J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Aug;56(2):149-151. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.2.149.
Lipoma Causing Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. yhahn@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1956519
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.2.149
Abstract
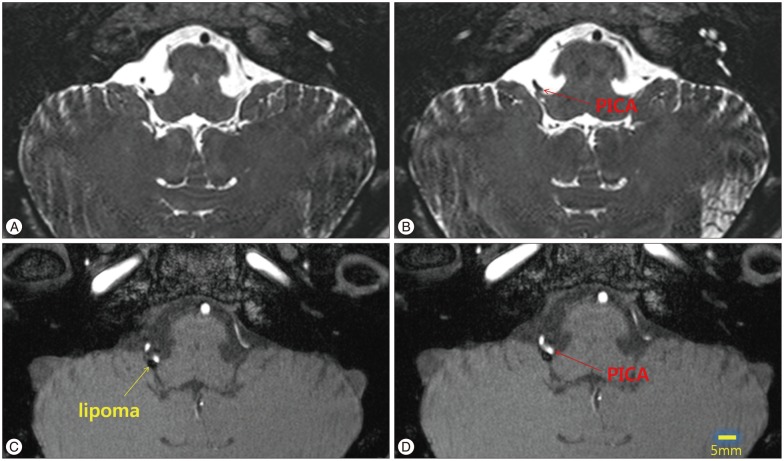
- The cerebello-pontine angle lipomas causing trigeminal neuralgia or hemifacial spasm are rare. A lipoma causing glossopharyngel neuralgia is also very rare. A 46-year-old woman complained of 2-year history of severe right throat pain, with ipsilateral episodic otalgic pain. The throat pain was described as an episodic lancinating character confined to the throat. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging revealed a suspicious offending posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) compressing lower cranial nerves including glossopharyngeal nerve. At surgery, a soft, yellowish mass (2x3x3 mm in size) was found incorporating the lateral aspect of proximal portion of 9th and 10th cranial nerves. Only microvascular decompression of the offending PICA was performed. Additional procedure was not performed. Her severe lancinating pain remained unchanged, immediate postoperatively. The neuralgic pain disappeared over a period of several weeks. In this particular patient with a fatty neurovascular lump causing glossopharyngeal neuralgia, microvascular decompression of offending vessel alone was enough to control the neuralgic pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Bioglue-Coated Teflon Sling Technique in Microvascular Decompression for Hemifacial Spasm Involving the Vertebral Artery
Seong Ho Lee, Jae Sung Park, Young Hwan Ahn
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(5):505-511. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.5.505.Microvascular Decompression for Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: Clinical Analyses of 30 Cases
Mi Kyung Kim, Jae Sung Park, Young Hwan Ahn
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(6):738-748. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2017.0506.010.
Reference
-
1. Alafaci C, Salpietro FM, Puglisi E, Tripodo E, Matalone D, Di Pietro G. Trigeminal pain caused by a cerebellopontine-angle lipoma. Case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg Sci. 2001; 45:110–113. PMID: 11533536.2. Barajas RF Jr, Chi J, Guo L, Barbaro N. Microvascular decompression in hemifacial spasm resulting from a cerebellopontine angle lipoma : case report. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63:E815–E816. discussion E816. PMID: 18981850.3. Brodsky JR, Smith TW, Litofsky S, Lee DJ. Lipoma of the cerebellopontine angle. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006; 27:271–274. PMID: 16798407.
Article4. Jannetta PJ. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by suboccipital and transtentorial cranial operations. Clin Neurosurg. 1977; 24:538–549. PMID: 583698.
Article5. Kato T, Sawamura Y, Abe H. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by a cerebellopontine-angle lipoma : case report. Surg Neurol. 1995; 44:33–35. PMID: 7482251.
Article6. Kawashima M, Matsushima T, Inoue T, Mineta T, Masuoka J, Hirakawa N. Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia through the transcondylar fossa (supracondylar transjugular tubercle) approach. Neurosurgery. 2010; (6 Suppl Operative):66:275–280. discussion 280. PMID: 20489516.
Article7. Kondo A. Follow-up results of using microvascular decompression for treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1998; 88:221–225. PMID: 9452227.
Article8. Moretti R, Torre P, Antonello RM, Bava A, Cazzato G. Gabapentin treatment of glossopharyngeal neuralgia : a follow-up of four years of a single case. Eur J Pain. 2002; 6:403–407. PMID: 12160515.
Article9. Mukherjee P, Street I, Irving RM. Intracranial lipomas affecting the cerebellopontine angle and internal auditory canal : a case series. Otol Neurotol. 2011; 32:670–675. PMID: 21358448.
Article10. Patel A, Kassam A, Horowitz M, Chang YF. Microvascular decompression in the management of glossopharyngeal neuralgia : analysis of 217 cases. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50:705–710. discussion 710-711. PMID: 11904019.11. Resnick DK, Jannetta PJ, Bissonnette D, Jho HD, Lanzino G. Microvascular decompression for glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:64–68. discussion 68-69. PMID: 7708170.
Article12. Stanic S, Franklin SD, Pappas CT, Stern RL. Gamma knife radiosurgery for recurrent glossopharyngeal neuralgia after microvascular decompression. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 2012; 90:188–191. PMID: 22678456.
Article13. Stieber VW, Bourland JD, Ellis TL. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia treated with gamma knife surgery : treatment outcome and failure analysis. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2005; 102(Suppl):155–157. PMID: 15662801.
Article14. White JR, Carlson ML, Van Gompel JJ, Neff BA, Driscoll CL, Lane JI, et al. Lipomas of the cerebellopontine angle and internal auditory canal : Primum Non Nocere. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:1531–1536. PMID: 23401141.15. Yilmaz N, Unal O, Kiymaz N, Yilmaz C, Etlik O. Intracranial lipomas--a clinical study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006; 108:363–368. PMID: 15893874.
Article16. Yomo S, Arkha Y, Donnet A, Régis J. Gamma Knife surgery for glossopharyngeal neuralgia : report of 2 cases. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110:559–563. PMID: 19025360.17. Zimmermann M, Kellermann S, Gerlach R, Seifert V. Cerebellopontine angle lipoma : case report and review of the literature. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1999; 141:1347–1351. PMID: 10672307.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia - A case report
- A Case of Glosspharyngeal Neuralgia
- Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia with Syncope Caused by Neurovascular Compression and Demonstration by High-Resolution MR Imaging: A Case Report
- Glossopharyngeal Nerve Block for Idiopathic Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: A case report
- A Case of Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia after Tonsillectomy