J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2002 Mar;27(2):122-134. 10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.122.
In vivo study on the biocompatibility of new resin-based root canal sealers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea.
- KMID: 1987271
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.122
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
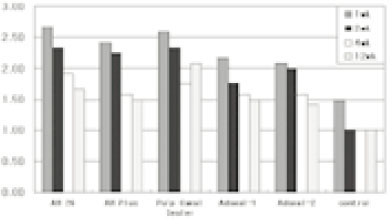
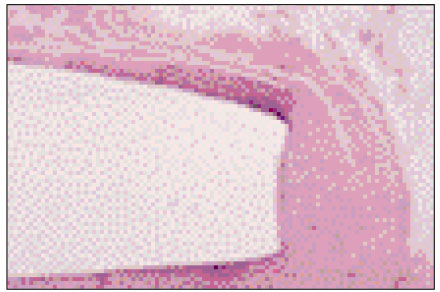
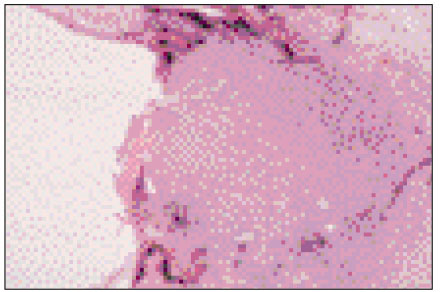
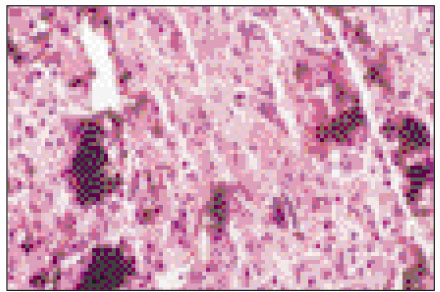
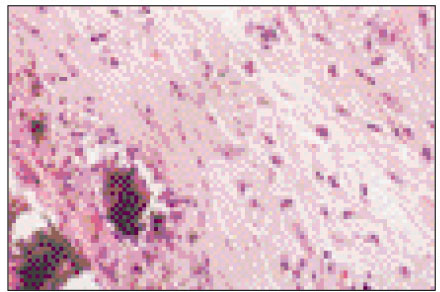
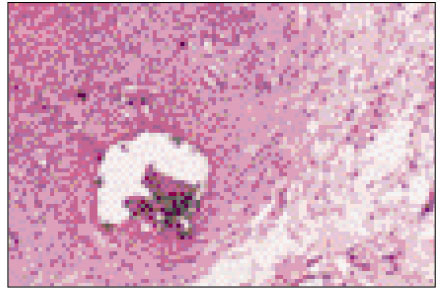
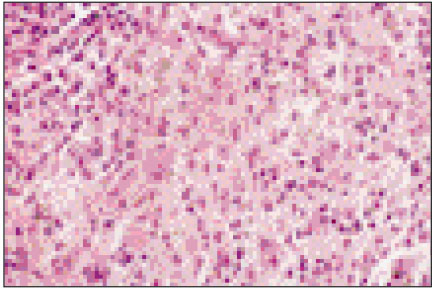
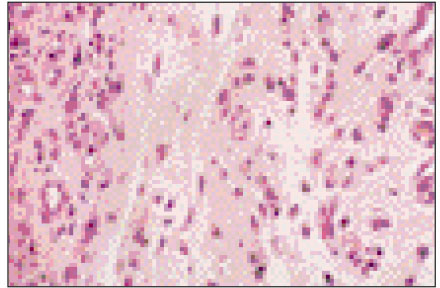
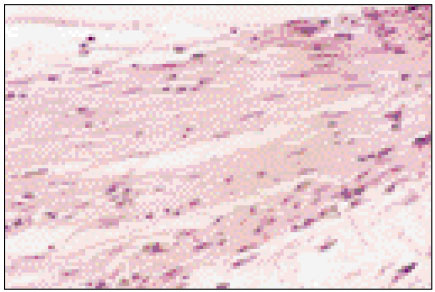
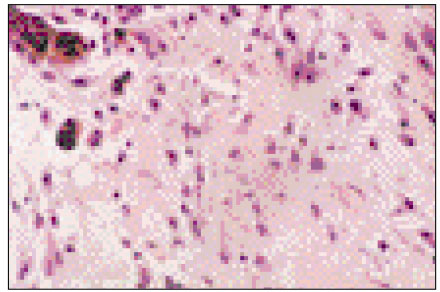
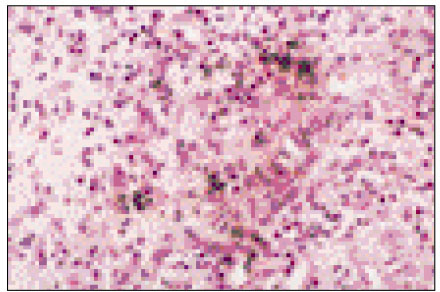
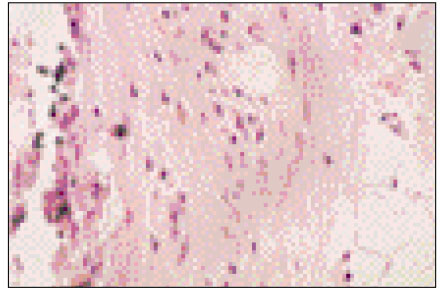
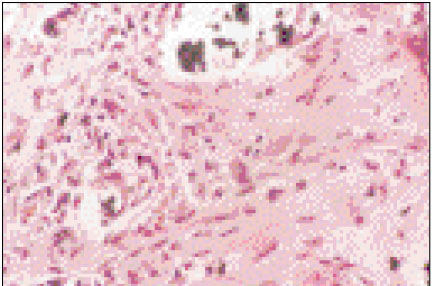
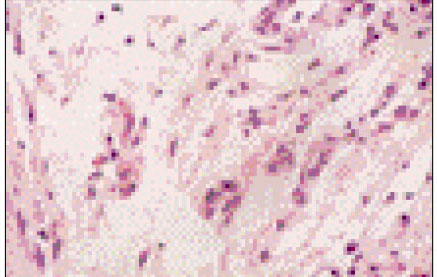
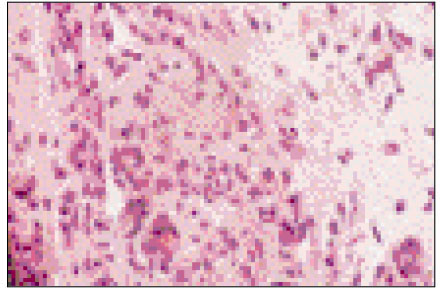
