Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Dec;64(6):370-374. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370.
Jackhammer Esophagus Treated by a Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive Disease Center, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Seoul, Seoul, Korea. cjy6695@dreamwiz.com
- 2Digestive Disease Center, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Bucheon, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2160670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.370
Abstract
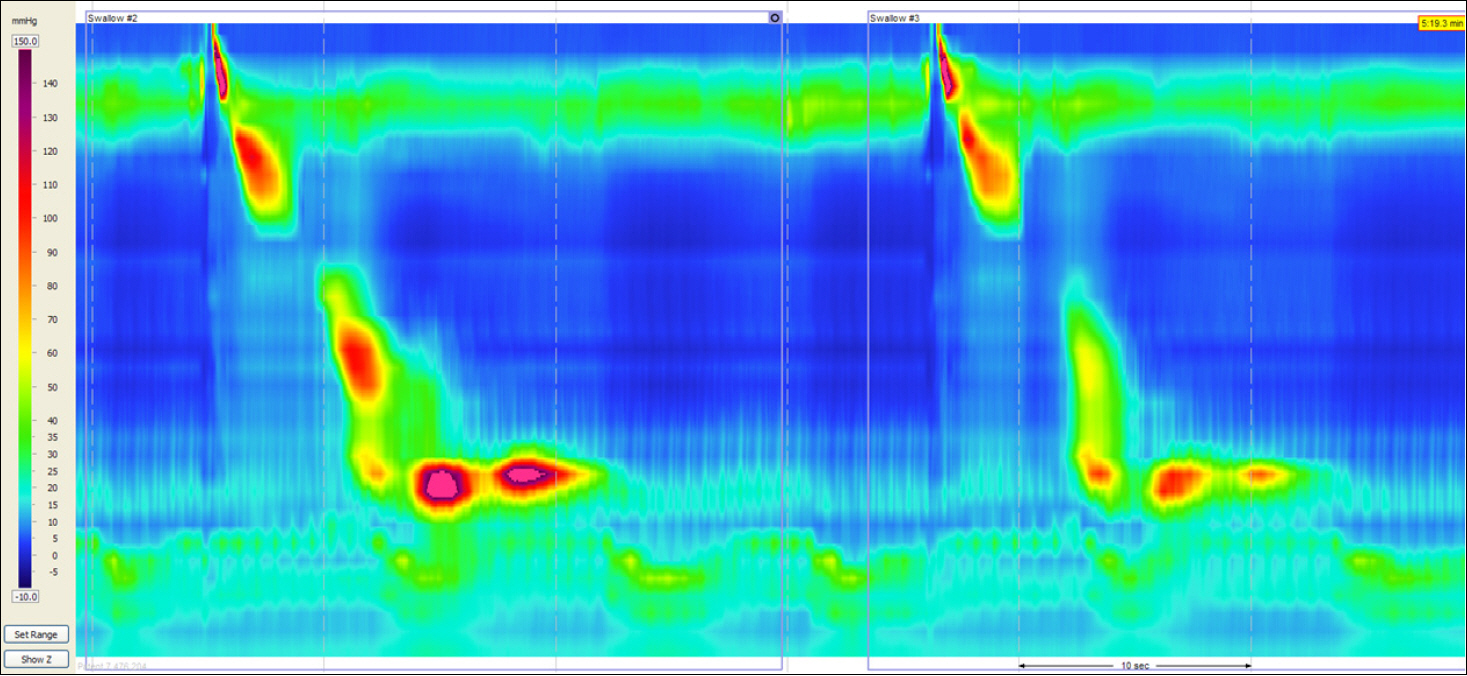
- A 49-year-old woman visited our hospital with dysphagia and chest pain. In another hospital, she was diagnosed as reflux esophagitis. Although she had taken proton pump inhibitor and prokinetics drugs for a long time, she was not relieved of any symptoms. On the basis of high resolution manometry and endoscopic ultrasonography findings, Jackhammer esophagus was diagnosed. In this patient, peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) was performed for long myotomy of thickened circular muscle. During the procedure, there