J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Aug;30(8):1129-1135. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.8.1129.
Differences in Features and Course of Mucosal Type Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis between Korean Infants and Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bhchoi@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2164508
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.8.1129
Abstract
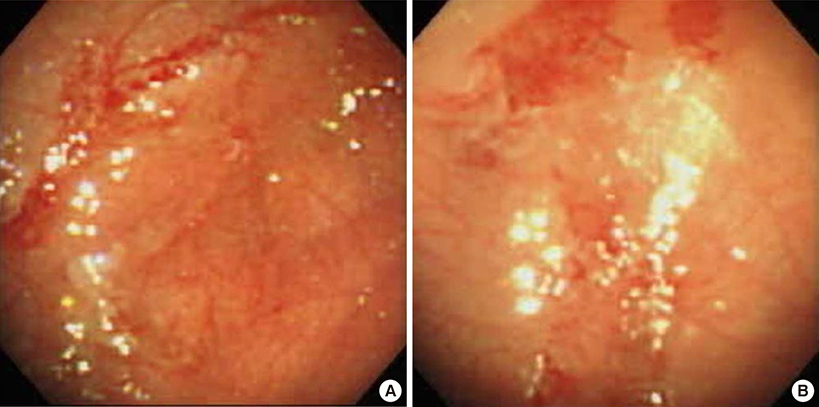
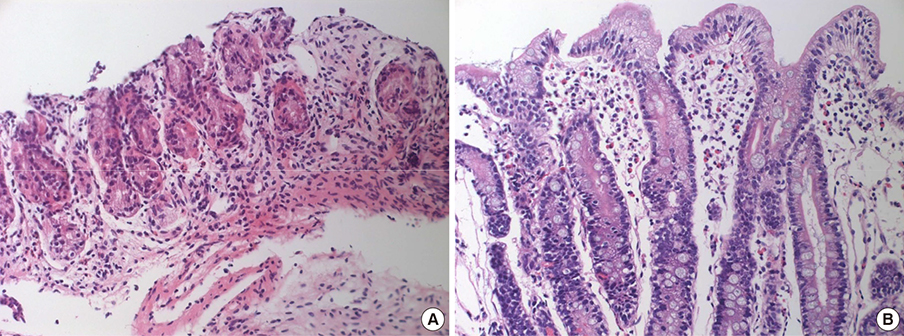
- Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a disorder characterized by eosinophilic infiltration of the bowel wall and various gastrointestinal (GI) manifestations. This study aimed to evaluate the characteristics of EGE in infants and children. A total of 22 patients were diagnosed with histologic EGE (hEGE) or possible EGE (pEGE). Serum specific IgE levels, peripheral eosinophil counts, and endoscopic biopsies were carried out. In the hEGE group (n = 13), initial symptoms included hematemesis, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Three of the subjects had normal endoscopic findings. Eight patients were categorized into the infant group and 5 into the child group. All patients in the infant group showed clinical improvement after switching from cow's milk feeding to special formula or breast feeding. The infant group showed a higher eosinophil count in the gastric mucosal biopsy than the child group. In the pEGE group (n = 9) initial symptoms included hematemesis, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Seven patients in this group showed a good response to treatment with restriction of the suspected foods and/or the administration of ketotifen. Both hEGE and pEGE groups showed clinical improvement after restriction of suspected foods in the majority of cases and also showed a similar clinical course. EGE should be considered in the differential diagnosis of patients with chronic abdominal pain, vomiting, and hematemesis of unknown cause. The infant group may have a better prognosis than the child group if treated properly.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Fecal Calprotectin as a Useful Non-Invasive Screening Marker for Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorder in Korean Children
In Hyuk Yoo, Jin Min Cho, Jung Yeon Joo, Hye Ran Yang
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(17):e120. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e120.Safety and Competency are the Main Priorities in Pediatric Endoscopy
Byung-Ho Choe
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(4):379-380. doi: 10.5946/ce.2020.124.
