Clin Endosc.
2016 Jan;49(1):81-85. 10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.81.
Communicating Tubular Esophageal Duplication Combined with Bronchoesophageal Fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Disease Center, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. endoscopy@cha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2166554
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.49.1.81
Abstract
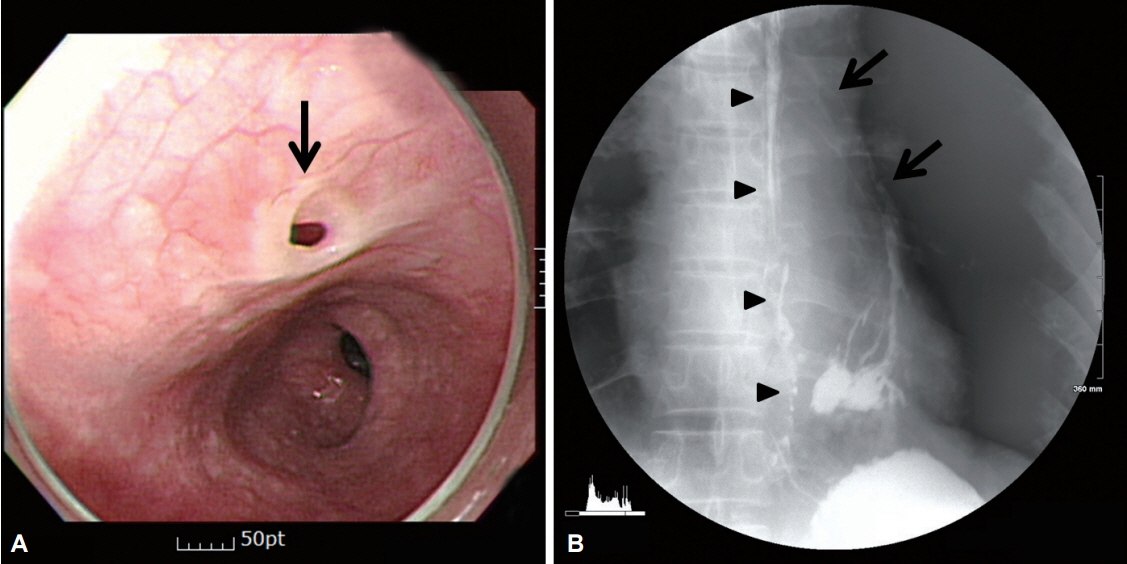
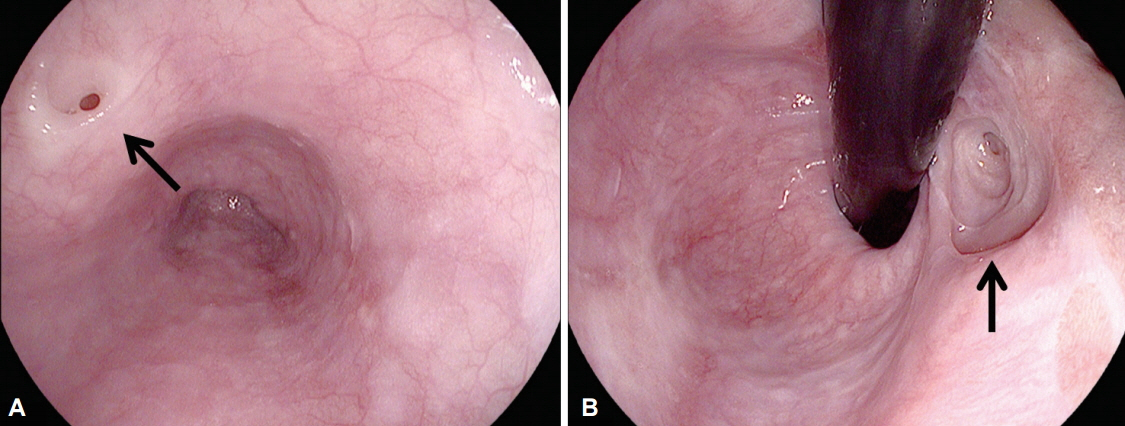
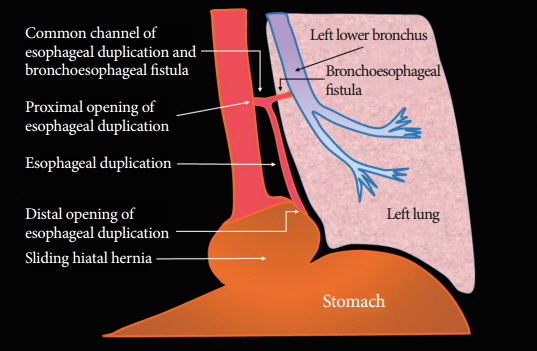
- Esophageal duplication (ED) is rarely diagnosed in adults and is usually asymptomatic. Especially, ED that is connected to the esophagus through a tubular communication and combined with bronchoesophageal fistula (BEF) is extremely rare and has never been reported in the English literature. This condition is very difficult to diagnose. Although some combinations of several modalities, such as upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, esophagography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and endoscopic ultrasonography, can be used for the diagnosis, the results might be inconclusive. Here, we report on a patient with communicating tubular ED that was incidentally diagnosed on the basis of endoscopy and esophagography during the postoperational evaluation of BEF.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arbona JL, Fazzi JG, Mayoral J. Congenital esophageal cysts: case report and review of literature. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984; 79:177–182.2. Phadke AY, Shah SK, Rajput SL, Bhandarkar PV, Abraham P. Incomplete tubular duplication of the esophagus lined by heterotopic gastric epithelium, presenting in adulthood. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:S35–S36.3. Kumar D, Samujh R, Rao KL. Infected esophageal duplication cyst simulating empyema. Indian Pediatr. 2003; 40:423–425.4. Bagheri R, Asnaashari AM, Afghani R. Esophageal duplication cyst. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2015; 23:332–334.
Article5. Kiratli PO, Aksoy T, Bozkurt MF, Orhan D. Detection of ectopic gastric mucosa using 99mTc pertechnetate: review of the literature. Ann Nucl Med. 2009; 23:97–105.
Article6. Yamamoto N, Yamakawa H, Saitho Y, Nomoto Y, Fujisawa T, Yamaguchi Y. Esophageal duplication with esophago-bronchial fistula. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1994; 42:286–291.7. Achildi O, Grewal H. Congenital anomalies of the esophagus. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2007; 40:219–244.
Article8. Lewis TM, Zacharakis E, Hoare J, Purkayastha S, Hanna GB. Gastrointestinal images: complete tubular duplication of the oesophagus in an adult. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010; 14:1340–1342.
Article9. Macpherson RI. Gastrointestinal tract duplications: clinical, pathologic, etiologic, and radiologic considerations. Radiographics. 1993; 13:1063–1080.
Article10. Joyce AM, Zhang PJ, Kochman ML. Complete endoscopic resection of an esophageal duplication cyst (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:288–289.
Article11. Coumaros D, Schneider A, Tsesmeli N, Geiss S, Becmeur F. Endoscopic management of a tubular esophageal duplication diagnosed in adolescence (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:827–830.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Tubular Duplication of the Esophagus
- A Bronchoesophageal Fistula Detected by Air Leaking Sound after Intubation
- A Case of Tubular Esophageal Duplication
- Surgical Treatment of Bronchoesophageal Fistula Caused by a Self-Expanding Esophageal Stent
- Esophageal Duplication Complicated with Perforation