Korean J Pain.
2011 Dec;24(4):231-234. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.231.
Spontaneous Vertebral Reduction during the Procedure of Kyphoplasty in a Patient with Kummell's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea. clonidine@empas.com
- KMID: 2074019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.231
Abstract
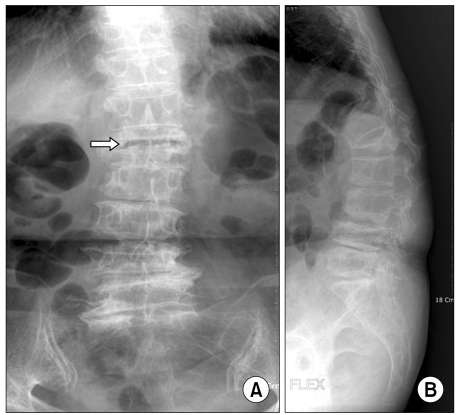
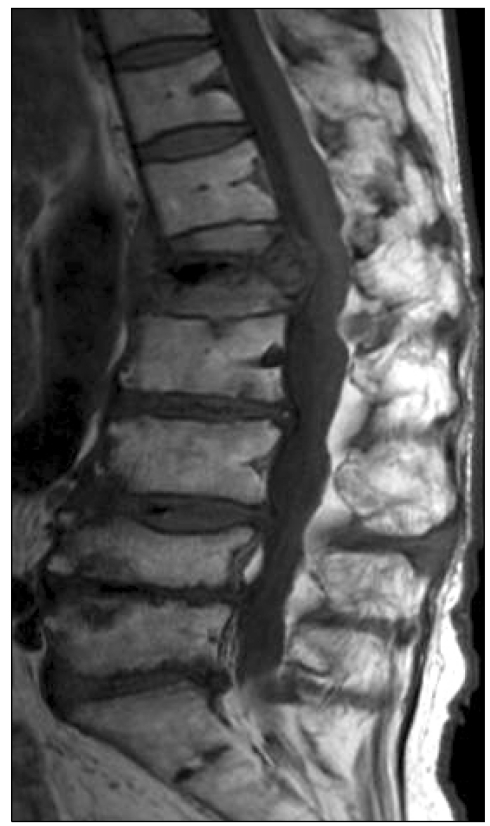
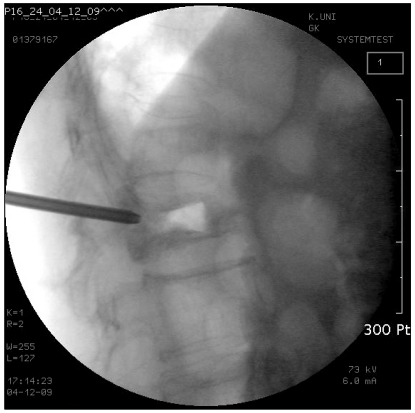
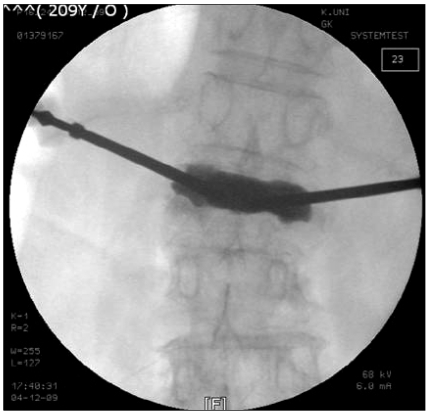
- Kummell's disease is a spinal disorder characterized by delayed post-traumatic collapse of a vertebral body with avascular necrosis. Although definitive treatment for Kummell's disease has not been established, it has been reported that percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty has shown good results. However, these procedures are not recommended for severely collapsed vertebral bodies because of the risk of cement leakage or technical difficulties. Authors report a rare case of spontaneous reduction in vertebral height by the insertion of a working cannula into the vertebral body in Kummell's disease.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
More Effective Way to Perform Complete Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Patients in Kummell’s Disease: A Case Report
Seung Hee Yoo, Ji Seon Chae, Minjin Lee, Bo Kyung Kang, Hahck Soo Park, Won-Joong Kim
Ewha Med J. 2021;44(3):80-83. doi: 10.12771/emj.2021.44.3.80.Cannula-induced Vertebral Reduction during Kyphoplasty in a Patient with Kummell's Disease
Ki Seong Eom, Tae Young Kim
Korean J Pain. 2012;25(2):131-132. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.2.131.
Reference
-
1. Van Eenenaam DP, el-Khoury GY. Delayed post-traumatic vertebral collapse (Kummell's disease): case report with serial radiographs, computed tomographic scans, and bone scans. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:1236–1241. PMID: 8362333.2. Young WF, Brown D, Kendler A, Clements D. Delayed post-traumatic osteonecrosis of a vertebral body (Kummell's disease). Acta Orthop Belg. 2002; 68:13–19. PMID: 11915453.3. Maldague BE, Noel HM, Malghem JJ. The intravertebral vacuum cleft: a sign of ischemic vertebral collapse. Radiology. 1978; 129:23–29. PMID: 693884.
Article4. Heini PF, Wälchli B, Berlemann U. Percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty with PMMA: operative technique and early results. A prospective study for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. Eur Spine J. 2000; 9:445–450. PMID: 11057541.
Article5. Masala S, Fiori R, Massari F, Simonetti G. Kyphoplasty: indications, contraindications and technique. Radiol Med. 2005; 110:97–105. PMID: 16163144.6. Masala S, Fiori R, Massari F, Cantonetti M, Postorino M, Simonetti G. Percutaneous kyphoplasty: indications and technique in the treatment of vertebral fractures from myeloma. Tumori. 2004; 90:22–26. PMID: 15143966.
Article7. McKiernan F, Jensen R, Faciszewski T. The dynamic mobility of vertebral compression fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2003; 18:24–29. PMID: 12510802.
Article8. Mathis JM, Barr JD, Belkoff SM, Barr MS, Jensen ME, Deramond H. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: a developing standard of care for vertebral compression fractures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:373–381. PMID: 11156786.9. Kempinsky WH, Morgan PP, Boniface WR. Osteoporotic kyphosis with paraplegia. Neurology. 1958; 8:181–186. PMID: 13517483.
Article10. Li KC, Li AF, Hsieh CH, Liao TH, Chen CH. Another option to treat Kümmell's disease with cord compression. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16:1479–1487. PMID: 16568304.
Article11. Choi YS, Lee MG, Lee HM, Jo JY, Jeong HJ, Lee CJ, et al. A case of balloon kyphoplasty in high risk under cement leakage: a case report. Korean J Pain. 2006; 19:261–265.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is Kummell's Disease a Independent Disease Entity?: Two Case Report
- Balloon Kyphoplasty: An Effective Treatment for Kummell Disease?
- Cannula-induced Vertebral Reduction during Kyphoplasty in a Patient with Kummell's Disease
- Comparison Vertebroplasty with Kyphoplasty in Delayed Post-traumatic Osteonecrosis of a Vertebral Body(Kummell's Disease)
- Delayed Bone Cement Displacement Following Balloon Kyphoplasty