J Korean Soc Surg Hand.
2014 Jun;19(2):57-64. 10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.2.57.
Factors Affecting the Occurrence of Distal Radioulnar Joint Arthritis after Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, The Armed Forces Dae Jeon Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ygchung@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.2.57
Abstract
- PURPOSE
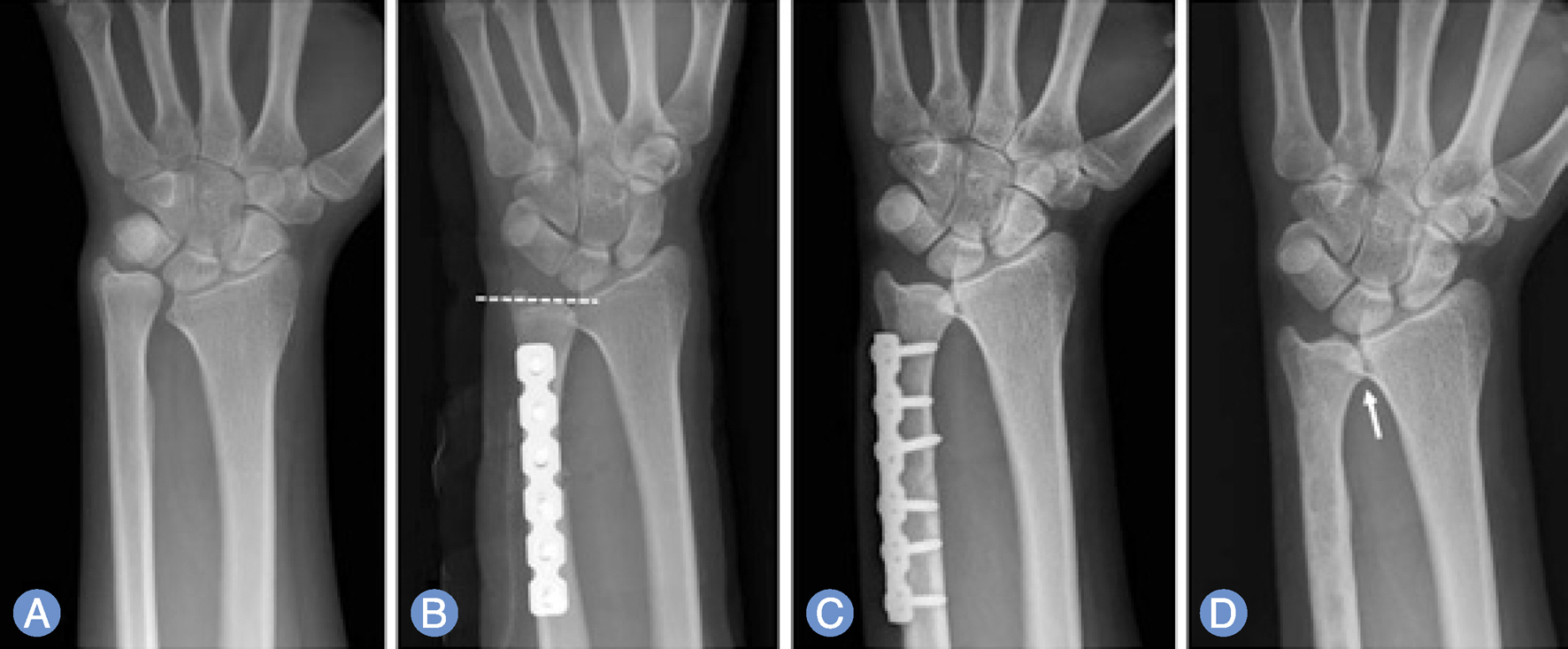
Ulnar shortening osteotmy is a common operation for the treatment of ulnar impaction syndrome. The purpose of this study was to evaluate factors that may affect the occurrence of distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) arthritis after ulnar shortening osteotomy.
