation in pediatric emergencies. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 73:1471–1477.11. Khetarpal S, Steinbrunn BS, McGonigal MD, Stafford R, Ney AL, Kalb DC, et al. Trauma faculty and trauma team activation: impact on trauma system function and patient outcome. J Trauma. 1999; 47:576–581.12. Franklin GA, Boaz PW, Spain DA, Lukan JK, Carrillo EH, Richardson JD. Prehospital hypotension as a valid indicator of trauma team activation. J Trauma. 2000; 48:1034–1037.13. Demetriades D, Sava J, Alo K, Newton E, Velmahos GC, Murray JA, et al. Old age as a criterion for trauma team activation. J Trauma. 2001; 51:754–756.14. Norwood SH, McAuley CE, Berne JD, Vallina VL, Creath RG, McLarty J. A prehospital glasgow coma scale score < or = 14 accurately predicts the need for full trauma team activation and patient hospitalization after motor vehicle collisions. J Trauma. 2002; 53:503–507.15. Craven JA. Paediatric and adolescent horse-related injuries: does the mechanism of injury justify a trauma response? Emerg Med Australas. 2008; 20:357–362.16. Qazi K, Kempf JA, Christopher NC, Gerson LW. Paramedic judgment of the need for trauma team activation for pediatric patients. Acad Emerg Med. 1998; 5:1002–1007.17. Shim H, Jang JY, Lee JG, Kim S, Kim MJ, Park YS, et al. Application of critical pathway in trauma patients. J Trauma Inj. 2012; 25:159–165.18. Lee DK, Lee KH, Cha KC, Park KH, Choi HJ, Kim H, et al. Effectiveness of simple trauma team activation criteria on prognosis of severe trauma patients. J Korean Soc Traumatol. 2009; 22:71–76.19. Cho S, Jung K, Yeom S, Park S, Kim H, Hwang S. Change of inter-facility transfer pattern in a regional trauma system after designation of trauma centers. J Korean Surg Soc. 2012; 82:8–12.20. Simpson E, MacAteer E, Visram A. Review of paediatric trauma admissions at the royal london hospital (February 98 to february 99). Paediatr Anaesth. 2000; 10:696–697.21. Copes WS, Staz CF, Konvolinka CW, Sacco WJ. American College of Surgeons audit filters: associations with patient outcome and resource utilization. J Trauma. 1995; 38:432–438.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Organization and Roles of the Trauma Team
- Is it reasonable emergency department doctor must activate the whole trauma team if they meet the patients who fell above 20 feet?
- Emergency department laparotomy for patients with severe abdominal trauma: a retrospective study at a single regional trauma center in Korea
- Pneumoperitoneum from vaginal cuff dehiscence following blunt trauma in a patient with a history of robotic hysterectomy in Korea: a case report
- Treatment of Renal Injury: Practical Approach