Korean J Radiol.
2014 Dec;15(6):827-835. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827.
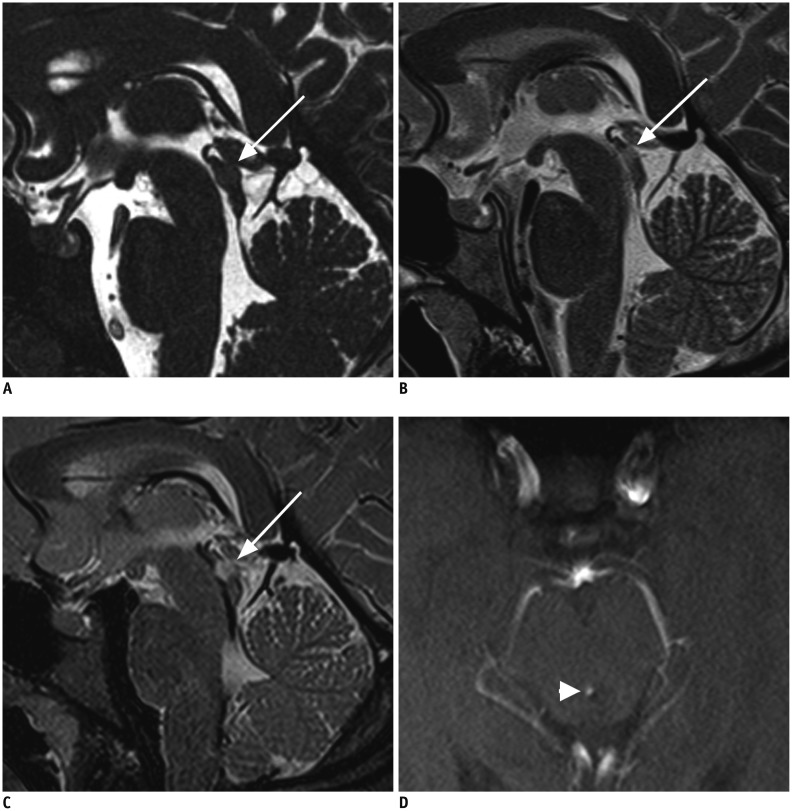
Evaluation of Aqueductal Patency in Patients with Hydrocephalus: Three-Dimensional High-Sampling-Efficiency Technique (SPACE) versus Two-Dimensional Turbo Spin Echo at 3 Tesla
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Gazi University, Ankara 06510, Turkey. drucar@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Gazi University, Ankara 06510, Turkey.
- KMID: 1794656
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the accuracy of diagnosing aqueductal patency and image quality between high spatial resolution three-dimensional (3D) high-sampling-efficiency technique (sampling perfection with application optimized contrast using different flip angle evolutions [SPACE]) and T2-weighted (T2W) two-dimensional (2D) turbo spin echo (TSE) at 3-T in patients with hydrocephalus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This retrospective study included 99 patients diagnosed with hydrocephalus. T2W 3D-SPACE was added to the routine sequences which consisted of T2W 2D-TSE, 3D-constructive interference steady state (CISS), and cine phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI). Two radiologists evaluated independently the patency of cerebral aqueduct and image quality on the T2W 2D-TSE and T2W 3D-SPACE. PC-MRI and 3D-CISS were used as the reference for aqueductal patency and image quality, respectively. Inter-observer agreement was calculated using kappa statistics.
RESULTS
The evaluation of the aqueductal patency by T2W 3D-SPACE and T2W 2D-TSE were in agreement with PC-MRI in 100% (99/99; sensitivity, 100% [83/83]; specificity, 100% [16/16]) and 83.8% (83/99; sensitivity, 100% [67/83]; specificity, 100% [16/16]), respectively (p < 0.001). No significant difference in image quality between T2W 2D-TSE and T2W 3D-SPACE (p = 0.056) occurred. The kappa values for inter-observer agreement were 0.714 for T2W 2D-TSE and 0.899 for T2W 3D-SPACE.
CONCLUSION
Three-dimensional-SPACE is superior to 2D-TSE for the evaluation of aqueductal patency in hydrocephalus. T2W 3D-SPACE may hold promise as a highly accurate alternative treatment to PC-MRI for the physiological and morphological evaluation of aqueductal patency.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dinçer A, Özek MM. Radiologic evaluation of pediatric hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011; 27:1543–1562. PMID: 21928020.
Article2. Schroeder HW, Schweim C, Schweim KH, Gaab MR. Analysis of aqueductal cerebrospinal fluid flow after endoscopic aqueductoplasty by using cine phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93:237–244. PMID: 10930009.
Article3. Sherman JL, Citrin CM. Magnetic resonance demonstration of normal CSF flow. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1986; 7:3–6. PMID: 3082142.
Article4. Yildiz H, Erdogan C, Yalcin R, Yazici Z, Hakyemez B, Parlak M, et al. Evaluation of communication between intracranial arachnoid cysts and cisterns with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:145–151. PMID: 15661716.5. Lee JH, Lee HK, Kim JK, Kim HJ, Park JK, Choi CG. CSF flow quantification of the cerebral aqueduct in normal volunteers using phase contrast cine MR imaging. Korean J Radiol. 2004; 5:81–86. PMID: 15235231.
