J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2013 Dec;19(2):150-155. 10.13029/jkaps.2013.19.2.150.
Tuberculous Iliopsoas Muscle Abscess Associated with Multiple Intraabdominal and Thoracic Abscesses in 9-year-old Boy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. choi1635@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1961506
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2013.19.2.150
Abstract
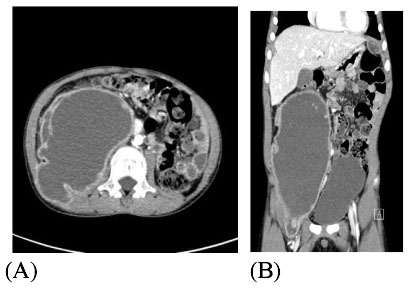
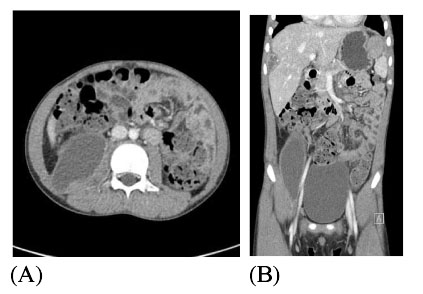
- Tuberculous Iliopsoas muscle abscess is a rare manifestation in patient with extrapulmonary tuberculosis and hardly observed in developed country. Paradoxical response to anti-tuberculous medication could make difficult therapeutic decision to clinicians. The authors report a case of tuberculous iliopsoas muscle abscess with multiple intraabdominal and thoracic abscesses in 9 year-old-boy who presented paradoxical response to anti-tuberculous treatment.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mynter H. Acute psoitis. Buffalo Med Surg J. 1881; 21:202–210.2. Navarro López V, Ramos JM, Meseguer V, Perez Arellano JL, Serrano R, Garcia Ordonez MA, et al. Microbiology and outcome of iliopsoas abscess in 124 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009; 88:120–130.3. Shields D, Robinson P, Crowley TP. Iliopsoas abscess-a review and update on the literature. Int J Surg. 2012; 10:466–469.4. Dahniya MH, Hanna RM, Grexa E, Cherian MJ, Niazy MN, Badr S, et al. Percutaneous drainage of tuberculous iliopsoas abscesses under image guidance. Australas Radiol. 1999; 43:444–447.5. Dinç H, Ahmetoglu A, Baykal S, Sari A, Sayil O, Gumele HR. Image-guided percutaneous drainage of tuberculous iliopsoas and spondylodiskitic abscesses: midterm results. Radiology. 2002; 225:353–358.6. Cheng VC, Ho PL, Lee RA, Chan KS, Chan KK, Woo PC, et al. Clinical spectrum of paradoxical deterioration during antituberculosis therapy in non-HIV-infected patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002; 21:803–809.7. Narita M, Ashkin D, Hollender ES, Pitchenik AE. Paradoxical worsening of tuberculosis following antiretroviral therapy in patients with AIDS. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998; 158:157–161.8. Cho OH, Park KH, Kim T, Song EH, Jang EY, Lee EJ, et al. Paradoxical responses in non-HIV-infected patients with peripheral lymph node tuberculosis. J Infect. 2009; 59:56–61.9. Jung JW, Shin JW, Kim JY, Park IW, Choi BW, Seo JS, et al. Risk factors for development of paradoxical response during anti-tuberculosis treatment in HIV-negative patients with pleural tuberculosis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2011; 223:199–204.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of Percutaneous Catheter Drainage for Tuberculous Iliopsoas Abscess associated with Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Ultrasonographic Features of Intra-abdominal Abscess
- Septic Hip Arthritis with Iliopsoas Abscess Detected after Spine Operation: A Case Report
- CT Findings and Types of Tuberculous Chest Wall Abscess
- Effectiveness of Fluoroscopic and US - Guided Percutaneous Catheter Drainage for Iliopsoas Abscess through the Anterolateral Transabdominal Approach