J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Feb;21(1):40-45. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.40.
The Hematologic Response to Anti-apoptotic Cytokine Therapy: Results of Pentoxifylline, Ciprofloxacin, and Dexamethasone Treatment for Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. hms@medical.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Diagnostic Laboratory Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, College of Medicine, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Medicine, Daegu Catholic University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2157780
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.40
Abstract
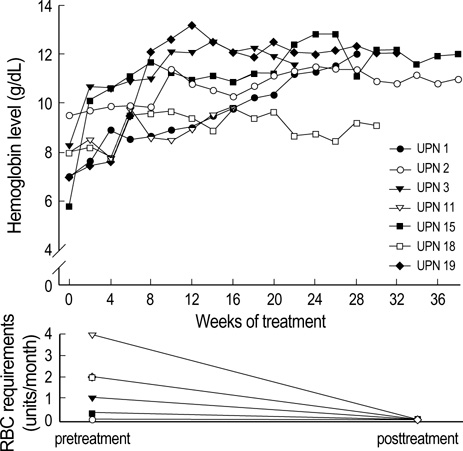
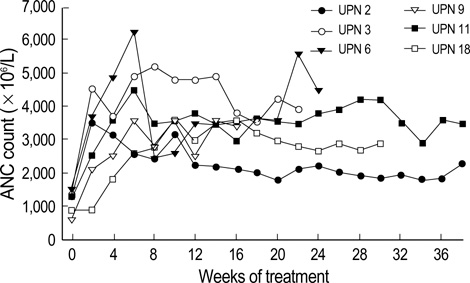
- TNF-alpha mediated apoptosis of the hematopoietic cells has been thought to contribute to the ineffective hematopoiesis observed in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). The combination of pentoxifylline (P) and ciprofloxacin (C) has been shown to reduce the serum levels of TNF-alpha, and an earlier trial of P and C with dexamethasone (D) provided good palliation for patients with MDS. The purpose of this study is to assess the hematologic response to PCD therapy for patients suffering with MDS. 21 of 25 patients who completed at least of 12 weeks of treatment were evaluable for the treatment efficacy. At baseline, the patient's median age was 60 yr (range: 18-75 yr). The diagnoses according to WHO classification included: RA (n=5), RCMD (n=10), RARS (n=1), RCMD/RS (n=1), RAEB (3), and CMML (n=1). 11 patients (52%) had at least single lineage response. 3 patients (11%) showed improvement of triple lineage cytopenia. There were no differences in the response rates between the FAB subtypes. The median time to response was 4 weeks (range: 2-12 weeks), and it is interesting that 9 of 11 patients who had a response remained without relapse for a median of 177 days (range: 78-634 days). These preliminary results indicate that anti-cytokine therapy with PCD is an effective and well tolerated palliative treatment for patients with MDS.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Anti-Infective Agents/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Anti-Inflammatory Agents/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Apoptosis/*drug effects
Ciprofloxacin/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Comparative Study
Dexamethasone/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Drug Therapy, Combination
Erythrocyte Count
Female
Hematologic Agents/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Myelodysplastic Syndromes/*blood/drug therapy
Nausea/chemically induced
Pentoxifylline/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Platelet Count
Time Factors
Treatment Outcome
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/*metabolism
Figure
Reference
-
1. Heaney ML, Golde DW. Myelodysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340:1649–1660.
Article2. Gersuk GM, Beckham C, Loken MR, Kiener P, Anderson JE, Farrand A, Troutt AB, Ledbetter JA, Deeg HJ. A role for tumour necrosis factor-alpha, Fas and Fas-Ligand in marrow failure associated with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1998. 103:176–188.3. Allampallam K, Shetty VT, Raza A. Cytokines and MDS. Cancer Treat Res. 2001. 108:93–100.
Article4. Broxmeyer HE, Williams DE, Lu L, Cooper S, Anderson SL, Beyer GS, Hoffman R, Rubin BY. The suppressive influences of human tumor necrosis factors on bone marrow hematopoietic progenitor cells from normal donors and patients with leukemia: synergism of tumor necrosis factor and interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986. 136:4487–4495.5. Roodman GD, Bird A, Hutzler D, Montgomery W. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and hematopoietic progenitors: effects of tumor necrosis factor on the growth of erythroid progenitors CFU-E and BFU-E and the hematopoietic cell lines K562, HL60, and HEL cells. Exp Hematol. 1987. 15:928–935.6. Means RT Jr, Krantz SB. Inhibition of human erythroid colony-forming units by tumor necrosis factor requires beta interferon. J Clin Invest. 1993. 91:416–419.
Article7. Sato T, Selleri C, Anderson S, Young NS, Maciejewski JP. Expression and modulation of cellular receptors for interferon-gamma, tumour necrosis factor, and Fas on human bone marrow CD34+ cells. Br J Haematol. 1997. 97:356–365.8. Sawanobori M, Yamaguchi S, Hasegawa M, Inoue M, Suzuki K, Kamiyama R, Hirokawa K, Kitagawa M. Expression of TNF receptors and related signaling molecules in the bone marrow from patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Res. 2003. 27:583–591.
