J Korean Surg Soc.
2010 Dec;79(Suppl 1):S45-S49. 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S45.
Hepatic Resection for Large Hepatic Metastasis of Adrenocortical Carcinoma after Cyberknife Treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. choiins@kyuh.co.kr
- KMID: 2040552
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2010.79.Suppl1.S45
Abstract
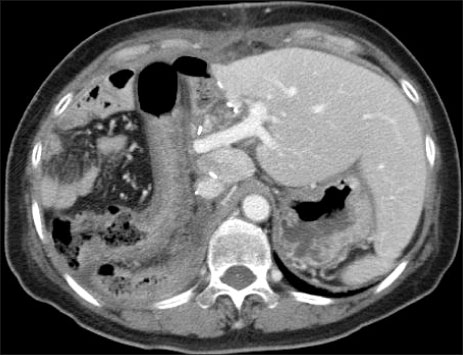
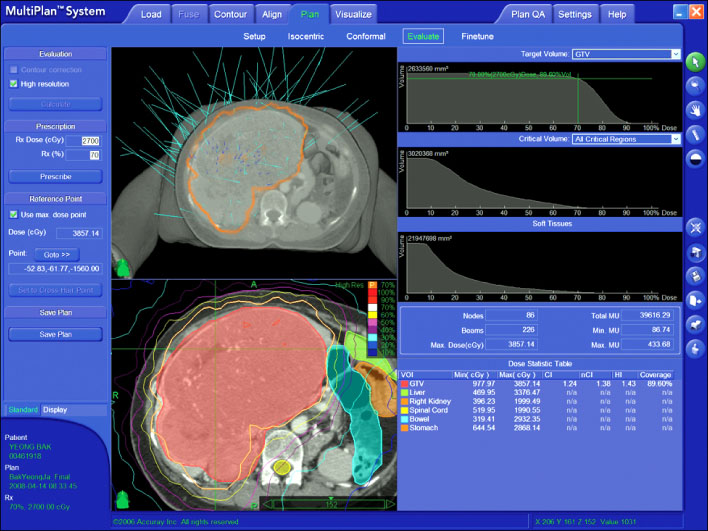
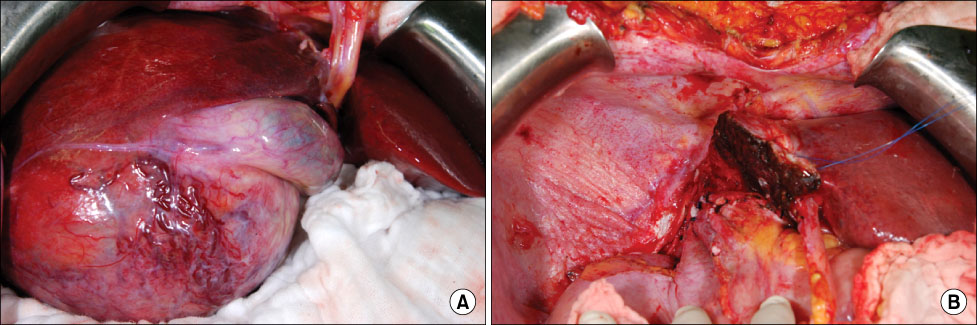
- Surgical resection is the best treatment for operable metastatic liver cancer. Large metastatic cancer usually has low operability, so a debulking modality of mass is needed to increase operability. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy were commonly used as neoadjuvant treatments. Cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery systems were only considered as one of the palliative treatment modalities for inoperable or surgically complex tumors. But, in this case, we applied Cyberknife as the preoperative debulking modality for large hepatic metastasis of adrenocortical carcinoma. After Cyberknife treatment 3 cyclex2,700 cGY, tumor size decreased (metastatic liver mass decreased to 15x9 cm from 19x12.5 cm, adrenal mass decreased to 5x3 cm from 7.4x4.5 cm). We could then resect the tumor completely by extended right hemihepatectomy & right adrenalectomy. A preoperative multidisciplinary approach, including chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be considered to increase operability. So, cyberknife can be considered an additional modality as a neoadjuvant radiotherapy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Di Carlo I, Toro A, Sparatore F, Cordio S. Liver resection for hepatic metastases from adrenocortical carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2006. 8:106–109.2. Grondal S, Cedermark B, Eriksson B, Grimelius L, Harach R, Kristoffersson A, et al. Adrenocortical carcinoma. A retrospective study of a rare tumor with a poor prognosis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1990. 16:500–506.3. Wajchenberg BL, Albergaria Pereira MA, Medonca BB, Latronico AC, Campos Carneiro P, Alves VA, et al. Adrenocortical carcinoma: clinical and laboratory observations. Cancer. 2000. 88:711–736.4. Kim YK, Lee TH, Kim C, Kim SJ, Kim H. Cyberknife radiosurgery for inoperable recurred oral cancer. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004. 30:65–68.5. Weng SF, Chang CC, Su DH, Chang YL. An adrenocortical carcinoma patient with multiple lung metastases: case report. Tzu Chi Med J. 2005. 17:105–109.6. Kim KH, Park JC, Lim SY, Sohn IS, Yun KH, Cho SH, et al. A case of non-functioning huge adrenocortical carcinoma extending into inferior vena cava and right atrium. J Korean Med Sci. 2006. 21:572–576.7. Muttarak M, Chotirosniramit A, Unsrisong K, Chiangmai WN. Adrenal carcinoma. Biomed Imaging Interv J. 2006. 2:e9.8. Ohwada S, Izumi M, Kawate S, Hamada K, Toya H, Togo N, et al. Surgical outcome of stage III and IV adrenocortical carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007. 37:108–113.9. Chang SD, Murphy M, Geis P, Martin DP, Hancock SL, Doty JR, et al. Clinical experience with image-guided robotic radiosurgery (the Cyberknife) in the treatment of brain and spinal cord tumors. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1998. 38:780–783.10. Ryu SI, Chang SD, Kim DH, Murphy MJ, Le QT, Martin DP, et al. Image-guided hypo-fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery to spinal lesions. Neurosurgery. 2001. 49:838–846.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Localized Esophageal Ulcerations after CyberKnife Treatment for Metastatic Hepatic Tumor of Colon Cancer
- Hepatic Resection in Patients with Liver Metastasis from Gastric Cancer
- Hepatic resection margin predicts survival in colorectal cancer with hepatic metastasis
- Liver Metastases in Colorectal Cancer
- Hepatic resection for isolated stomach cancer liver metastases: A single-center experience