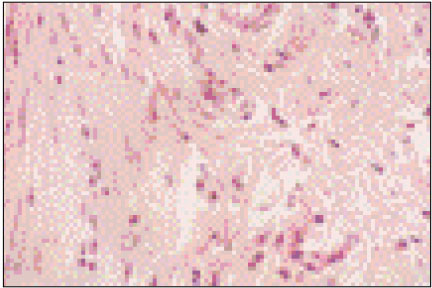
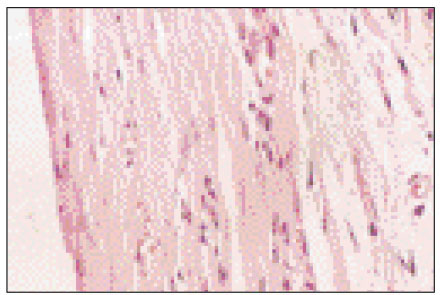
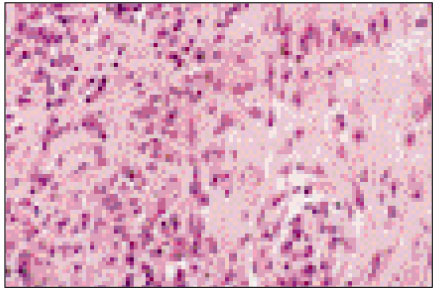
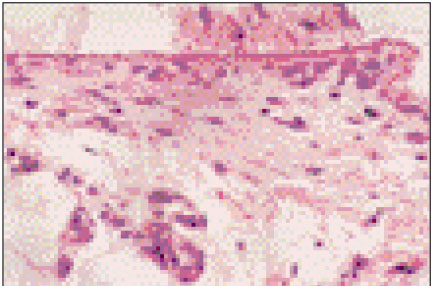
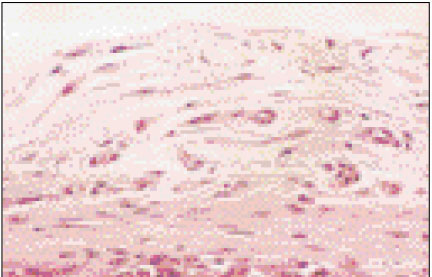
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
Hee-Jung Kim, Seung-Ho Baek, Woo-Cheol Lee, Han-Soo Park, Kwang-Shik Bae
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2004;29(6):498-503. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.498.
Reference
-
1. Grossman LI, Olivet S, Del-Rio CE. Endodontic practice. 1988. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Fabiger.2. Rowe AH. Effect of root filling materials on the periapical tissues. Br Dent J. 1967. 122:98–102.3. Nguyen TN. Obturation of the root canal system. Pathways of the pulp. 1991. 5th ed. St. Louis: CV Mosby.4. Zmener O, Guglieimotti MB, Cabrini RL. Biocompatibility of two calcium hydroxide-based endodontic sealers: a quantitative study in the subcutaneous connective tissue of the rat. J Endod. 1988. 14:229–235.
