Pediatr Infect Vaccine.
2015 Apr;22(1):36-39. 10.14776/piv.2015.22.1.36.
A Case of Childhood Typhoid Fever Complicated with Acute Nephritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. byelhana@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 1791515
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2015.22.1.36
Abstract
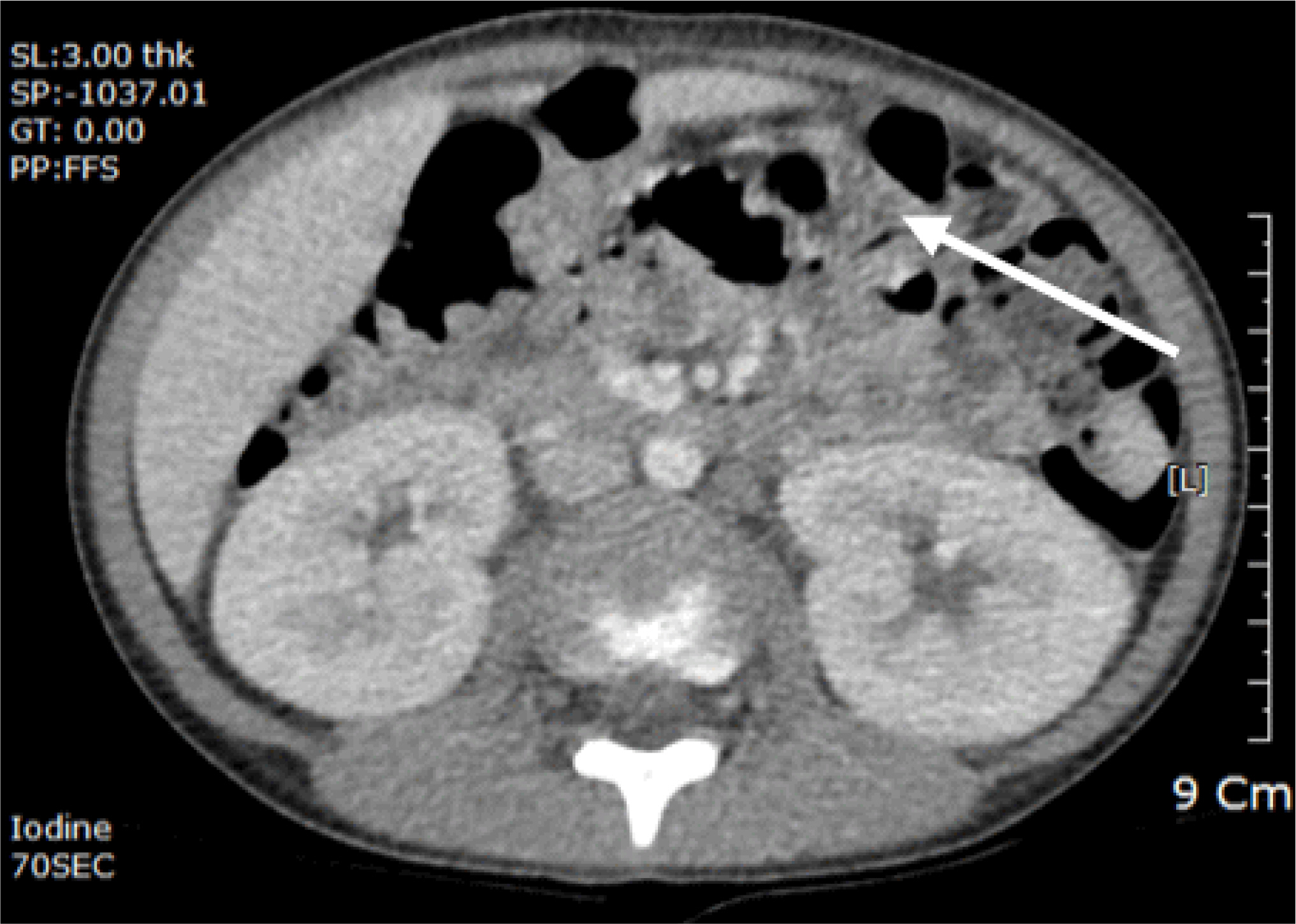
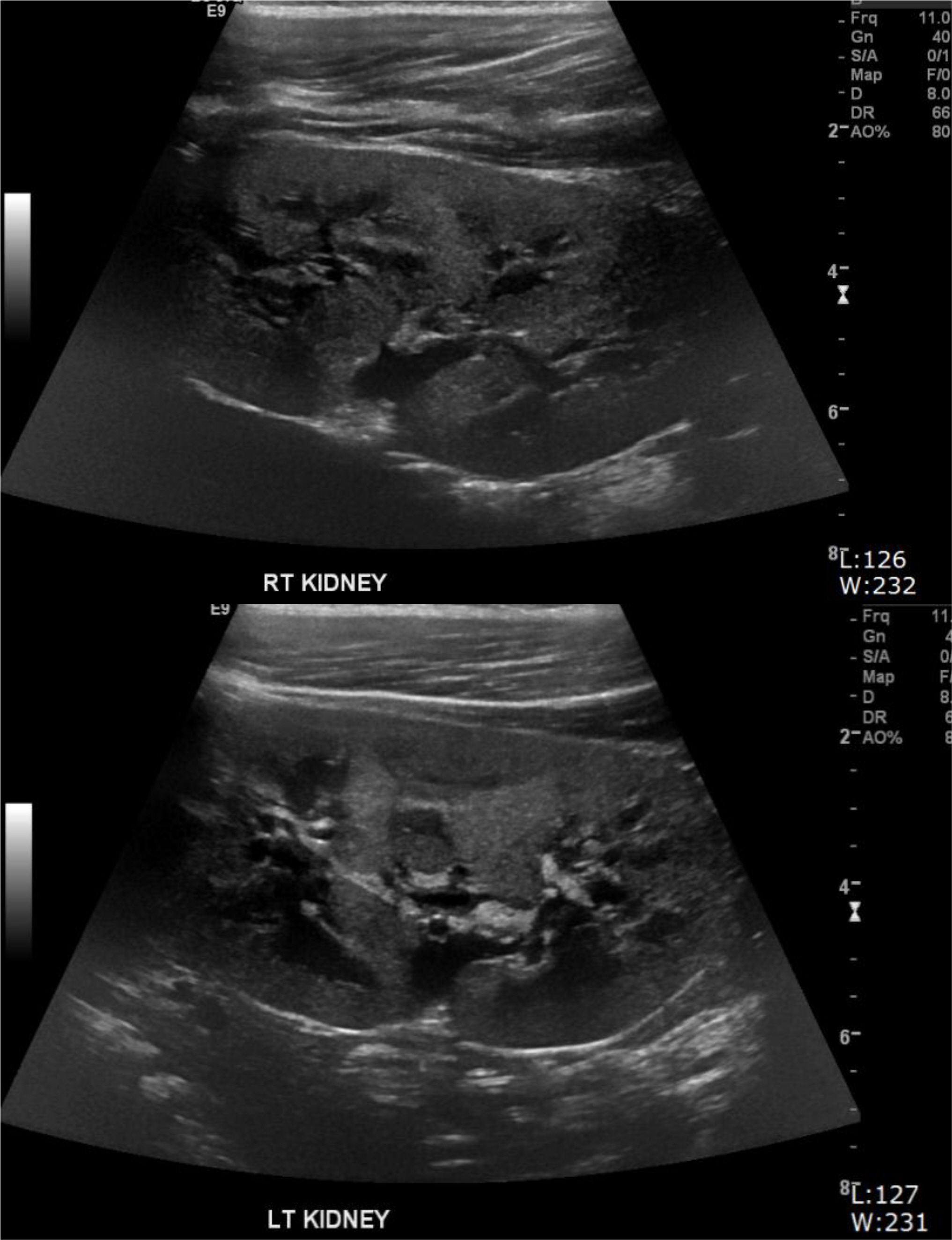
- Typhoid fever can cause serious complications, such as enterobrosia, meningitis, pneumonia, myocarditis, hepatitis, osteomyelitis, and disseminated intravascular coagulation in 10-15% of the patients. Kidney complications are very rare, and a few cases have been reported in children. We are reporting a case of childhood typhoid fever complicated with acute nephritis present with albuminuria, hypertension, and renal failure.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee IK. Summary of communicable disease outbreak during thirty fifth week in 2007. Communicable disease weekly report. 2007. 6z1–35.2. Zulfigar AB. Enteric fever. In:. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme IW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed.Philadelphia: WB Sounders C0;2011. p. 955.3. Qutaishat SS, Stemper ME, Spencer SK, Borchardt MA, Opitz IC, Monson TA, et al. Transmission of Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium DT 104 to infants through mother's breast milk. Pediatrics. 