J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Apr;25(4):546-551. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.4.546.
Long Term Follow-up Results of External Beam Radiotherapy as Primary Treatment for Retinoblastoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea. mskim@kcch.re.kr
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Lee's Eye institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1792923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.4.546
Abstract
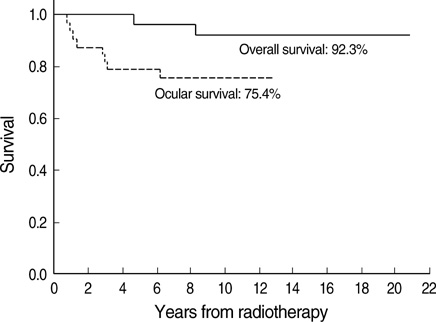
- The authors reviewed their experiences of external beam radiotherapy (EBR) as an initial treatment in retinoblastoma patients to determine its long-term effect on subsequent tumor control and complications. A total of 32 eyes in 25 patients that underwent EBR for retinoblastoma were reviewed retrospectively. The patients consisted of 21 boys and 4 girls of median age at treatment of 7.1 months. Radiation doses ranged from 35 to 59.4 Gy. The 10-yr ocular and patient survivals were 75.4% and 92.3%, respectively. Nine of the 32 eyes progressed; 7 of these were enucleated and 2 were salvaged by focal treatment. According to the Reese-Ellsworth classification, 4 of 5 eyes of Group II, 13 of 16 Group III eyes, 2 of 4 Group IV eyes, and 5 of 7 Group V eyes were retained, and of the 32 eyes, 13 had visual acuity better than 20/200. Eleven patients experienced a radiation-induced complication. No patient developed a second malignancy during follow-up. Despite the limited number of patients enrolled, EBR may provide a mean of preserving eyeball and vision for some advanced lesions.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. John Y, Malcolm S, Steven R, Jonathan L, Greta B. Retinoblastoma. Cancer incidence and survival among children and adolescents. 1999. National Cancer Institute.2. Phillips C, Sexton M, Wheeler G, McKenzie J. Retinoblastoma: review of 30 years' experience with external beam radiotherapy. Australas Radiol. 2003. 47:226–230.3. Schipper J. An accurate and simple method for megavoltage radiation therapy of retinoblastoma. Radiother Oncol. 1983. 1:31–41.
Article4. McCormick B, Ellsworth R, Abramson D, Haik B, Tome M, Grabowski E, LoSasso T. Radiation therapy for retinoblastoma: comparison of results with lens-sparing versus lateral beam techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988. 15:567–574.
Article5. Weiss DR, Cassady JR, Petersen R. Retinblastoma: a modification in radiation therapy technique. Radiology. 1975. 114:705–708.6. Krasin MJ, Crawford BT, Zhu Y, Evans ES, Sontag MR, Kun LE, Merchant TE. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for children with intraocular retinoblastoma: potential sparing of the bony orbit. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2004. 16:215–222.7. Reisner ML, Viegas CM, Grazziotin RZ, Santos Batista DV, Carneiro TM, Mendonca de Araujo CM, Marchiori E. Retinoblastoma--comparative analysis of external radiotherapy techniques, including an IMRT technique. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. 67:933–941.
Article8. Pagani JJ, Bassett LW, Winter J, Gold RH, Brawer M. Osteogenic sarcoma after retinoblastoma radiotherapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979. 133:699–702.
Article9. Kleinerman RA, Tucker MA, Tarone RE, Abramson DH, Seddon JM, Stovall M, Li FP, Fraumeni JF Jr. Risk of new cancers after radiotherapy in long-term survivors of retinoblastoma: an extended follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 2005. 23:2272–2279.
Article10. Sohajda Z, Damjanovich J, Bardi E, Szegedi I, Berta A, Kiss C. Combined local treatment and chemotherapy in the management of bilateral retinoblastomas in Hungary. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2006. 28:399–401.
Article11. Rouic LL, Aerts I, Levy-Gabriel C, Dendale R, Sastre X, Esteve M, Asselain B, Bours D, Doz F, Desjardins L. Conservative treatments of intraocular retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 2008. 115:1405–1410.