were no significant complications and she was discharged uneventfully. Symptoms were completely improved during three months after POEM. Here, we report on a case of Jackhammer esophagus treated by POEM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
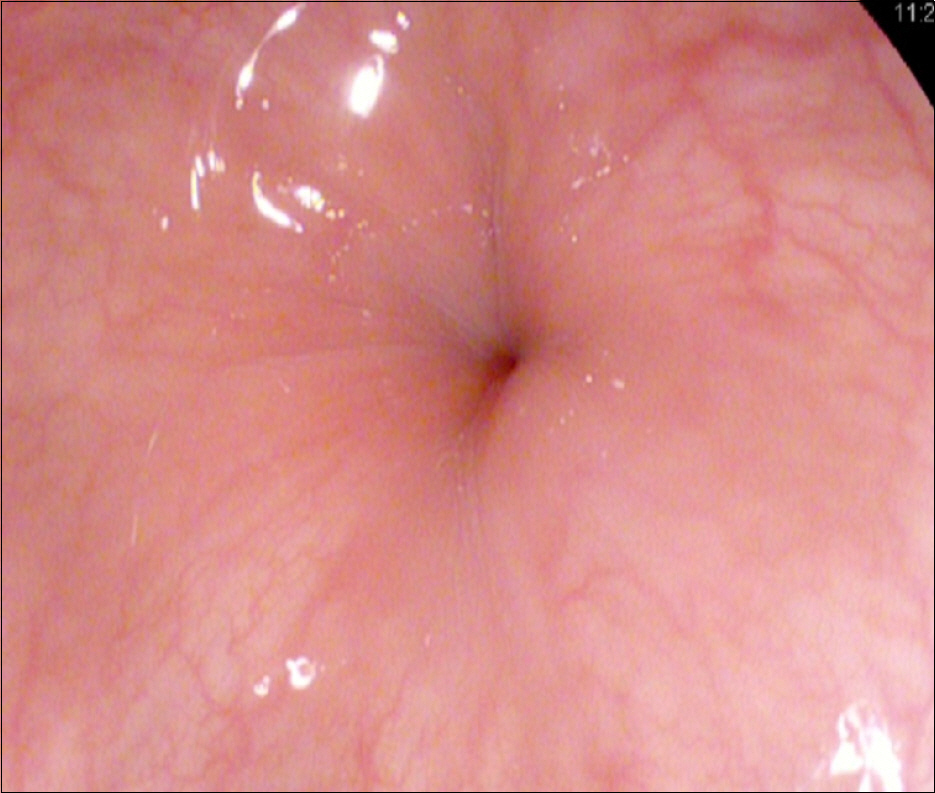
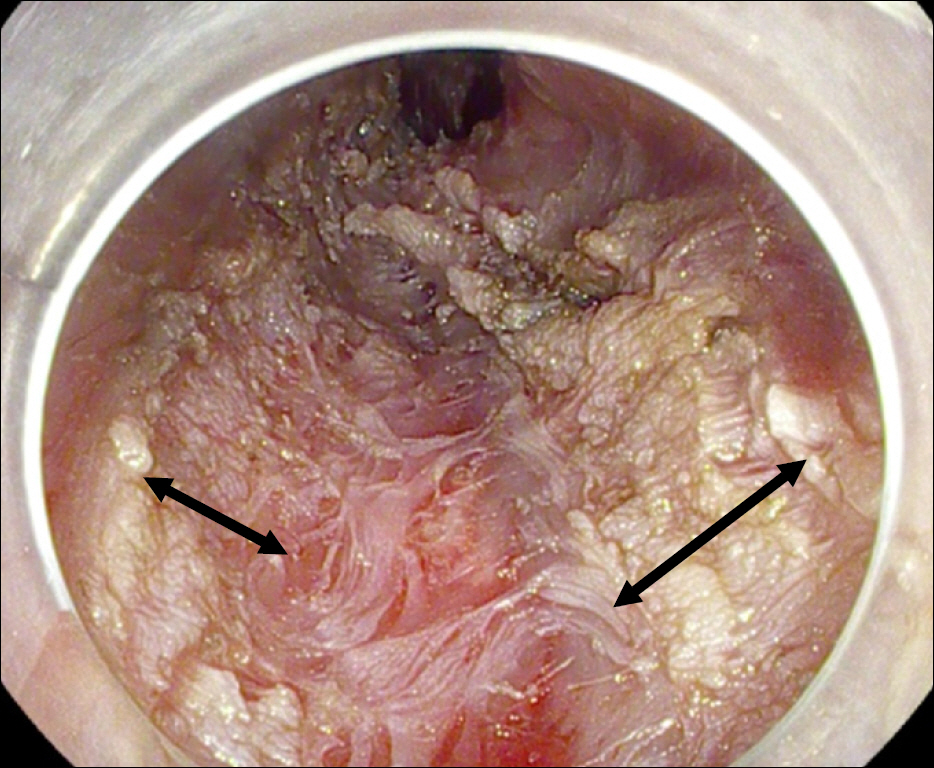
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Noncardiac Chest Pain: Update on the Diagnosis and Management
Yang Won Min, Poong-Lyul Rhee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2015;65(2):76-84. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2015.65.2.76.Experience with Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia and Spastic Esophageal Motility Disorders at a Tertiary U.S. Center
Maen Masadeh, Peter Nau, Subhash Chandra, Jagpal Klair, John Keech, Kalpaj Parekh, Rami El Abiad, Henning Gerke
Clin Endosc. 2020;53(3):321-327. doi: 10.5946/ce.2019.110.Current Status of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
Young Kwan Cho, Seong Hwan Kim
Clin Endosc. 2018;51(1):13-18. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.165.
