Clin Endosc.
2015 May;48(3):256-259. 10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.256.
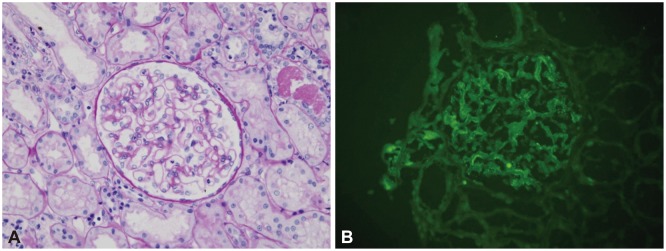
Gastric Syphilis and Membranous Glomerulonephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. sonjh@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- KMID: 2148576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.256
Abstract
- Syphilis is a chronic systemic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Gastric involvement and nephrotic syndrome are uncommon but well documented complications of syphilis, but the co-occurrence of these two complications in the same patient is extremely rare. Thus, because of their nonspecific presentation, suspicion of gastric syphilis (GS) and nephrotic syndrome is essential for diagnosis. Patients should be investigated thoroughly and a diagnosis made based on clinical, endoscopic, and histological findings, in order to initiate appropriate therapy. We report of a 34-year-old male patient with a history of epigastric pain and a diagnosis of GS and syphilis-associated membranous glomerulonephritis confirmed by gastroscopy and kidney biopsy, who was treated successfully with penicillin G benzathine. This case report provides information on the typical features of GS that should help raise awareness of this rare disease entity among clinicians, resulting in earlier diagnosis and administration of appropriate therapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Borrmann Type 4 Advanced Gastric Cancer: Focus on the Development of Scirrhous Gastric Cancer
Kyoungwon Jung, Moo In Park, Sung Eun Kim, Seun Ja Park
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(4):336-345. doi: 10.5946/ce.2016.057.
Reference
-
1. Mylona EE, Baraboutis IG, Papastamopoulos V, et al. Gastric syphilis: a systematic review of published cases of the last 50 years. Sex Transm Dis. 2010; 37:177–183. PMID: 20023597.
Article2. Hook EW 3rd, Marra CM. Acquired syphilis in adults. N Engl J Med. 1992; 326:1060–1069. PMID: 1549153.
Article3. Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Disease web statics system: syphilis [Internet]. Osong: Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;c2002. cited 2014 Mar 2. Available from: http://is.cdc.go.kr/nstat/index.jsp/.4. Souza Varella Frazão M, Guimarães Vilaça T, Olavo Aragão Andrade Carneiro F, et al. Endoscopic aspects of gastric syphilis. Case Rep Med. 2012; 2012:646525. PMID: 22924047.
Article5. Hunte W, al-Ghraoui F, Cohen RJ. Secondary syphilis and the nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993; 3:1351–1355. PMID: 8439646.
Article6. Handoko ML, Duijvestein M, Scheepstra CG, de Fijter CW. Syphilis: a reversible cause of nephrotic syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013:pii: bcr2012008279.
Article7. Fujisaki T, Tatewaki M, Fujisaki J. A case of gastric syphilis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 6:A34. PMID: 18407796.
Article8. Greenstein DB, Wilcox CM, Schwartz DA. Gastric syphilis. Report of seven cases and review of the literature. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994; 18:4–9. PMID: 8113584.9. Anai H, Okada Y, Okubo K, et al. Gastric syphilis simulating linitis plastica type of gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 1990; 36:624–626. PMID: 2279662.
Article10. Abdu RA, Carter K, Pomidor WJ. Gastric syphilis mimicking linitis plastica. Arch Surg. 1993; 128:103–104. PMID: 8418771.
Article11. Winters HA, Notar-Francesco V, Bromberg K, et al. Gastric syphilis: five recent cases and a review of the literature. Ann Intern Med. 1992; 116:314–319. PMID: 1733388.
Article12. Tang AL, Thin RN, Croft DN. Nephrotic syndrome and hepatitis in early syphilis. Postgrad Med J. 1989; 65:14–15. PMID: 2780445.
Article13. Kwon HH, Woo CM, Oh HJ, et al. Nephrotic syndrome, hepatitis and gastric involvement in secondary syphilis. Korean J Nephrol. 2004; 23:152–157.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Nephrotic Syndrome, Hepatitis and Gastric Involvement in Secondary Syphilis
- Etiologic diseases of membranous glomerulonephritis,
- A Case of Guillain-Barre Syndrome associated with Membranous Glomerulonephritis and Uveitis
- Primary Sjogren's Syndrome Associated with Membranous Glomerulonephritis
- A Case of Basal Cell Carcinoma in a Patient with Membranous Glomerulonephritis