Article12. Antoneli CB, Ribeiro KC, Steinhorst F, Novaes PE, Chojniak MM, Malogolowkin M. Treatment of retinoblastoma patients with chemoreduction plus local therapy: experience of the AC Camargo Hospital, Brazil. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2006. 28:342–345.
Article13. Kim H, Lee JW, Kang HJ, Park HJ, Kim YY, Shin HY, Yu YS, Kim IH, Ahn HS. Clinical results of chemotherapy based treatment in retinoblastoma patients: a single center experience. Cancer Res Treat. 2008. 40:164–171.
Article14. Shields CL, Shields JA, Cater J, Othmane I, Singh AD, Micaily B. Plaque radiotherapy for retinoblastoma: long-term tumor control and treatment complications in 208 tumors. Ophthalmology. 2001. 108:2116–2121.
Article15. Schueler AO, Fluhs D, Anastassiou G, Jurklies C, Neuhauser M, Schilling H, Bornfeld N, Sauerwein W. Beta-ray brachytherapy with 106Ru plaques for retinoblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. 65:1212–1221.16. Shields CL, Mashayekhi A, Sun H, Uysal Y, Friere J, Komarnicky L, Shields JA. Iodine 125 plaque radiotherapy as salvage treatment for retinoblastoma recurrence after chemoreduction in 84 tumors. Ophthalmology. 2006. 113:2087–2092.
Article17. Munier FL, Verwey J, Pica A, Balmer A, Zografos L, Abouzeid H, Timmerman B, Goitein G, Moeckli R. New developments in external beam radiotherapy for retinoblastoma: from lens to normal tissue-sparing techniques. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008. 36:78–89.
Article18. Sahgal A, Millar BA, Michaels H, Jaywant S, Chan HS, Heon E, Gallie B, Laperriere N. Focal stereotactic external beam radiotherapy as a vision-sparing method for the treatment of peripapillary and perimacular retinoblastoma: preliminary results. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2006. 18:628–634.
Article19. Cormack RA, Kooy HM, Bellerive MR, Loeffler JS, Petersen RA, Tarbell NJ. A stereotactic radiation therapy device for retinoblastoma using a noncircular collimator and intensity filter. Med Phys. 1998. 25:1438–1442.
Article20. Krengli M, Hug EB, Adams JA, Smith AR, Tarbell NJ, Munzenrider JE. Proton radiation therapy for retinoblastoma: comparison of various intraocular tumor locations and beam arrangements. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 61:583–593.
Article21. Lee CT, Bilton SD, Famiglietti RM, Riley BA, Mahajan A, Chang EL, Maor MH, Woo SY, Cox JD, Smith AR. Treatment planning with protons for pediatric retinoblastoma, medulloblastoma, and pelvic sarcoma: how do protons compare with other conformal techniques? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005. 63:362–372.
Article22. Merchant TE, Gould CJ, Wilson MW, Hilton NE, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Haik BG. Episcleral plaque brachytherapy for retinoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2004. 43:134–139.
Article23. Abouzeid H, Moeckli R, Gaillard MC, Beck-Popovic M, Pica A, Zografos L, Balmer A, Pampallona S, Munier FL. (106)Ruthenium brachytherapy for retinoblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. 71:821–828.
Article24. Hernandez JC, Brady LW, Shields JA, Shields CL, DePotter P, Karlsson UL, Markoe AM, Amendola BE, Singh A. External beam radiation for retinoblastoma: results, patterns of failure, and a proposal for treatment guidelines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996. 35:125–132.
Article25. Blach LE, McCormick B, Abramson DH. External beam radiation therapy and retinoblastoma: long-term results in the comparison of two techniques. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996. 35:45–51.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Retinoblastoma: The Role of External Beam Radiotherapy
- Late-onset Osteosarcoma in Bilateral Retinoblastoma Survivor
- Differences in radiotherapy application according to regional disease characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Three Cases of Trilateral Retinoblastoma
- Bilateral retinoblastoma: Long-term follow-up results from a single institution