J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 Feb;72(2):140-142. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.2.140.
Fat Deposition in the Urinary Bladder Wall: Incidental Finding on Abdominal Computed Tomography: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. aquamsk@naver.com
- KMID: 2002812
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.2.140
Abstract
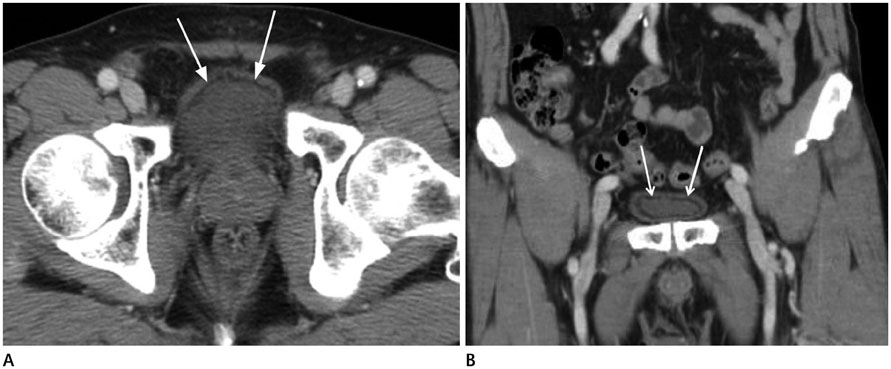
- In a computed tomography (CT) scan, fat deposition in the urinary bladder wall is seen as a linear hypoattenuating band surrounded by soft tissue density. It is uncommon, but is often seen in normal cases. However, there is no report of fat deposition in the urinary bladder wall in Korea. The authors encountered a 62-year-old male patient who showed an incidental hypoattenuating band in the urinary bladder wall on abdominal CT. The patient showed no clinical signs related to fat deposition in the urinary bladder wall. When the patient's previous abdominal CT was retrospectively reviewed, the same CT finding was seen. This linear hypoattenuating band within the urinary bladder wall should be considered as a normal CT finding, although it is uncommon.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Philip AT, Amin MB, Tamboli P, Lee TJ, Hill CE, Ro JY. Intravesical adipose tissue: a quantitative study of its presence and location with implications for therapy and prognosis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000; 24:1286–1290.2. Thickman D. Fat within the wall of the urinary bladder: computed tomographic appearance. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2009; 33:695–697.3. Patel RR, Javors BR. Intramural vesicular fat--an uncommon CT finding. Clin Imaging. 2012; 36:75–76.4. Martínez-Moya M, Domínguez-Pérez ÁD, Frutos-Arenas J. Fat-fluid intravessical level: a new sign of bladder rupture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:W373–W374.5. Panchal VJ, Chen R, Ghahremani GG. Non-tropical chyluria: CT diagnosis. Abdom Imaging. 2012; 37:494–500.6. Grupper M, Kravtsov A, Potasman I. Emphysematous cystitis: illustrative case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2007; 86:47–53.7. Bochner BH, Nichols PW, Skinner DG. Overstaging of transitional cell carcinoma: clinical significance of lamina propria fat within the urinary bladder. Urology. 1995; 45:528–531.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Heterotopic Pancreas with Abundant Fat Tissue in the Stomach: A Case Report
- Ectopic Prostate Tissue in the Posterior Wall of the Bladder
- The Role of Computed Tomography of the Bladder Cancer with Perivesical Fat Infiltration
- A Case of Leiomyoma of the Urinary Bladder with Voiding Difficulty
- CT Findings of Primary Localized Amyloidosis of the Urinary Bladder: A Case Report