Reference
-
References
1. Roman S, Tutuian R. Esophageal hypertensive peristaltic disorders. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):32–39.
Article2. Agrawal A, Hila A, Tutuian R, Mainie I, Castell DO. Clinical relevance of the nutcracker esophagus: suggested revision of criteria for diagnosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 40:504–509.
Article3. Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ. Oesophageal high-resolution manometry: moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008; 57:405–423.
Article4. Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Kahrilas PJ, Pandolfino JE, Schwizer W, Smout AJ. International High Resolution Manometry Working Group. Chicago classification criteria of esophageal motility disorders defined in high resolution esophageal pressure topography. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):57–65.5. Roman S, Kahrilas PJ. Management of spastic disorders of the esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2013; 42:27–43.
Article6. Patti MG, Pellegrini CA, Arcerito M, Tong J, Mulvihill SJ, Way LW. Comparison of medical and minimally invasive surgical therapy for primary esophageal motility disorders. Arch Surg. 1995; 130:609–615.
Article7. Pandolfino JE, Kwiatek MA, Nealis T, Bulsiewicz W, Post J, Kahrilas PJ. Achalasia: a new clinically relevant classification by high-reso-lution manometry. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1526–1533.
Article8. Rohof WO, Salvador R, Annese V, et al. Outcomes of treatment for achalasia depend on manometric subtype. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:718–725.
Article9. Inoue H, Minami H, Kobayashi Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for esophageal achalasia. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:265–271.
Article10. Costamagna G, Marchese M, Familiari P, Tringali A, Inoue H, Perri V. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) for oesophageal achalasia: preliminary results in humans. Dig Liver Dis. 2012; 44:827–832.
Article11. Lee BH, Shim KY, Hong SJ, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for treatment of achalasia: initial results of a korean study. Clin Endosc. 2013; 46:161–167.
Article12. Shiwaku H, Inoue H, Beppu R, et al. Successful treatment of diffuse esophageal spasm by peroral endoscopic myotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:149–150.
Article13. Sharata A, Kurian AA, Dunst CM, Bhayani NH, Reavis KM, Swanstrom LL. Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) is safe and effective in the setting of prior endoscopic intervention. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013; 17:1188–1192.
Article14. Khashab MA, Saxena P, Kumbhari V, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy as a platform for the treatment of spastic esophageal disorders refractory to medical therapy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79:136–139.15. Roman S, Pandolfino JE, Chen J, Boris L, Luger D, Kahrilas PJ. Phenotypes and clinical context of hypercontractility in high-res-olution esophageal pressure topography (EPT). Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:37–45.
Article16. Vanuytsel T, Bisschops R, Farre R, et al. Botulinum toxin reduces dysphagia in patients with nonachalasia primary esophageal motility disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11:1115–1121.e2.
Article17. Kandulski A, Fuchs KH, Weigt J, Malfertheiner P. Jackhammer esophagus: high-resolution manometry and therapeutic approach using peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). Dis Esophagus. 2014. doi: 10.1111/dote.12182. [Epub ahead of print].
Article18. Louis H, Covas A, Coppens E, Deviere J. Distal esophageal spasm treated by peroral endoscopic myotomy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1926–1927.
Article19. Dogan I, Puckett JL, Padda BS, Mittal RK. Prevalence of increased esophageal muscle thickness in patients with esophageal symptoms. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:137–145.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Esophageal Motility Disorders
- Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience
- Two-Stage Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Sigmoid-Type Achalasia
- Hybrid Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia with Prior Treatment Failure