2003; 6:1442–6.4. Park IK, Seok WW, Choi B], Kim HM, Lim BK, Yoon SS, et al. Salmonella enterica serovar London infections associated with consumption of infant formula. Yonsei Med I. 2004; 45:43–8.5. Lim HS. Contributing factors of infectious waterborne and foodborne outbreaks in Korea. I Korean Med Assoc. 2007; 50:582–91.
Article6. Lim HS, Min YS, Lee K, Lim SH. Epidemiologic investigation into an outbreak of typhoid fever recognized by electronic data interchange in gyeongsanbuk—do, 2003. Korean I Epidemiol. 2004; 26:59–68.7. Shin SY, Hong JY, Bae IM. An Epidemic survey for salmonellosis occurred on a baby's first birthday banquet in Ieju Island. Korean J Epidemiol. 2004; 26:27–38.8. Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G, White N], Farrar I]. Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1770–82.9. Ianssen van Doorn K, Pierard D, Verbeelen D. Typhoid fever. N Engl I Med. 2003; 20:1182–4.10. Hayashi M, Kouzu H, Nishihara M, Takahashi T, Furuhashi M, Sakamoto K, et al. Acute renal failure likely due to acute nephritis syndrome associated with typhoid fever. Intern Med. 2005; 44:1074–7.11. Sreedharan R, Avnar ED. Acute renal failure. In:. