Restor Dent Endod.
2012 Aug;37(3):160-164. 10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.160.
The reduction methods of operator's radiation dose for portable dental X-ray machines
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology, Dankook University College of Dentistry, Cheonan, Korea. wjhan@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 1995656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.160
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This study was aimed to investigate the methods to reduce operator's radiation dose when taking intraoral radiographs with portable dental X-ray machines.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
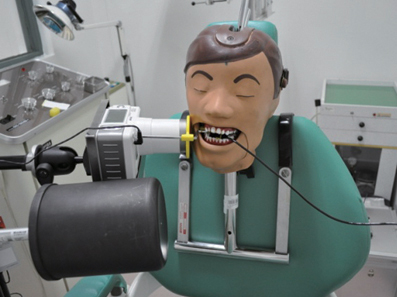
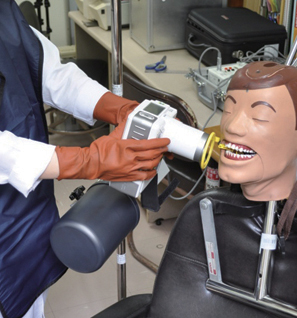
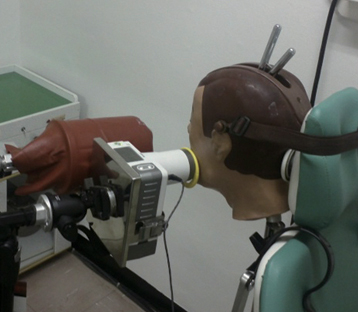
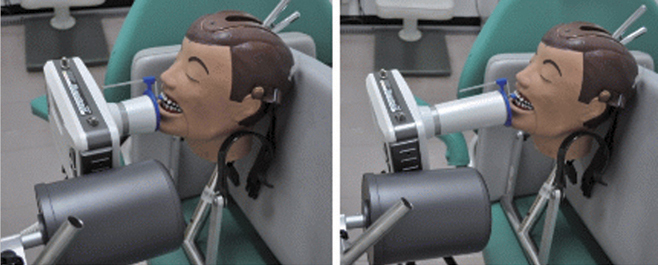
Two kinds of portable dental X-ray machines (DX3000, Dexcowin and Rextar, Posdion) were used. Operator's radiation dose was measured with an 1,800 cc ionization chamber (RadCal Corp.) at the hand level of X-ray tubehead and at the operator's chest and waist levels with and without the backscatter shield. The operator's radiation dose at the hand level was measured with and without lead gloves and with long and short cones.
RESULTS
The backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the hand level of X-ray tubehead to 23 - 32%, the lead gloves to 26 - 31%, and long cone to 48 - 52%. And the backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the operator's chest and waist levels to 0.1 - 37%.
CONCLUSIONS
When portable dental X-ray systems are used, it is recommended to select X-ray machine attached with a backscatter shield and a long cone and to wear the lead gloves.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
Restor Dent Endod. 2013;38(3):146-153. doi: 10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.146.
Reference
-
1. Coy JD. Use of lightweight X-ray machine and processor during Riverine medical readiness training exercise on the Amazon River. Mil Med. 1991. 156:623–628.
Article2. Van Dis ML, Miles DA, Parks ET, Razmus TF. Information yield from a hand-held dental x-ray unit. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993. 76:381–385.
Article3. Coy J. Hand-held dental X-ray (HDX) with medical collimator: use in casualty radiology. Mil Med. 1996. 161:428–431.
Article4. Coy J, Vandre RH, Davidson WR. Use of the hand-held dental X-ray machine during joint operation, NATO exercise Display Determination-92. Mil Med. 1997. 162:575–577.
Article5. Varghese S, Kimmel A, Radmer T, Bradley TG, Bahcall J. In vitro evaluation of the XR-15 portable x-ray unit for forensic odontology. J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2004. 22:5–8.6. Charlton DG. Portable dental equipment: dental units and x-ray equipment. Gen Dent. 2009. 57:336–341.7. Hermsen KP, Jaeger SS, Jaeger MA. Radiation safety for the NOMAD™ portable X-ray system in a temporary morgue setting. J Forensic Sci. 2008. 53:917–921.
Article8. Department of Licensing and regulatory affairs. Ionizing radiation rules, Part 9. Dental X-ray installations, R325.5396. Hand-held portable dental x-ray systems. Available from: http://www.michigan.gov/lara/0,4601,7-154-35299_28142_3579-46448--,00.html (updated 2012 July 30).9. Ohio department of Health. Dental radiationgenerating equipment. Available from: http://www.odh.ohio.gov/~/media/ODH/ASSETS/Files/rules/final/37011-66/37011-66-06.ashx (updated 2012 July 30).10. Washington state legislature. Radiation safety and diagnostic image quality standards for dental facilities, chapter 246-225A-085 Hand-held X-ray system. Available from: http://apps.leg.wa.gov/wac/default.aspx?cite=246-225A&full=true#246-225A-085 (updated 2012 July 30).11. Kim EK. Leakage and scattered radiation from hand-held dental x-ray unit. Korean J Oral Maxillofac Radiol. 2007. 37:65–68.12. National Institute of Food and Drug Safety Evaluation. Regulation for the safety management of diagnostic x-ray equipments. Available from: http://www.nifds.go.kr/nifds/01_about/about08.jsp?mode=view&article_no=4813&pager.offset=0&board_no=2 (updated 2012 July 30).13. Danforth RA, Herschaft EE, Leonowich JA. Operator exposure to scatter radiation from a portable hand-held dental radiation emitting device (Aribex™ NOMAD™) while making 915 intraoral dental radiographs. J Forensic Sci. 2009. 54:415–421.
Article14. Goren AD, Bonvento M, Biernacki J, Colosi DC. Radiation exposure with the NOMAD™ portable X-ray system. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008. 37:109–112.15. Gray JE, Bailey ED, Ludlow JB. Dental staff doses with handheld dental intraoral x-ray units. Health Phys. 2012. 102:137–142.
Article16. White SC, Pharoah MJ. Oral radiology; principles and interpretation. 2009. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby-Year Book Inc.;148–149.17. Aribex, Inc. Aribex NOMAD™ dental portable x-ray system for intraoral radiographic imaging. User manual. 2006. Orem UT: Aribex, Inc.;Available from: http://aribex.com/portable-x-ray-machine/dental-x-raymachine/nomad-x-ray/nomad-safety (update 2012 Jan 30).18. Pittayapat P, Oliveira-Santos C, Thevissen P, Michielsen K, Bergans N, Willems G, Debruyckere D, Jacobs R. Image quality assessment and medical physics evaluation of different portable dental X-ray units. Forensic Sci Int. 2010. 201:112–117.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Absorbed and effective dose for periapical radiography using portable and wall type dental X-ray machines
- Absorbed and effective dose from periapical radiography by portable intraoral x-ray machine
- Leakage and scattered radiation from hand-held dental x-ray unit
- Correlation between the Portable X-ray and the Radiation Exposure dose in the Emergency Department: Cohort Study
- A dose monitoring system for dental radiography