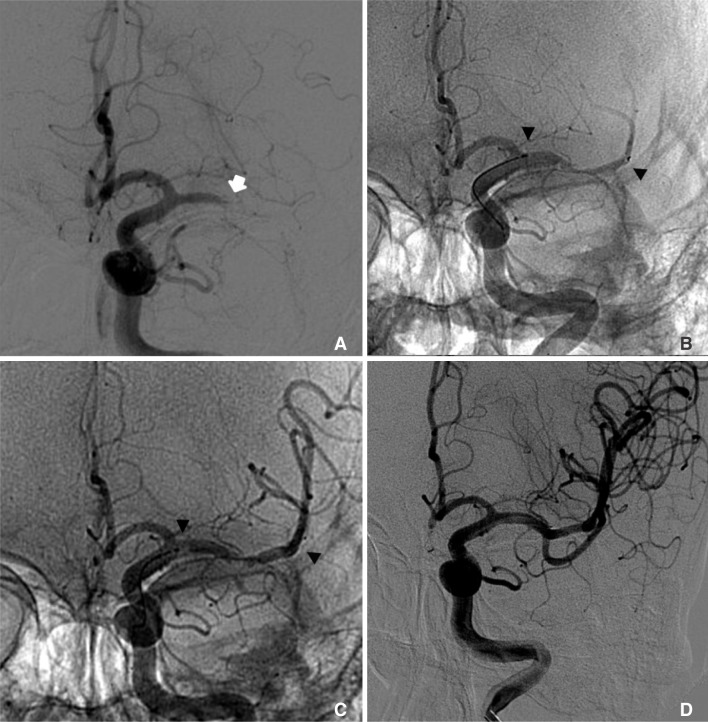
Neurointervention.
2015 Feb;10(1):22-27. 10.5469/neuroint.2015.10.1.22.
Adjuvant Tirofiban Injection Through Deployed Solitaire Stent As a Rescue Technique After failed Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Busan Paik Hospital, School of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Busan Paik Hospital, School of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. hwjeong2000@lycos.co.kr
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Busan Paik Hospital, School of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1910756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2015.10.1.22
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We present our experiences of intra-arterial tirofiban injection through a deployed Solitaire stent as a rescue therapy after failed mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data on 18 patients treated with adjunctive tirofiban injection through a temporarily deployed Solitaire stent after failed mechanical thrombectomy were retrospectively reviewed. Solitaire stent was used as a primary thrombectomy device in 16 of 18 patients. Two patients received manual aspiration thrombectomy initially. If initial mechanical thrombectomy failed, tirofiban was injected intra-arterially through the deployed Solitaire stent and then subsequent Solitaire thrombectomy was performed.
RESULTS
Fourteen patients had occlusions in the middle cerebral artery, 2 in the distal internal carotid artery, and 2 in the basilar artery. Successful recanalization was achieved in 14 patients (77.7%) after intra-arterial injection of tirofiban and subsequent Solitaire thrombectomy. Three patients without successful recanalization after rescue method received angioplasty with stenting. Overall, successful recanalization (TICI grades 2b and 3) was achieved in 17 (94.4%) of 18 patients. Periprocedural complications occurred in 5 patients: distal migration of emboli in 5 patients and vessel perforation in 1. Three patients died. Good functional outcome (mRS < or = 2) was achieved in 9 patients (50.0%) at 3 months.
CONCLUSION
Rescue intra-arterial injection of tirofiban through a temporarily deployed Solitaire stent may facilitate further recanalization in cases of failed mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saver JL, Jahan R, Levy EI, Jovin TG, Baxter B, Nogueira RG, et al. Solitaire flow restoration device versus the Merci Retriever in patients with acute ischaemic stroke (SWIFT): a randomised, parallel-group, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2012; 380(9849):1241–1249. PMID: 22932715.
Article2. Yoon YH, Yoon W, Jung MY, Yim NY, Kim BC, Kang HK. Outcome of mechanical thrombectomy with Solitaire stent as first-line intra-arterial treatment in intracranial internal carotid artery occlusion. Neuroradiology. 2013; 55:999–1005. PMID: 23703034.
Article3. Kurre W, Aguilar-Perez M, Schmid E, Sperber W, Bazner H, Henkes H. Clinical experience with the pREset stent retriever for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke--a review of 271 consecutive cases. Neuroradiology. 2014; 56:397–403. PMID: 24619135.
Article4. Park JH, Park SK, Jang KS, Jang DK, Han YM. Critical use of balloon angioplasty after recanalization failure with retrievable stent in acute cerebral artery occlusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2013; 53:77–82. PMID: 23560170.
Article5. Klisch J, Sychra V, Strasilla C, Taschner CA, Reinhard M, Urbach H, et al. Double solitaire mechanical thrombectomy in acute stroke: effective rescue strategy for refractory artery occlusions? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014.
Article6. Mpotsaris A, Bussmeyer M, Loehr C, Oelerich M, Buchner H, Weber W. Mechanical thrombectomy in severe acute stroke: preliminary results of the Solitaire stent. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2012; 83:117–118. PMID: 21212105.7. Castano C, Dorado L, Guerrero C, Millan M, Gomis M, Perez de la Ossa N, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy with the Solitaire AB device in large artery occlusions of the anterior circulation: a pilot study. Stroke. 2010; 41:1836–1840. PMID: 20538693.8. Miteff F, Faulder KC, Goh AC, Steinfort BS, Sue C, Harrington TJ. Mechanical thrombectomy with a self-expanding retrievable intracranial stent (Solitaire AB): experience in 26 patients with acute cerebral artery occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1078–1081. PMID: 21493763.9. Inhibition of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor with tirofiban in unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction. Platelet Receptor Inhibition in Ischemic Syndrome Management in Patients Limited by Unstable Signs and Symptoms (PRISM-PLUS) Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1488–1497. PMID: 9599103.10. Siebler M, Hennerici MG, Schneider D, von Reutern GM, Seitz RJ, Rother J, et al. Safety of Tirofiban in acute Ischemic Stroke: the SaTIS trial. Stroke. 2011; 42:2388–2392. PMID: 21852609.11. Baik SK, Oh SJ, Park KP, Lee JH. Intra-arterial tirofiban infusion for partial recanalization with stagnant flow in hyperacute cerebral ischemic stroke. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011; 17:442–451. PMID: 22192548.
Article12. Junghans U, Seitz RJ, Aulich A, Freund HJ, Siebler M. Bleeding risk of tirofiban, a nonpeptide GPIIb/IIIa platelet receptor antagonist in progressive stroke: an open pilot study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2001; 12:308–312. PMID: 11721100.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mechanical Solitaire Thrombectomy with Low-Dose Booster Tirofiban Injection
- Mechanical Thrombectomy Using a Solitaire Stent in Acute Ischemic Stroke: The Relationship between the Visible Antegrade Flow on First Device Deployment and Final Success in Revascularization
- Safety and Efficacy of Mechanical Thrombectomy with Solitaire Stent Retrieval for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review
- The Limitations of Thrombectomy with Solitaire(TM) AB as First-line Treatment in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single Center Experience
- Refinement of a Thrombectomy Technique to Treat Acute Ischemic Stroke: Technical Note on Microcatheter Advance during Retrieving Self-Expandable Stent