J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2005 Mar;30(2):138-144. 10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.138.
Effect of sonicated extracts of Enterococcus faecalis on the production of matrix metalloproteinase-8 by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Korea. limss@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1987006
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.2.138
Abstract
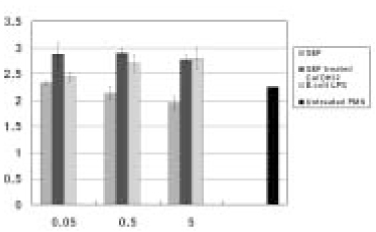
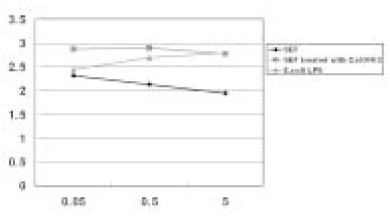
- This in vitro study monitored MMP-8 production on PMN by stimulated with the following three groups; Sonicated extracts of E. faecalis (SEF), SEF treated with Ca(OH)2 (12.5mg/ml) for 7 days, and lipopolysaccharides (LPS) of E. coli. The level of MMP-8 in each group was immediately measured by ELISA. The data were analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test and Mann-Whitney U test. In the SEF group, the level of production of MMP-8 was higher than the negative control group in low concentration (0.05microg/ml) of SEF (p < 0.05), but it decreased with an increase in the concentration of SEF (p < 0.05). In the case of SEF treated with Ca(OH)2, all of the MMP levels were higher than negative control group (p < 0.05), but no statistical difference was found among the different SEF concentrations (p > 0.05). All of the levels in E. coli LPS were increased with increasing concentrations (p < 0.05). According to this study we could summarize as follows: 1. MMP-8 was expressed at low level in untreated PMN group and the levels of MMP-8 were upregulated in PMN stimulated by E. coli LPS groups. 2. In the SEF groups, the level of production of MMP-8 decreased with an increase in the concentration of SEF (p < 0.05). So E. faecalis may have suppressive effect on the production of MMP-8 by PMN. 3. In the case of SEF treated with Ca(OH)2, all of the MMP levels at different SEF concentrations were higher than untreated PMN group (p < 0.05), but no statistical difference was found among the different SEF concentrations (p > 0.05).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of PPARγ on human dental pulp cells
Jeong-Hee Kim
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2006;31(3):203-214. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.3.203.
Reference
-
1. Kakehashi S, Stanley HR, Fitzgerald RJ. The effects of surgical exposures of dental pulps in germ-free and conventional laboratory rat. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965. 20:340–344.2. Sundqvist G, Figdor D, Persson S, Sjögren U. Microbiologic analysis of the teeth with failed endodontic treatment and outcome of conservative retreatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998. 85:86–93.
Article3. Byström A, Claesson R, Sundquvist G. The antibacterial effect of camphorated paramonochlorophenol, camphorated phenol and calcium hydroxide in the treatment of infected root canals. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985. 1:170–175.
Article4. Sjögren U, Figdor D, Spangberg L, Sundqvist G. The antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as a short-term intracanal dressing. Int Endod J. 1991. 24:119–125.
Article5. Molander A, Reit C, Dahlen G, Kvist T. Microbiological status of root-filled teeth with apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 1998. 31:1–7.
Article6. Love RM. Enterococcus faecalis-a mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int Endod J. 2001. 34:399–405.7. Evans M, Davies JK, Sundqvist G, Figdor D. Mechanisms involved in the resistance of Enterococcus faecalis to calcium hydroxide. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:221–228.
Article8. Birkedal-Hansen H. Proteolytic remodellation of extra-cellular matrix. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995. 7:728–735.9. Shin SJ, Lee JI, Baek SH, Lim SS. Tissue levels of matrix metalloproteinases in pulps and periapical lesions. J Endod. 2002. 28:313–315.
Article10. Mainardi CL, Pourmotabbed TF, Hasty KA. Inflammatory phagocytes and connective tissue degrading metalloproteinases. Am J Med Sci. 1991. 302:171–175.
Article11. Hanemaaijer R, Sorsa T, Konttinen YT, Ding Y, Sutinen M, Visser H, van Hinsbergh VW, Helaakoski T, Kainulainen T, Ronka H, Tschesche H, Salo T. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 is expressed in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and doxycycline. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:31504–31509.