METHODS
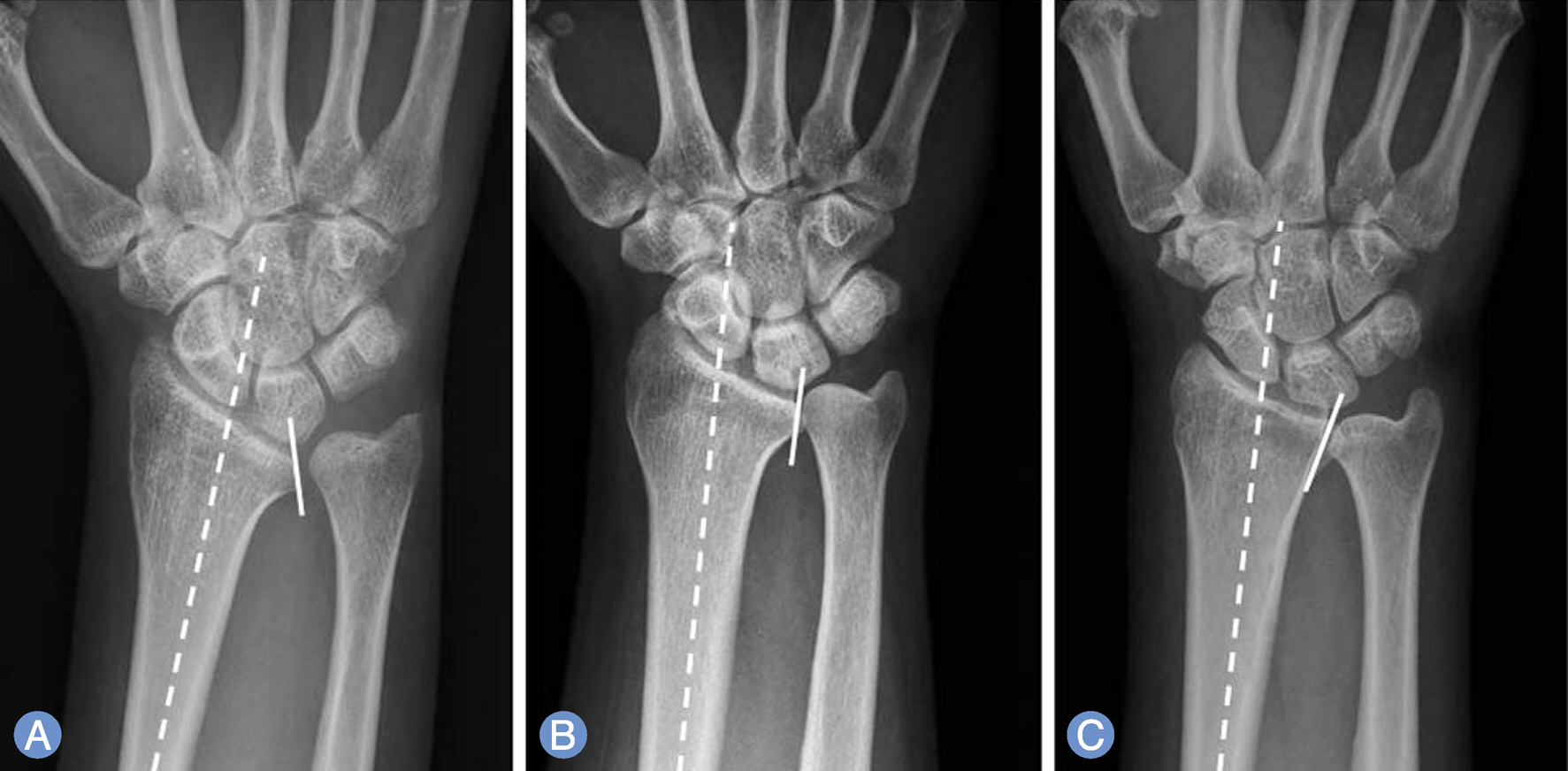
From September 2005 to August 2012, we performed 81 ulnar shortening osteotomies for ulnar impaction syndrome, and evaluated occurrence or deterioration of DRUJ arthritis in 58 patients with a minimum follow-up of 1 year. We analyzed potential factors that may affect the occurrence of DRUJ arthritis, such as, age, sex, hand dominance, pre- and postoperative ulnar variance, preexisting DRUJ arthritis, types of radial sigmoid notch, amount of ulnar shortening, and follow up period.