Article9. Mundle SD, Reza S, Ali A, Mativi Y, Shetty V, Venugopal P, Gregory SA, Raza A. Correlation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) with high Caspase 3-like activity in myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer Lett. 1999. 140:201–207.10. Peddie CM, Wolf CR, McLellan LI, Collins AR, Bowen DT. Oxidative DNA damage in CD34+ myelodysplastic cells is associated with intracellular redox changes and elevated plasma tumour necrosis factor-alpha concentration. Br J Haematol. 1997. 99:625–631.11. Raza A, Venugopal P, Genzer S. Hiddemann W, Buchner T, Wormann B, editors. Pilot study of pentoxifylline and ciprofloxacin with or without dexamethasone produces encouraging results in myelodysplastic syndromes: acute leukemias VII. Experimental Approaches and Novel Therapies. 1998. New York: Springer-Verlag;42–51.12. Raza A. Anti-TNF therapies in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, sepsis, and myelodysplastic syndromes. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. 50:229–235.
Article13. Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, Sultan C. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982. 51:189–199.
Article14. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Diebold J, Flandrin G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Vardiman J, Lister TA, Bloomfield CD. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues: report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting-Airlie House, Virginia, November 1997. J Clin Oncol. 1999. 17:3835–3849.
Article15. Greenberg P, Cox C, LeBeau MM, Fenaux P, Morel P, Sanz G, Sanz M, Vallespi T, Hamblin T, Oscier D, Ohyashiki K, Toyama K, Aul C, Mufti G, Bennett J. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 1997. 89:2079–2088.
Article16. Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kantarjian H, Pinto A, Schiffer CA, Nimer SD, Lowenberg B, Beran M, de Witte TM, Stone RM, Mittelman M, Sanz GF, Wijermans PW, Gore S, Greenberg PL. World Health Organization (WHO) international working group. Report of an international working group to standardize response criteria for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2000. 96:3671–3674.17. Raza A, Meyer P, Dutt D, Zorat F, Lisak L, Nascimben F, du Randt M, Kaspar C, Goldberg C, Loew J, Dar S, Gezer S, Venugopal P, Zeldis J. Thalidomide produces transfusion independence in long-standing refractory anemias of patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2001. 98:958–965.
Article18. List AF, Brasfield F, Heaton R, Glinsmann-Gibson B, Crook L, Taetle R, Capizzi R. Stimulation of hematopoiesis by amifostine in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 1997. 90:3364–3369.
Article19. Deeg HJ, Gotlib J, Beckham C, Dugan K, Holmberg L, Schubert M, Appelbaum F, Greenberg P. Soluble TNF receptor fusion protein (etanercept) for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome: a pilot study. Leukemia. 2002. 16:162–164.
Article20. Raza A, Qawi H, Andric T, Dar S, Lisak L, Huang RW, Venugopal P, Gezer S, Gregory SA, Hsu WT, Loew J, Robin E, Rifkin S, Shah R, Divgi A, Taylor R, Grosset A. Pentoxifylline, ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone improve the ineffective hematopoiesis in myelodysplastic syndrome patients; malignancy. Hematology. 2000. 5:275–284.21. Raza A, Qawi H, Lisak L, Andric T, Dar S, Andrews C, Venugopal P, Gezer S, Gregory S, Loew J, Robin E, Rifkin S, Hsu WT, Huang RW. Patients with myelodysplastic syndromes benefit from palliative therapy with amifostine, pentoxifylline, and ciprofloxacin with or without dexamethasone. Blood. 2000. 95:1580–1587.
Article22. Maciejewski JP, Risitano AM, Sloand EM, Wisch L, Geller N, Barrett JA, Young NS. A pilot study of the recombinant soluble human tumour necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome. Br J Haematol. 2002. 117:119–126.
Article23. Deeg HJ, Jiang PY, Holmberg LA, Scott B, Petersdorf EW, Appelbaum FR. Hematologic responses of patients with MDS to antithymocyte globulin plus etanercept correlate with improved flow scores of marrow cells. Leuk Res. 2004. 28:1177–1180.24. Raza A, Candoni A, Khan U, Lisak L, Tahir S, Silvestri F, Billmeier J, Alvi MI, Mumtaz M, Gezer S, Venugopal P, Reddy P, Galili N. Remicade as TNF suppressor in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. 45:2099–2104.
Article25. Daskalakis M, Nguyen TT, Nguyen C, Guldberg P, Kohler G, Wijermans P, Jones PA, Lubbert M. Demethylation of a hypermethylated P15/INK4B gene in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome by 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine (decitabine) treatment. Blood. 2002. 100:2957–2964.
Article26. Kurzrock R, Albitar M, Cortes JE, Estey EH, Faderl SH, Garcia-Manero G, Thomas DA, Giles FJ, Ryback ME, Thibault A, De Porre P, Kantarjian HM. Phase II study of R115777, a farnesyl transferase inhibitor, in myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2004. 22:1287–1292.
Article27. List A, Beran M, DiPersio J, Slack J, Vey N, Rosenfeld CS, Greenberg P. Opportunities for Trisenox (arsenic trioxide) in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia. 2003. 17:1499–1507.
Article28. Silverman LR, Demakos EP, Peterson BL, Kornblith AB, Holland JC, Odchimar-Reissig R, Stone RM, Nelson D, Powell BL, DeCastro CM, Ellerton J, Larson RA, Schiffer CA, Holland JF. Randomized controlled trial of azacitidine in patients with the myelodysplastic syndrome: a study of the cancer and leukemia group B. J Clin Oncol. 2002. 20:2429–2440.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone in experimental pseudomonas endophthalmitis
- Two cases of disseminated tuberculosis associated with the myelodysplastic syndrome
- Protective Effect of Pentoxifylline and Ciprofloxacin on Dimethylnitrosamine-induced Hepatic Fibrosis in Rats
- Effects of Dexamethasone on expressions of IFN-gamma and IL-4 by PBMCs in response to IL-12
- A Case of Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Behcet's Disease