Article12. Palosaari H, Wahlgren J, Larmas M, Ronka H, Sorsa T, Salo T, Tjaderhane L. The expression of MMP-8 in human odontoblasts and dental pulp cells is down-regulated by TGF-beta1. J Dent Res. 2000. 79:77–84.
Article13. Wahlgren J, Salo T, Teronen O, Luoto H, Sorsa T, Tjaderhane L. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) in pulpal and periapical inflammation and periapical root-canal exudates. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:897–904.
Article14. Yoshida H, Jontell M, Sundqvist G, Bergenholtz G. Effect of sonicated material from Fusobacterium nucleatum on the functional capacity of accessory cells derived from dental pulp. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1995. 10:208–212.
Article15. Kurita-Ochiai T, Ochiai K, Ikeda T. Immunosuppressive effect induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: effect on immunoglobulin production and lymphokine synthesis. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1992. 7(6):338–343.
Article16. Son HH, Lim S, Shon W, Kim HS, Lee W. Effects of sonicated Enterococcus faecalis extracts on Interleukin-2 and Interleukin-4. J Endod. 2004. 30:701–703.17. Peciuliene V, Reynaud AH, Balciuniene I, Haapasalo M. Isolation of yeasts and enteric bacteria in root-filled teeth with chronic apical periodontitis. Int Endod J. 2001. 34:429–434.
Article18. Fabricius L, Dahlen G, Holm SE, Moller AJ. Influence of combinations of oral bacteria on periapical tissues of monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1982. 90:200–206.
Article19. Hartke A, Giard JC, Laplace JM, Auffray Y. Survival of Enterococcus faecalis in an oligotrophic microcosm:changes in morphology, development of general stress resistance, and analysis of protein synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998. 64:4238–4245.
Article20. Orstavik D, Haapasalo M. Disinfection by endodontic irrigants and dressings of experimentally infected dentinal tubules. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1990. 6:142–149.
Article21. Heithersay GS. Calcium hydroxide in the treatment of pulpless teeth with associated pathology. J Br Endod Soc. 1975. 8:74–93.
Article22. Siqueira JF Jr, Lopes HP. Mechanisms of antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide: a critical review. Int Endod J. 1999. 32:361–369.
Article23. Wang JD, Hume WR. Diffusion of hydrogen ion and hydroxyl ion from various sources through dentine. Int Endod J. 1988. 21:17–26.
Article24. Nerwich A, Figdor D, Messer HH. pH changes in root dentin over a 4-week period following root canal dressing with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 1993. 19:302–306.
Article25. Haapasalo HK, Siren EK, Waltimo TM, Orstavik D, Haapasalo MP. Inactivation of local root canal medicaments by dentine: an in vitro study. Int Endod J. 2000. 33:126–131.
Article26. Haapasalo M, Orstavik D. In vitro infection and disinfection of dentinal tubules. J Dent Res. 1987. 66:1375–1379.27. Safavi KE, Spangberg LS, Langeland K. Root canal dentinal tubule disinfection. J Endod. 1990. 16:207–210.
Article28. Vahdaty A, Pitt Ford TR, Wilson RF. Efficacy of chlorhexidine in disinfecting dentinal tubules in vitro. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1993. 9:243–248.
Article29. Delany GM, Patterson SS, Miller CH, Newton CW. The effect of chlorhexidine gluconate irrigation on the root canal flora of freshly extracted necrotic teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982. 53:518–523.
Article30. Ohara P, Torabinejad M, Kettering JD. Antibacterial effects of various endodontic irrigants on selected anaerobic bacteria. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1993. 9:95–100.
Article31. Jeansonne MJ. White RRA comparison of 2.0% chlorhexidine gluconate and 5.25% sodium hypochlorite as antimicrobial endodontic irrigants. J Endod. 1994. 20:276–278.
Article32. Siqueira JF Jr, Batista MM, Fraga RC, de Uzeda M. Antibacterial effects of endodontic irrigants on black-pigmented gram-negative anaerobes and facultative bacteria. J Endod. 1998. 24:414–416.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Enterococcus faecalis sonicated extracts on IL-2, IL-4 and TGF-beta1 production from human lymphocytes
- The effect of Treponema denticola immunoinhibitory protein on cytokine expression in T cells
- A Case of Bilateral Endogenous Enterococcus Faecalis Endophthalmitis in Liver Abscess
- Antimicrobial Effect of Ethanol Extract of Garcinia mangostana L. against Enterococcus faecalis Isolated from Human Oral Cavity
- EGCC inhibits tumor growth by inbibiting Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 induction in UM-SCC-1 cells