J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Jun;23(3):526-528. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.526.
A Case of Anaphylaxis to Chlorhexidine during Digital Rectal Examination
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Department of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. allergy@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 1786895
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.526
Abstract
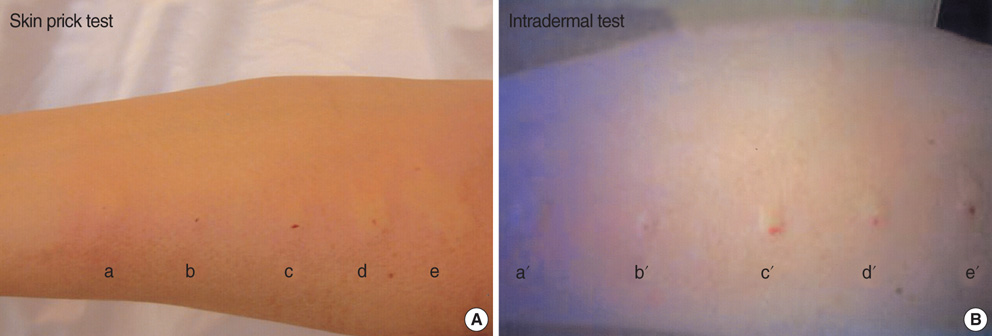
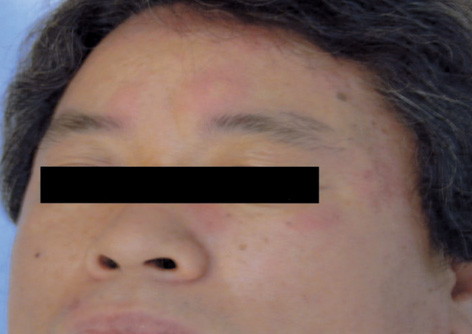
- Chlorhexidine is widely used as an antiseptic and disinfectant in medical and nonmedical environments. Although the sensitization rate seems to be low, its ubiquitous use raises the possibility of sensitization in many patients and medical care workers. We describe a patient with anaphylaxis during digital rectal examination with chlorhexidine jelly. Urticaria, angioedema, dyspnea, and hypotension developed within a few minutes of the rectal examination. The patient fully recovered after treatment with epinephrine and corticosteroids. Skin tests for chlorhexidine were undertaken 5 weeks later, showing positive prick and intradermal skin tests. Within 30 min of the skin test, the patient complained of febrile sensation, chest tightness, angioedema, and urticaria on the face and trunk. An enzyme allergosorbent test for latex was negative. We present this case to alert clinicians about hypersensitivity to chlorhexidine that could potentially be life-threatening. We suggest that chlorhexidine should be recognized as a causative agent of anaphylaxis during procedural interventions.
MeSH Terms
-
Administration, Topical
Adrenal Cortex Hormones/administration & dosage
Anaphylaxis/*chemically induced/drug therapy
Anti-Infective Agents, Local/administration & dosage/*adverse effects
Chlorhexidine/administration & dosage/*adverse effects
*Digital Rectal Examination
Epinephrine/administration & dosage
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Sympathomimetics/administration & dosage
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Overview of anaphylaxis in Korea: diagnosis and management
Gwang Cheon Jang, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sun Hee Choi, Woo-Jung Song, Soo-Young Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Hye-Ryun Kang, Yeong-Min Ye, Hyun-Jung Jin, Mi Yong Shin, Soo-Jin Lee, Hye One Kim, Jihyun Kim, Jae-Woo Jung, Hee-Bom Moon, Youngmin Ahn
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(3):181-196. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.3.181.
Reference
-
1. Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Stevens WJ. Anaphylaxis to an urethral lubricant: chlorhexidine as the "hidden" allergen. Acta Clin Belg. 2004. 59:358–360.
Article2. Torricelli R, Wuthrich B. Life threatening anaphylactic shock due to skin application of chlorhexidine. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996. 26:112.3. Jayathillake A, Mason DF, Broome K. Allergy to chlorhexidine gluconate in urethral gel: report of four cases and review of the literature. Urology. 2003. 61:837.4. Kim TH, Cho SJ, Kim HJ, Noh GJ. Chlorhexidine anaphylaxis after urethral catheterization during anesthesia: a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007. 52:104–106.5. Krautheim AB, Jermann TH, Bircher AJ. Chlorhexidine anaphylaxis: case report and review of the literature. Contact Dermatitis. 2004. 50:113–116.
Article6. Wicki J, Deluze C, Cirafici L, Desmeules J. Anaphylactic shock induced by intraurethral use of chlorhexidine. Allergy. 1999. 54:768–769.
Article7. Garvey LH, Roed-Petersen J, Husum B. Anaphylactic reactions in anaesthetized patients- four cases of chlorhexidine allergy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2001. 45:1290–1294.8. Thong BY, Yeow-Chan . Anaphylaxis during surgical and interventional procedures. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004. 92:619–628.
Article9. Layton GT, Stanworth DR, Amos HE. The incidence of IgE and IgG antibodies to chlorhexidine. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989. 19:307–314.
Article10. Ebo DG, Stevens WJ, Bridts CH, Matthieu L. Contact allergic dermatitis and life- threatening anaphylaxis to chlorhexidine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998. 101:128–129.11. Okano M, Nomura M, Hata S, Okada N, Sato K, Kitano Y, Tashiro M, Yoshimoto Y, Hama R, Aoki T. Anaphylactic symptoms due to chlorhexidine gluconate. Arch Dermatol. 1989. 125:50–52.
Article12. Stephens R, Mythen M, Kallis P, Davies DW, Egner W, Rickards A. Two episodes of life-threatening anaphylaxis in the same patient to a chlorhexidine-sulphadiazine-coated central venous catheter. Br J Anaesth. 2001. 87:306–308.
Article13. Winrow MJ. Metabolic studies with radiolabelled chlorhexidine in animals and man. J Periodontal Res Suppl. 1973. 12:45–48.
Article14. Fisher M. Intradermal testing after anaphylactoid reaction to anaesthetic drugs: practical aspects of performance and interpretation. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1984. 12:115–120.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anaphylaxis to Chlorhexidine-Impregnated Central Venous Catheters in Spine Surgery
- Chlorhexidine Anaphylaxis after Urethral Catheterization during Anesthesia : A case report
- A Case of Immunologic Contact Urticaria to Chlorhexidine
- Rectal Injury Associated with Pelvic Fracture
- Chlorhexidine: a hidden life-threatening allergen