Reference
-
1. Weller PF. Eosinophilia and eosinophil-related disorders. In : Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, Simons FE, editors. Middleton's allergy: principles & practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier;2009. p. 859–877.2. Kaijser R. Zur Kenntnis der allergischen affektionen des verdauungskanals vom standput des chirurgen aus. Arch Klin Chir. 1937; 188:36–64.3. Klein NC, Hargrove RL, Sleisenger MH, Jeffries GH. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 1970; 49:299–319.4. Lucendo AJ, Arias A. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: an update. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 6:591–601.5. Zhang L, Duan L, Ding S, Lu J, Jin Z, Cui R, McNutt M, Wang A. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: clinical manifestations and morphological characteristics, a retrospective study of 42 patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:1074–1080.6. Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:11–28. quiz 97. Choi SJ, Jang YJ, Choe BH, Cho SH, Ryeom H, Hong SJ, Lee D. Eosinophilic gastritis with gastric outlet obstruction mimicking infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014; 59:e9–e11.8. Talley NJ, Shorter RG, Phillips SF, Zinsmeister AR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a clinicopathological study of patients with disease of the mucosa, muscle layer, and subserosal tissues. Gut. 1990; 31:54–58.9. Zuo L, Rothenberg ME. Gastrointestinal eosinophilia. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007; 27:443–455.10. DeBrosse CW, Rothenberg ME. Allergy and eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). Curr Opin Immunol. 2008; 20:703–708.11. Guajardo JR, Plotnick LM, Fende JM, Collins MH, Putnam PE, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophil-associated gastrointestinal disorders: a world-wide-web based registry. J Pediatr. 2002; 141:576–581.12. Vanderhoof JA, Young RJ. Allergic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2001; 4:553–556.13. Sampson HA. Food allergy. Part 1: immunopathogenesis and clinical disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:717–728.14. Aquino A, Dòmini M, Rossi C, D'Incecco C, Fakhro A, Lelli Chiesa P. Pyloric stenosis due to eosinophilic gastroenteritis: presentation of two cases in mono-ovular twins. Eur J Pediatr. 1999; 158:172–173.15. Tien FM, Wu JF, Jeng YM, Hsu HY, Ni YH, Chang MH, Lin DT, Chen HL. Clinical features and treatment responses of children with eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Pediatr Neonatol. 2011; 52:272–278.16. Khan S, Orenstein SR. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008; 37:333–348.17. Kelly KJ. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000; 30:S28–S35.18. Katz AJ, Goldman H, Grand RJ. Gastric mucosal biopsy in eosinophilic (allergic) gastroenteritis. Gastroenterology. 1977; 73:705–709.19. Lee M, Hodges WG, Huggins TL, Lee EL. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. South Med J. 1996; 89:189–194.20. Bolukbas FF, Bolukbas C, Uzunkoy A, Baba F, Horoz M, Ozturk E. A dramatic response to ketotifen in a case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis mimicking abdominal emergency. Dig Dis Sci. 2004; 49:1782–1785.21. Daikh BE, Ryan CK, Schwartz RH. Montelukast reduces peripheral blood eosinophilia but not tissue eosinophilia or symptoms in a patient with eosinophilic gastroenteritis and esophageal stricture. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003; 90:23–27.22. Bischoff SC. Food allergy and eosinophilic gastroenteritis and colitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 10:238–245.23. Lombardi C, Salmi A, Passalacqua G. An adult case of eosinophilic pyloric stenosis maintained on remission with oral budesonide. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 43:29–30.24. Ingle SB, Patle YG, Murdeshwar HG, Pujari GP. A case of early eosinophilic gastroenteritis with dramatic response to steroids. J Crohns Colitis. 2011; 5:71–72.25. Kellermayer R, Tatevian N, Klish W, Shulman RJ. Steroid responsive eosinophilic gastric outlet obstruction in a child. World J Gastroenterol. 2008; 14:2270–2271.26. Teng X, Xu L, Wu J, Sun M, Guo J, Mao Z. Clinical and morphological features of serosal form of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in a retrospective study of 10 children. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2013; 32:276–283.27. Alabsi HS, Reschak GL, Fustino NJ, Beltroy EP, Sramek JE, Alabsi SY. Neonatal eosinophilic gastroenteritis: possible in utero sensitization to cow's milk protein. Neonatal Netw. 2013; 32:316–322.28. Yamada Y, Kato M, Toki F, Watanabe M, Nishi A, Matsushita I, Hirato J, Hayashi Y. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorder in an infant with feeding dysfunction. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 158:Suppl 1. 83–86.29. Lee HY, Kim CJ. A case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004; 7:239–242.30. Yi ES, Kim MJ, Ha SY, Lee YM, Choi KE, Choe YH. A case of non-IgE-mediated eosinophilic gastroenteritis presenting as ascites. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011; 14:181–186.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Combined eosinophilic gastroenteritis and ulcerative colitis successfully treated by vedolizumab: a case report
- A case of subserosal type of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites
- Serosal Type Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis