Korean J Pain.
2011 Dec;24(4):226-230. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.226.
Lumbar Plexopathy Caused by Metastatic Tumor, Which Was Mistaken for Postoperative Femoral Neuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea. maestro@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Busan St. Mary's Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2074018
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.4.226
Abstract
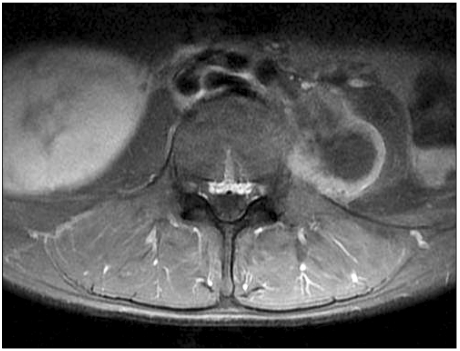
- Surgical excision was performed on a 30-years old woman with a painful mass on her left thigh. The pathologic findings on the mass indicated fibromatosis. After the operation, she complained of allodynia and spontaneous pain at the operation site and ipsilateral lower leg. We treated her based on postoperative femoral neuropathy, but symptom was aggravated. We found a large liposarcoma in her left iliopsoas muscle which compressed the lumbar plexus. In conclusion, the cause of pain was lumbar plexopathy related to a mass in the left iliopsoas muscle. Prompt diagnosis of acute neuropathic pain after an operation is important and management must be based on exact causes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kehlet H, Rathmell JP. Persistent postsurgical pain: the path forward through better design of clinical studies. Anesthesiology. 2010; 112:514–515. PMID: 20124977.2. Niraj G, Rowbotham DJ. Persistent postoperative pain: where are we now? Br J Anaesth. 2011; 107:25–29. PMID: 21610014.
Article3. Pechter EA, Smith PB. Transient femoral neuropathy after abdominoplasty. Ann Plast Surg. 2008; 61:492–493. PMID: 18948773.
Article4. Van Veer H, Coosemans W, Pirenne J, Monbaliu D. Acute femoral neuropathy: a rare complication after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42:4384–4388. PMID: 21168704.
Article5. Wilson M, Ramage L, Yoong W, Swinhoe J. Femoral neuropathy after vaginal surgery: a complication of the lithotomy position. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2011; 31:90–91. PMID: 21281008.
Article6. Crombie IK, Davies HT, Macrae WA. Cut and thrust: antecedent surgery and trauma among patients attending a chronic pain clinic. Pain. 1998; 76:167–171. PMID: 9696470.
Article7. Kehlet H, Jensen TS, Woolf CJ. Persistent postsurgical pain: risk factors and prevention. Lancet. 2006; 367:1618–1625. PMID: 16698416.
Article8. Planner AC, Donaghy M, Moore NR. Causes of lumbosacral plexopathy. Clin Radiol. 2006; 61:987–995. PMID: 17097418.
Article9. Lee GH. The Korean pain society. Disc herniation. Pain medicine. 2007. 3rd ed. Seoul: Koonja Publishing Inc;p. 271–277.10. Al-Ajmi A, Rousseff RT, Khuraibet AJ. Iatrogenic femoral neuropathy: two cases and literature update. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2010; 12:66–75. PMID: 21386773.
Article11. Tong HC. Specificity of needle electromyography for lumbar radiculopathy in 55- to 79-yr-old subjects with low back pain and sciatica without stenosis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90:233–238. PMID: 21297400.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ischemic Lumbar Flexopainy: Caused by Obstruction of Iliolumbar Artery
- Lumbar plexopathy after radical nephrectomy: A case report
- Femoral Neuropathy caused by Iliopsoas Hematoma: A Case Report
- A Case of Femoral Neuropathy after Renal Transplantation
- Conduction Studies of the Saphenous Nerve in Normal Subjects and Patients with Femoral Neuropathy