Article6. Algin O, Hakyemez B, Parlak M. Phase-contrast MRI and 3D-CISS versus contrast-enhanced MR cisternography on the evaluation of the aqueductal stenosis. Neuroradiology. 2010; 52:99–108. PMID: 19756563.
Article7. Dinçer A, Kohan S, Ozek MM. Is all "communicating" hydrocephalus really communicating? Prospective study on the value of 3D-constructive interference in steady state sequence at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:1898–1906. PMID: 19643921.
Article8. Li T, Mirowitz SA. Fast T2-weighted MR imaging: impact of variation in pulse sequence parameters on image quality and artifacts. Magn Reson Imaging. 2003; 21:745–753. PMID: 14559339.
Article9. Arizono S, Isoda H, Maetani YS, Hirokawa Y, Shimada K, Nakamoto Y, et al. High-spatial-resolution three-dimensional MR cholangiography using a high-sampling-efficiency technique (SPACE) at 3T: comparison with the conventional constant flip angle sequence in healthy volunteers. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008; 28:685–690. PMID: 18777552.
Article10. Rosenkrantz AB, Neil J, Kong X, Melamed J, Babb JS, Taneja SS, et al. Prostate cancer: comparison of 3D T2-weighted with conventional 2D T2-weighted imaging for image quality and tumor detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:446–452. PMID: 20093608.
Article11. Haystead CM, Dale BM, Merkle EM. N/2 ghosting artifacts: elimination at 3.0-T MR cholangiography with SPACE pulse sequence. Radiology. 2008; 246:589–559. PMID: 18227547.
Article12. Hecht EM, Yitta S, Lim RP, Fitzgerald EF, Storey P, Babb JS, et al. Preliminary clinical experience at 3 T with a 3D T2-weighted sequence compared with multiplanar 2D for evaluation of the female pelvis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 197:W346–W352. PMID: 21785064.
Article13. Algin O, Turkbey B. Evaluation of aqueductal stenosis by 3D sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions sequence: preliminary results with 3T MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:740–746. PMID: 22173764.
Article14. Dinçer A, Yildiz E, Kohan S, Memet Özek M. Analysis of endoscopic third ventriculostomy patency by MRI: value of different pulse sequences, the sequence parameters, and the imaging planes for investigation of flow void. Childs Nerv Syst. 2011; 27:127–135. PMID: 20632013.
Article15. Connor SE, O'Gorman R, Summers P, Simmons A, Moore EM, Chandler C, et al. SPAMM, cine phase contrast imaging and fast spin-echo T2-weighted imaging in the study of intracranial cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow. Clin Radiol. 2001; 56:763–772. PMID: 11585399.
Article16. Mugler JP 3rd, Bao S, Mulkern RV, Guttmann CR, Robertson RL, Jolesz FA, et al. Optimized single-slab three-dimensional spin-echo MR imaging of the brain. Radiology. 2000; 216:891–899. PMID: 10966728.
Article17. Song Q, Zeng M, Chen C, Ma J, Yun H, Rao S, et al. Non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography using T2-weighted 3-dimensional fat-suppressed turbo spin echo (SPACE): diagnostic performance and comparison with contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography using volume interpolated breath-hold examination in the detection of portosystemic and portohepatic collaterals. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2012; 36:675–680. PMID: 23192204.18. Rosenkrantz AB, Patel JM, Babb JS, Storey P, Hecht EM. Liver MRI at 3 T using a respiratory-triggered time-efficient 3D T2-weighted technique: impact on artifacts and image quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 194:634–641. PMID: 20173139.
Article19. Algin O, Turkbey B, Ozmen E, Ocakoglu G, Karaoglanoglu M, Arslan H. Evaluation of spontaneous third ventriculostomy by three-dimensional sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip-angle evolutions (3D-SPACE) sequence by 3T MR imaging: preliminary results with variant flip-angle mode. J Neuroradiol. 2013; 40:11–18. PMID: 22305437.
Article20. Malko JA, Hoffman JC Jr, McClees EC, Davis PC, Braun IF. A phantom study of intracranial CSF signal loss due to pulsatile motion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988; 9:83–89. PMID: 3124589.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utility of Two Types of MR Cisternography for Patency Evaluation of Aqueduct and Third Ventriculostomy Site: Three Dimensional Sagittal Fast Spin Echo Sequence and Steady-State Coherent Fast Gradient Echo Sequence
- MR Cholangiopancreatography: Comparison Between Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence and Three-Dimensional Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence with SENSE Technique
- The Detection of Gallstones on MR Cholangiopancreatography: Comparison between the Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence and the Three-Dimensional Turbo Spin-Echo Pulse Sequence with the SENSE Technique
- Evaluation of Chondromalacia in the Knee Joint using Three Dimensional Fourier Transformation Constructive Interference in Steady State(CISS)
- Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of Isotropic Ankle Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Three-Dimensional Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin Echo versus Three-Dimensional Isotropic Fast Field Echo Sequences