Article5. Gulati N, Chandra S, Aggarwal PK, Jaiswal JN, Singh M. Cytotoxicity of eugenol in sealer containing zincoxide. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1991. 7:181–185.
Article6. Molloy D, Goldman M, White RR, Kabani S. Comparative tissue tolerance of a new endodontic sealer. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992. 73:490–493.
Article7. Nikolaos E, Ioannis K. Experimental study of the biocompatibility of four root canal sealers and their influence on the Zinc and Calcium content of several tissues. J Endod. 1995. 21:122–127.
Article8. Susan B, Timur E. The investigation of biocompatibility and apical microleakage of tricalcium phosphate based root canal sealers. J Endod. 1997. 23:105–109.
Article9. Ioannis K, Nikolaos E. In vivo comparison of the biocompatibility of two root canal sealers implanted into the subcutaneous connective tissue of rats. J Endod. 1998. 24:82–85.
Article10. Ioannis K, Ioannis V. Experimental study of the biocompatibility of a new glass-inomer root canal sealer. J Endod. 1996. 22:395–398.11. Federation Dentaire International. Recommended standard practices for biological evaluation of dental materials. Int Dent J. 1980. 30:140–188.12. Tronstad L, Barnett F, Falx M. Solubility and Biocompatibility of calcium-hydroxide containing root canal sealers. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1988. 4:152–159.
Article13. Langeland K, Olsson B, Pascon EA. Biological evaluation of Hydron. J Endod. 1981. 7:196–204.
Article14. International Organization for Standardization Biological evaluation of medical Devices-Part 6. Tests for local effects after implantation. 1st ed. 10993–10996.15. Olsson B, Sliwkowski A, Langeland K. Subcutaneous implantation for the biological evaluation of endodontic material. J Endod. 1981. 7:355–369.
Article16. Orstavic D, Mjör IA. Histopathologyand x-ray microanalysis of the subcutaneous tissue response to endodontic sealers. J Endod. 1988. 14:13–23.17. Langeland K. Correlation of screening tests to usage tests. J Endod. 1978. 4:300–303.
Article18. Pascon EA, Leonard MR, Safavi K, Langerland K. Tissue reaction to endodontic materials: methods, criteria, assessment and observations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1991. 72:222–237.
Article19. Spangberg LS, Barbosa SV, Lavigne GD. AH26 releases formaldehyde. J Endod. 1993. 19:596–598.
Article20. Granchi D, Stea S, Ciapetti G, Cavedagna D, Stea S, Pizzoferrato A. Endodontic cements induce alterations in the cell cycle of in vitro cultured osteoblasts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. 79:359–366.
Article21. Takahara K, Onodera A, Matsumoto K. Toxicity of root canal sealers on rat bone cells in primary culture. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990. 23:200–207.
Article22. Geurtsen W, Leinenbach F, Krage T, Leyhausen G. Cytotoxicity of four root canal sealers in permanent 3T3 cells and primary human periodontal ligament fibroblast cultures. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998. 85:592–597.
Article23. Schweikl H, Schmalz G, Stimmelmayr H, Bey B. Mutagenicity of AH26 in an in vitro mammalian cell mutation assay. J Endod. 1995. 21:407–410.
Article24. Ersev H, Schmalz G, Bayirli G, Scheikl H. Cytotoxic and mutagenic potencies of various root canal filling materials in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in vitro. J Endod. 1999. 25:359–363.
Article25. Cohen BI, Pagnillo MK, Musikant BL, Deutsch AS. An in vitro study of the cytotoxicity of two root canal sealers. J Endod. 2000. 26:228–229.
Article26. Tai K, Huang F, Chang Y. Cytotoxic evaluation of root canal filling materials on primary human oral fibroblast cultures and a permanent hamster cell line. J Endod. 2001. 27:571–573.
Article27. Becker RM, Hume WR, Wolinsky LE. Release of eugenol from mixtures of ZO-E in vitro. J Pedod. 1983. 8:71–77.28. Markowitz K, Moynihan M, Liu M, Kim S. Biological properties of eugenol and zinc oxide-eugenol. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1992. 73:729–737.29. Maseki T, Nakata K, Kohsaka T, Kobayashi F, Hirano S, Nakamura H. Lack of correlation between the amount of eugenol released from zinc oxide-eugenol sealer and cytotoxicity of the sealer. J Endod. 1991. 17:76–79.
Article30. Meryon SD, Johnson SG, Smith AJ. Eugenol release and the cytotoxicity of different zinc oxide-eugenol combinations. J Dent. 1988. 16:66–70.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: a literature review
- Cytotoxicity of resin-based root canal sealer, adseal
- Evaluation of the radiopacity and cytotoxicity of resinous root canal sealers
- Biocompatibility and Bioactivity of Four Different Root Canal Sealers in Osteoblastic Cell Line MC3T3-El
- Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of newly developed calcium phosphate-based root canal sealers