Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2014 Sep;7(3):205-209. 10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.205.
Relationship Between Preepiglottic Space Invasion and Lymphatic Metastasis in Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy With Cricohyoidopexy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. entkms@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1973471
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2014.7.3.205
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The aim of this study was to determine the role of preepiglottic space (PES) invasion in lymph node metastasis and prognosis in patients undergoing supracricoid partial laryngectomy (SCPL) with cricohyoidopexy (CHP).
METHODS
A retrospective review of 42 previously untreated patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx that underwent surgery was performed. The mean age of the subjects was 61.3 years, and the male-to-female ratio was 38:4. Regarding their pathological stages, there were 3, 8, 22, and 9 cases of stage T1 to T4, respectively. Concerning the disease stage of the cervical lymph nodes, there were 30, 5, 6, and 1 cases with N0 to N3, respectively.
RESULTS
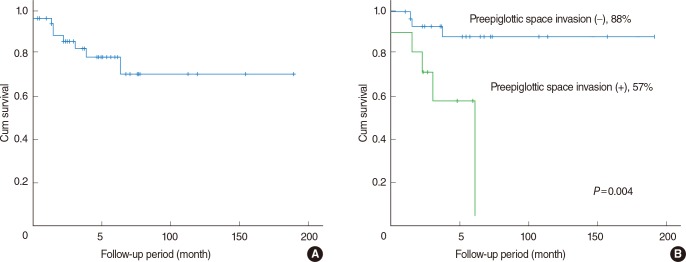
The PES invasion rate was 23.8% (10/42). Significant correlations were found between PES invasion and cervical lymph node metastasis (P=0.002). Seven of the 10 patients (70.0%) with PES invasion had cervical lymph node metastasis, whereas only 5 of the 32 patients (15.6%) without any evidence of PES invasion had lymph node metastasis. There was also a significant correlation of PES invasion with age (P=0.002) and T stage (P=0.030). However, there was no significant relationship between gender, primary tumor site, anterior commissure invasion, subglottic extension, paraglottic space invasion and PES invasion. There was a 5-year disease-specific survival of 70%. PES invasion served as a statistically significant prognostic factor for disease-specific survival (P=0.004). Cervical nodal metastasis (P=0.003) and subglottic extension (P=0.01) were also statistically significant prognostic factors associated with disease-specific survival.
CONCLUSION
The PES invasion was significantly related to the cervical lymph node metastasis and prognosis in patients undergoing SCPL with CHP.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G, Menard M, Brasnu D. Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidoepiglottopexy: a partial laryngeal procedure for glottic carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990; 6. 99(6 Pt 1):421–426. PMID: 2350125.
Article2. Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Weinstein G, Menard M, Brasnu D. Supracricoid laryngectomy with cricohyoidopexy: a partial laryngeal procedure for selected supraglottic and transglottic carcinomas. Laryngoscope. 1990; 7. 100(7):735–741. PMID: 2362533.3. Brasnu D, Menard M, Fabre A, Janot F, Laccourreye H. Partial supracricoid laryngectomies: techniques, indications and results. J Otolaryngol. 1988; 6. 17(4):173–178. PMID: 3398106.4. Levine PA, Brasnu DF, Ruparelia A, Laccourreye O. Management of advanced-stage laryngeal cancer. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1997; 2. 30(1):101–112. PMID: 8995139.
Article5. Lee WT, Rizzi M, Scharpf J, Lorenz RR, Saxton JP, Adelstein DJ, et al. Impact of preepiglottic space tumor involvement on concurrent chemoradiation therapy. Am J Otolaryngol. 2010; May-Jun. 31(3):185–188. PMID: 20015743.
Article6. Zeitels SM, Vaughan CW. Preepiglottic space invasion in "early" epiglottic cancer. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1991; 10. 100(10):789–792. PMID: 1952643.
Article7. Pogura JH. Surgical pathology of cancer of the larnyx. Laryngoscope. 1955; 10. 65(10):867–926. PMID: 13264674.8. Dursun G, Keser R, Akturk T, Akiner MN, Demireller A, Sak SD. The significance of pre-epiglottic space invasion in supraglottic laryngeal carcinomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1997; 254(Suppl 1):S110–S112. PMID: 9065642.
Article9. Ljumanovic R, Langendijk JA, Schenk B, Van Wattingen M, Knol DL, Leemans CR, et al. Supraglottic carcinoma treated with curative radiation therapy: identification of prognostic groups with MR imaging. Radiology. 2004; 8. 232(2):440–448. PMID: 15286316.
Article10. Sun DI, Cho KJ, Cho JH, Joo YH, Jung CK, Kim MS. Pathological validation of supracricoid partial laryngectomy in laryngeal cancer. Clin Otolaryngol. 2009; 4. 34(2):132–139. PMID: 19413611.
Article11. Szyfter W, Leszczynska M, Wierzbicka M. Outcome after supracricoid laryngectomies in the material of ENT Department, Poznan University of Medical Sciences. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011; 6. 268(6):879–883. PMID: 21305310.
Article12. Cho KJ, Joo YH, Sun DI, Kim MS. Supracricoid laryngectomy: oncologic validity and functional safety. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 12. 267(12):1919–1925. PMID: 20490818.
Article13. Sanchez-Cuadrado I, Castro A, Bernaldez R, Del Palacio A, Gavilan J. Oncologic outcomes after supracricoid partial laryngectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2011; 6. 144(6):910–914. PMID: 21493316.
Article14. Sato K, Kurita S, Hirano M. Location of the preepiglottic space and its relationship to the paraglottic space. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993; 12. 102(12):930–934. PMID: 8285513.
Article15. Kirchner JA, Som ML. Clinical and histological observations on supraglottic cancer. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1971; 10. 80(5):638–645. PMID: 18478663.
Article16. Gregor RT. The preepiglottic space revisited: is it significant? Am J Otolaryngol. 1990; May-Jun. 11(3):161–164. PMID: 2382783.17. Zeitels SM, Vaughan CW, Domanowski GF. Endoscopic management of early supraglottic cancer. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1990; 12. 99(12):951–956. PMID: 2244727.
Article18. Petrovic Z, Krejovic B, Djukic V, Stankovic P. Primary surgical treatment for carcinoma of the larynx: influence of the local invasion. J Laryngol Otol. 1991; 5. 105(5):353–355. PMID: 2040837.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Vocal Function before and after Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy
- Supracricoid partial laryngectomy in recurrent or advanced laryngeal cancer
- The CT Evaluation of Neoarytenoid Soft Tissue after an Arytenoidectomy during a Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy
- Evaluation of the Swallowing after Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy with Modified Barium Swallow
- A New 'Y' Shape Partial Laryngectomy for Supraglottic Carcinoma with Anterior Commissure Invasion or Encroachment