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed.Philadelphia: WB Sounders Co;2011. p. 1818.12. Sitprija V, Pipatanagul V, Boonpucknavig V, Boonpucknavig S. Glomerulitis in typhoid fever, Ann Intern Med. 1974; 81:210–3.13. Oh 1M, Lee NR, Yim HE, Yoo KH, Ieong WY, Hong YS, et a1. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis With renal failure complicated by typhoid fever, J Korean Soc Pediatr Nephrol. 2010; 14:236–9.14. Buysen IG, Houthoff H], Kredjet RT, Arisz L. Acute interstitial nephritis: a clinical and morphological study in 27 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1990. 5294–9.
Article15. Shin P]. Lee HS, Cho BS, Ahn CI, Yang MH. Acute tubular necrosis associated with typhoid fever, Korean I Pediatr. 1994; 37:250–6.16. Murithi AK, Leung N, Valeri AM, Cornell LD, Sethi S, Fidler ME et a1. Biopsy—proven acute interstitial nephritis, 1993—2011: A case series, Am I Kidney Dis. 2014; 64:558–66.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis with Renal Failure Complicated by Typhoid Fever
- Two Cases of Typhoid Fever Complicated by Acute Renal Failure
- A Case of Typhoid Fever Complicated by Sensorineural Hearing Loss, Acute Pancreatitis and Hepatitis
- A Case of Icteric Typhoid Hepatitis Complicated with Splenic Infarction
- A Case of Typhoid Fever Complicated with Massive Fatal Hemoptysis