J Korean Soc Radiol.
2015 May;72(5):313-318. 10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.313.
Mechanical Thrombectomy Using a Solitaire Stent in Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Relationship between the Visible Antegrade Flow on First Device Deployment and Final Success in Revascularization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. bhlee@paik.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 1793886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.72.5.313
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the relationship between the successful revascularization on the first Solitaire stent deployment and the successful revascularization on the final angiography in acute ischemic stroke.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From February 2012 to April 2014, 24 patients who underwent Solitaire stent thrombectomy as the first thrombectomy method for treatment of acute ischemic strokes were retrospectively reviewed. When the first Solitaire stent was deployed, 9 patients showed revascularization (Group 1) and 15 patients did not show revascularization (Group 2). Revascularization immediately after the first Solitaire stent removal and on the final angiography were comparatively assessed between the 2 groups. Statistical analysis was performed by the Fisher exact test and Student's t-test.
RESULTS
The rates of revascularization maintenance immediately after the first Solitaire stent removal were 89% in Group 1 and 27% in Group 2, respectively (p = 0.009), and the rates of final successful revascularization were 100% in Group 1 and 47% in Group 2, respectively (p = 0.009). There was a statistically significant difference between the 2 groups.
CONCLUSION
Revascularization on the first Solitaire stent deployment can be a useful predictor in evaluating the success of final revascularization in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
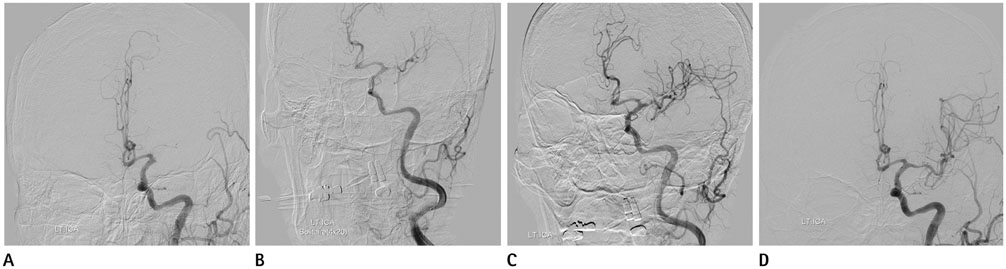
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Endovascular Therapy for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: Comparison between Patients with and without Underlying Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis
Gun Soo Kim, Seul Kee Kim, Byeong Hyeon Baek, Youn Young Lee, Woong Yoon
J Korean Soc Radiol. 2017;76(4):287-293. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.4.287.
Reference
-
1. Khatri P, Abruzzo T, Yeatts SD, Nichols C, Broderick JP, Tomsick TA, et al. Good clinical outcome after ischemic stroke with successful revascularization is time-dependent. Neurology. 2009; 73:1066–1072.2. IMS Study Investigators. Combined intravenous and intra-arterial recanalization for acute ischemic stroke: the Interventional Management of Stroke Study. Stroke. 2004; 35:904–911.3. Castaño C, Dorado L, Guerrero C, Millán M, Gomis M, Perez de la Ossa N, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation: a pilot study. Stroke. 2010; 41:1836–1840.4. Costalat V, Machi P, Lobotesis K, Maldonado I, Vendrell JF, Riquelme C, et al. Rescue, combined, and stand-alone thrombectomy in the management of large vessel occlusion stroke using the solitaire device: a prospective 50-patient single-center study: timing, safety, and efficacy. Stroke. 2011; 42:1929–1935.5. Machi P, Costalat V, Lobotesis K, Maldonado IL, Vendrell JF, Riquelme C, et al. Solitaire FR thrombectomy system: immediate results in 56 consecutive acute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012; 4:62–66.6. Park H, Hwang GJ, Jin SC, Jung CK, Bang JS, Han MK, et al. A retrieval thrombectomy technique with the Solitaire stent in a large cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:1625–1631.7. Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003; 34:e109–e137.8. Penumbra Pivotal Stroke Trial Investigators. The penumbra pivotal stroke trial: safety and effectiveness of a new generation of mechanical devices for clot removal in intracranial large vessel occlusive disease. Stroke. 2009; 40:2761–2768.9. Smith WS, Sung G, Saver J, Budzik R, Duckwiler G, Liebeskind DS, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: final results of the Multi MERCI trial. Stroke. 2008; 39:1205–1212.10. Roth C, Papanagiotou P, Behnke S, Walter S, Haass A, Becker C, et al. Stent-assisted mechanical recanalization for treatment of acute intracerebral artery occlusions. Stroke. 2010; 41:2559–2567.11. Lee BH, Hwang YJ, Hong KS, Cho YJ. Efficacy and safety of an early Solitaire stent retrieval technique for acute ischemic stroke. Jpn J Radiol. 2013; 31:608–613.12. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–34.13. Mattle HP, Arnold M, Georgiadis D, Baumann C, Nedeltchev K, Benninger D, et al. Comparison of intraarterial and intravenous thrombolysis for ischemic stroke with hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign. Stroke. 2008; 39:379–383.14. Somford DM, Nederkoorn PJ, Rutgers DR, Kappelle LJ, Mali WP, van der Grond J. Proximal and distal hyperattenuating middle cerebral artery signs at CT: different prognostic implications. Radiology. 2002; 223:667–671.15. Gralla J, Burkhardt M, Schroth G, El-Koussy M, Reinert M, Nedeltchev K, et al. Occlusion length is a crucial determinant of efficiency and complication rate in thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:247–252.16. Rosenthal ES, Schwamm LH, Roccatagliata L, Coutts SB, Demchuk AM, Schaefer PW, et al. Role of recanalization in acute stroke outcome: rationale for a CT angiogram-based "benefit of recanalization" model. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1471–1475.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Limitations of Thrombectomy with Solitaire(TM) AB as First-line Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single Center Experience
- Safety and Efficacy of Mechanical Thrombectomy with Solitaire Stent Retrieval for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review
- Refinement of a Thrombectomy Technique to Treat Acute Ischemic Stroke: Technical Note on Microcatheter Advance during Retrieving Self-Expandable Stent
- Unexpected Detachment of Solitaire Stents during Mechanical Thrombectomy
- Adjuvant Tirofiban Injection Through Deployed Solitaire Stent As a Rescue Technique After failed Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke