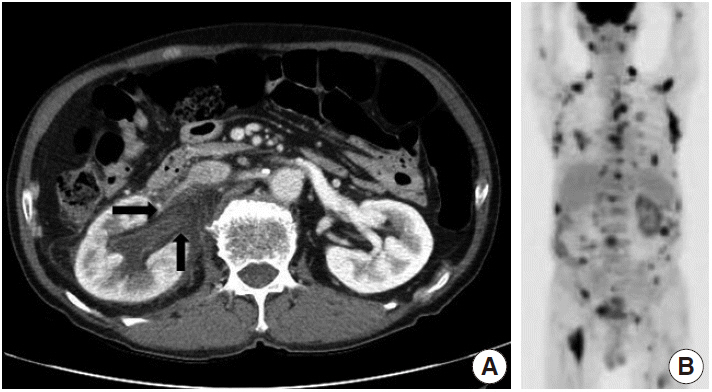
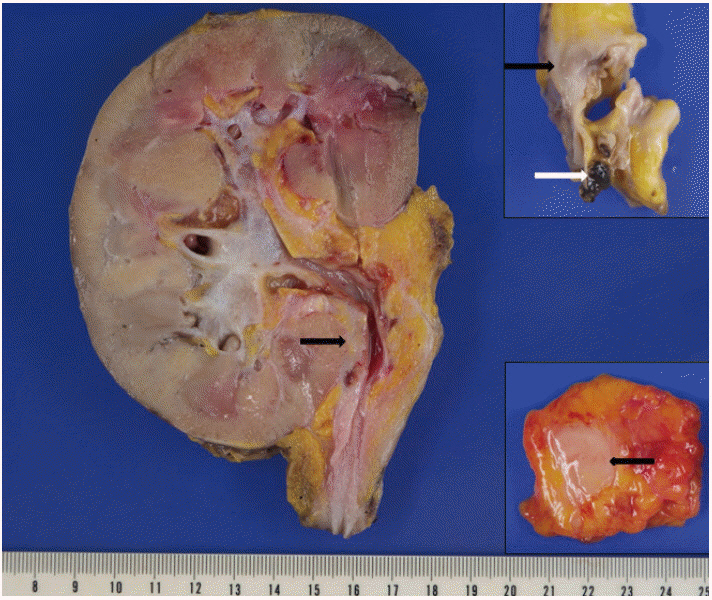
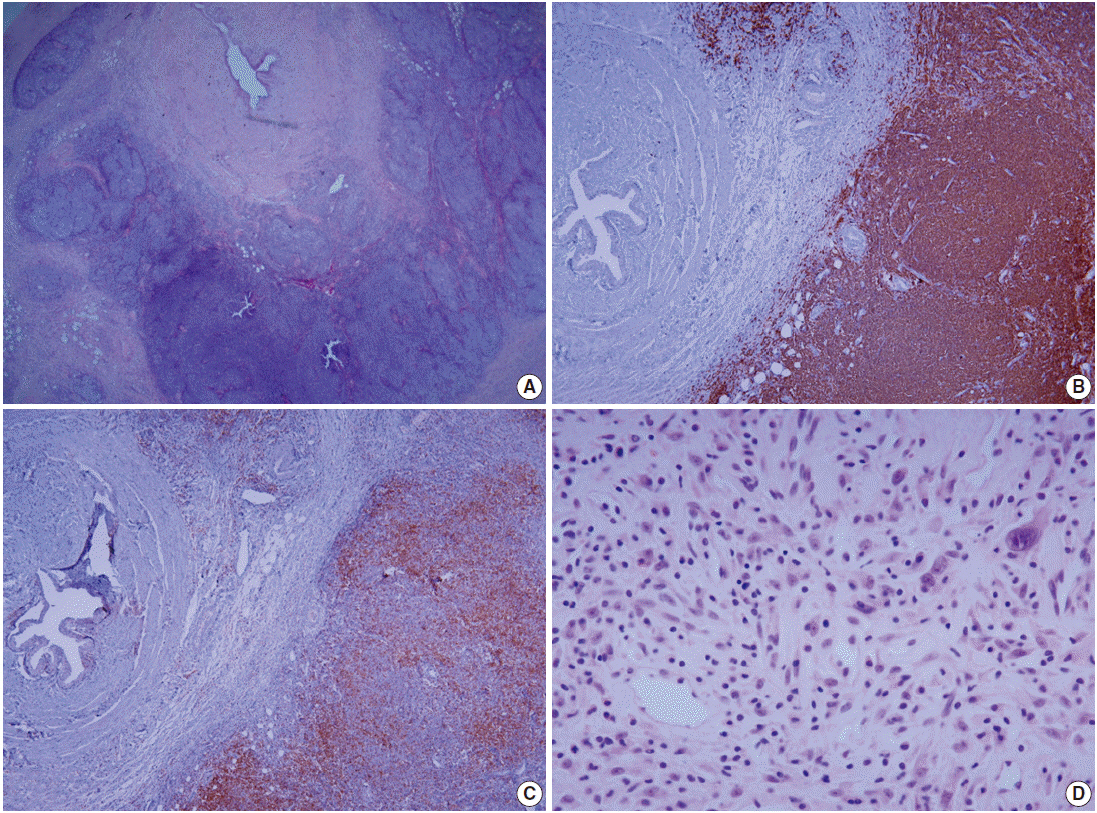
J Pathol Transl Med.
2015 Jul;49(4):339-342. 10.4132/jptm.2015.04.28.
Ureteral Marginal Zone Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue, Chronic Inflammation, and Renal Artery Atherosclerosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jrhuh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2151145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2015.04.28
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Otsuki H, Ito K, Sato K, et al. Malignant lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue involving the renal pelvis and the entire ureter: a case report. Oncol Lett. 2013; 5:1625–8.
Article2. Thieblemont C, Bertoni F, Copie-Bergman C, Ferreri AJ, Ponzoni M. Chronic inflammation and extra-nodal marginal-zone lymphomas of MALT-type. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014; 24:33–42.
Article3. Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics tumors of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Press;2004.4. Araki K, Kubota Y, Iijima Y, et al. Indolent behaviour of low-grade B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue involved in salivary glands, renal sinus and prostate. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1998; 32:234–6.5. Qiu L, Unger PD, Dillon RW, Strauchen JA. Low-grade mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma involving the kidney: report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006; 130:86–9.
Article6. Mita K, Ohnishi Y, Edahiro T, Fujii T, Yamasaki A, Shimamoto F. Primary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma in the renal pelvis. Urol Int. 2002; 69:241–3.
Article7. Hara M, Satake M, Ogino H, et al. Primary ureteral mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma: pathological and radiological findings. Radiat Med. 2002; 20:41–4.8. Matsuda I, Zozumi M, Tsuchida YA, et al. Primary extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue type with malakoplakia in the urinary bladder: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:5280–4.9. Thieblemont C, Berger F, Dumontet C, et al. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma is a disseminated disease in one third of 158 patients analyzed. Blood. 2000; 95:802–6.
Article10. Hansson GK, Robertson AK, SÖderberg-Nauclér C. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006; 1:297–329.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Primary Pulmonary Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of the MALT Type
- Role of Chemotherapy in Gastric Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Type
- A Case of Primary Nodal Type Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma of the Intra-Parotid Lymph Node Mistaken to Primary Benign Parotid Mass
- A Case of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma in Nasopharynx and Thyroid Gland
- Endoscopic Findings of Gastric Extranodal Marginal Zone B-Cell Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma