Clin Orthop Surg.
2013 Dec;5(4):334-337. 10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.334.
Glomus Tumor of Hoffa's Fat Pad and Its Management by Arthroscopic Excision
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India. kamalpgi@gmail.com
- 2Department of Histopathology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India.
- 3Department of Orthopaedics, London Health Sciences Center, London, ON, Canada.
- KMID: 1787038
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.334
Abstract
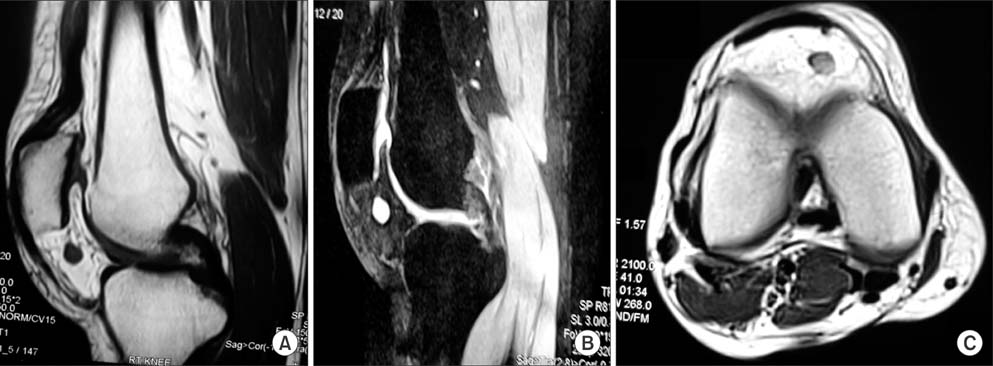
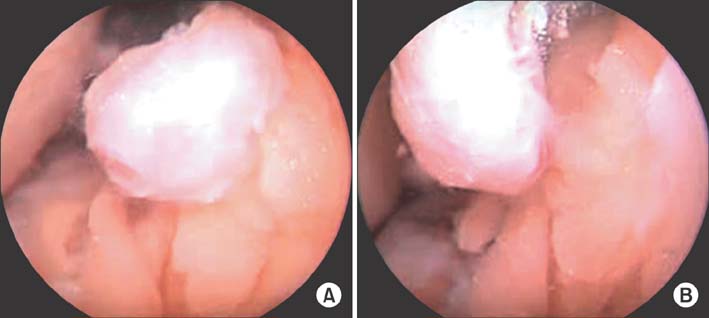
- We present a rare case of glomus tumor of Hoffa's fat pad in a 42-year-old woman. Magnetic resonance imaging findings along with the characteristic clinical picture led us to suspect a glomus tumor as the possible etiology. An ischemia test was found to be positive and this further substantiated our diagnosis. An arthroscopic excision was performed and the histology confirmed the diagnosis of glomus tumor of Hoffa's fat pad. The patient responded well to the excision with immediate complete resolution of pain and she remains asymptomatic at the last follow-up after 15 months. To our knowledge, this is the second reported case of glomus tumor of Hoffa's fat pad and the first ever to be managed by simple arthroscopic excision. The tumor poses a great challenge to an orthopedic surgeon. However, knowledge of its characteristic clinical presentation and the recognition of such a rare entity can help achieve an early diagnosis and timely management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Glomus Tumor Causing Knee Pain
Hee-Gon Park, Sung-Hyun Kim, Jee-Won Ryu
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2017;52(3):279-284. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2017.52.3.279.
Reference
-
1. Amillo S, Arriola FJ, Munoz G. Extradigital glomus tumour causing thigh pain: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79(1):104–106.2. Caughey DE, Highton TC. Glomus tumour of the knee: report of a case. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966; 48(1):134–137.3. Kato S, Fujii H, Yoshida A, Hinoki S. Glomus tumor beneath the plica synovialis in the knee: a case report. Knee. 2007; 14(2):164–166.4. Clark ML, O'Hara C, Dobson PJ, Smith AL. Glomus tumor and knee pain: a report of four cases. Knee. 2009; 16(3):231–234.5. Mabit C, Pecout C, Arnaud JP. Glomus tumor in the patellar ligament: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(1):140–141.6. Hardy P, Muller GP, Got C, Lortat-Jacob A, Benoit J. Glomus tumor of the fat pad. Arthroscopy. 1998; 14(3):325–328.7. Wood W. On painful subcutaneous tubercles. Edinb Med J. 1812; 8(5):283–291.8. Masson P. Le glomus neuro-myo-arteriel des regions tactiles et ses tumeurs. Lyon Chir. 1924; 21:257–280.9. Kohout E, Stout AP. The glomus tumor in children. Cancer. 1961; 14(3):555–566.10. Hildreth DH. The ischemia test for glomus tumor: a new diagnostic test. Rev Surg. 1970; 27(2):147–148.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of a Extrasynovial Ossifying Chondrolipoangioma in the Infrapatellar Fat Pad: Advanced Stage of Hoffa's Disease
- A Case of Localized Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor in the Infrapatellar Fat Pad of the Knee
- Glomus Tumor in The Infrapatellar Fat Pad: A Case Report
- A Case of Solitary Glomus Tumor
- Subungual Glomus Tumor: Report of A Case