RESULTS
DRUJ arthritis occurred or deteriorated in 32 out of the 58 patients. Regression analysis indicated a significant correlation between the type of radial sigmoid notch (type 1) and DRUJ arthritis. Other factors were not found to be correlated with occurrence or deterioration of DRUJ arthritis.
CONCLUSION
This study suggests that patients with type 1 radial sigmoid notch (ulnar inclination of more than 10 degrees) are more likely to develop DRUJ arthritis after ulnar shortening osteotomy.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Friedman SL, Palmer AK. The ulnar impaction syndrome. Hand Clin. 1991; 7:295–310.
Article2. Milch H. Colles’ fracture. Bull Hosp Joint Dis. 1950; 11:61–74.3. Darrow JC Jr, Linscheid RL, Dobyns JH, Mann JM 3rd, Wood MB, Beckenbaugh RD. Distal ulnar recession for disorders of the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:482–91.
Article4. Chun S, Palmer AK. The ulnar impaction syndrome: follow-up of ulnar shortening osteotomy. J Hand Surg Am. 1993; 18:46–53.
Article5. Palmer AK, Werner FW. Biomechanics of the distal radioulnar joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; (187):26–35.
Article6. Kreder HJ, Hanel DP, McKee M, Jupiter J, McGillivary G, Swiontkowski MF. X-ray film measurements for healed distal radius fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21:31–9.
Article7. Tolat AR, Stanley JK, Trail IA. A cadaveric study of the anatomy and stability of the distal radioulnar joint in the coronal and transverse planes. J Hand Surg Br. 1996; 21:587–94.
Article8. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16:494–502.
Article9. Nakamura R, Tanaka Y, Imaeda T, Miura T. The influence of age and sex on ulnar variance. J Hand Surg Br. 1991; 16:84–8.
Article10. Sagerman SD, Zogby RG, Palmer AK, Werner FW, Fortino MD. Relative articular inclination of the distal radioulnar joint: a radiographic study. J Hand Surg Am. 1995; 20:597–601.
Article11. Baek GH, Lee HJ, Gong HS, et al. Long-term outcomes of ulnar shortening osteotomy for idiopathic ulnar impaction syndrome: at least 5-years follow-up. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011; 3:295–301.
Article12. Minami A, Kato H. Ulnar shortening for triangular fibrocartilage complex tears associated with ulnar positive variance. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23:904–8.
Article13. Koppel M, Hargreaves I, Herbert T. Ulnar shortening osteotomy for ulnar carpal instability and ulnar carpal impaction. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 1997; 22:451–6.14. Nishiwaki M, Nakamura T, Nakao Y, Nagura T, Toyama Y. Ulnar shortening effect on distal radioulnar joint stability: a biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:719–26.
Article15. Kleinman WB, Graham TJ. The distal radioulnar joint capsule: clinical anatomy and role in posttraumatic limitation of forearm rotation. J Hand Surg Am. 1998; 23:588–99.
Article16. Schuind F, An KN, Berglund L, et al. The distal radioulnar ligaments: a biomechanical study. J Hand Surg Am. 1991; 16:1106–14.
Article17. Ward LD, Ambrose CG, Masson MV, Levaro F. The role of the distal radioulnar ligaments, interosseous membrane, and joint capsule in distal radioulnar joint stability. J Hand Surg Am. 2000; 25:341–51.
Article18. Baek GH, Chung MS, Lee YH, Gong HS, Lee S, Kim HH. Ulnar shortening osteotomy in idiopathic ulnar impaction syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2649–54.
Article19. Miura T, Firoozbakhsh K, Cheema T, Moneim MS, Edmunds M, Meltzer S. Dynamic effects of joint-leveling procedure on pressure at the distal radioulnar joint. J Hand Surg Am. 2005; 30:711–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Long-term Outcomes of Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Idiopathic Ulnar Impaction Syndrome: At Least 5-Years Follow-up
- Distal Radioulnar Joint Arthritis
- Traumatic Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injuries and Instability of the Distal Radioulnar Joint
- Treatment of Dislocation of distal Radio - ulnar Joint: Comparison of Long - term follow - up Results between the Reconstruction and Darrach Operation Group
- Delayed Diagnosis of Volar Dislocation of the Distal Ulna after Treatment of the Radial Shaft Fracture