J Korean Med Assoc.
2006 Apr;49(4):342-346. 10.5124/jkma.2006.49.4.342.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Korea. ssLee@Chest.pe.kr
- KMID: 1958288
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2006.49.4.342
Abstract
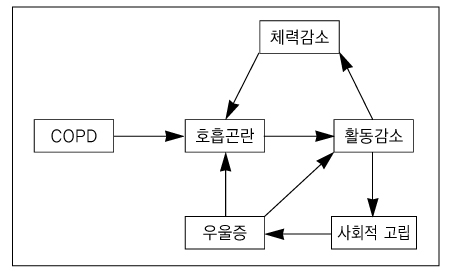
- Pulmonary rehabilitation is a multidisciplinary program of care for patients with chronic respiratory impairment that is individually tailored and designed to optimize physical and social performance and autonomy. It can reduce symptoms, decrease disability, increase participation in physical and social activities, and improve the overall quality of life for individuals with chronic respiratory disease. Pulmonary rehabilitation consists of exercise training, patient and family education, psychosocial and behavioral intervention. The exercise training should be performed at least five times per week for 30 min in each session. The intensity of aerobic exercise training should be more than 60 per cent of the peak oxygen consumption.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Thoracic Society Statement. Pulmonary rehabilitation-1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 159:1666–1682.2. Killian KJ, Leblanc P, Martin DH, Summers E, Jones NL, Campbell EJ, et al. Exercise capacity and ventilatory, circulatory, and symtom limitation in patients with chronic airflow limitaion. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992. 146:935–940.
Article3. Rochester CL. Exercise training in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2003. 40:5 Suppl 2. 59–80.
Article4. Global strategy fo the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. NHLBI/WHO workshop report 2004. (updated).5. British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Subcommittee on Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Pulmonary rehabilitation. Thorax. 2001. 56:827–834.6. Kaminsky LA, Bonzhein KA, et al. ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise testing and Prescription. 5th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.7. Casaburi R, Patessio A, Ioli F, Zanaboni S, Donner CF, Wasserman K. Reductions in exercise lactic acidosis and ventilation as a result of exercise training in patients with obstructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991. 143:9–18.
Article8. Lacasse Y, Brosseau L, Milne S, Martin S, Wong E, Goldstein RS, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002. 3:CD003793.
Article9. Troosters T, Gosselink R, Van Hove P, Derom E, Barch P, Decramer M, et al. REVALIS Study Group. Effects of pulmonary rehabilitation in a clinical setting [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 165:A735.10. Jensen PS. Risk, Protective factors, and supportive interventions in chronic airway obstruction. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983. 40:1203–1207.
Article11. Spruit MA, Gosselink R, Troosters T, De Paepe C, Decramer M. Resistance versus endurance training in patients with COPD and skeletal muscle weakness. Eur Respir J. 2002. 19:1072–1078.
Article12. de Godoy DV, de Godoy RF. A randomized controlled trial of the effect of psychotherapy on anxiety and depression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003. 84:1154–1157.
Article13. Laaban JP, Kouchakji B, Dore MF, Orvoen-Frija E, David P, Rochemaure J. Nutritional status of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and acute respiratory failure. Chest. 1993. 103:1362–1368.
Article14. Schols AM, Soeters PB, Mostert R, Pluymers RJ, Wouters EF. Physiologic effects of nutritional support and anabolic steroids in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a placebo-controlled randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 152:1.
Article15. Steiner MC, Barton RL, Singh SJ, Morgan MD. Nutritional enhancement of exercise performance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax. 2003. 58:745–751.
Article16. Na JO, Kim DS, Yoon SH, Jegal YJ, Kim WS, Kim MW, et al. A simple and easy home-based pulmonary rehabilitation programme for patients with Chronic Lung Diseases. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis Dis. 2005. 63:30–36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- The Study on the Effects of a Respiratory Rehabilitation Program for COPD Patients
- Cor Pulmonale with Particular Reference to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Highly Effective but Often Overlooked
- The Effects of Self-Efficacy Promoting Pulmonary Rehabilitation Program in Out-Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease