Yonsei Med J.
2007 Dec;48(6):1035-1038. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.1035.
A Case of Successful Intrapleural Chemotherapy with Cisplatin Plus Cytarabine for Intractable Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Affiliations
-
- 11Yonsei Cancer Center, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Hemato-Oncology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Kyonggi-do, Korea. ytkim@nhimc.or.kr
- KMID: 1786221
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.6.1035
Abstract
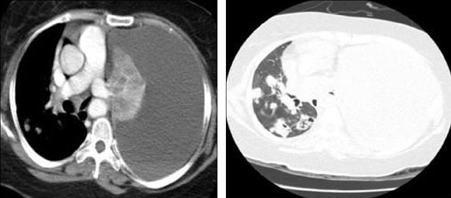
- When conventional treatments of malignant pleural effusion, such as repeated thoracentesis, closed thoracotomy and pleurodesis by instilled sclerosing agents, are ineffective, there are few alternative therapies available. Our case involves a 47-year-old woman with uterine cervical carcinoma suffering from malignant pleural effusion. She presented with a chief complaint of severe dyspnea, and was classified as an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of 4. Her underlying cervical carcinoma progressed despite various systemic chemotherapy regimens. In addition, pleural effusion persisted in spite of 4 weeks of drainage through the thoracotomy tube and talc pleurodesis. Under such circumstances, we attempted intrapleural chemotherapy with cisplatin plus cytarabine, which resulted in significant decrease of the pleural effusion. No serious systemic toxicities, including myelosuppression, were observed. As a result, the patient's dyspnea was relieved, and her ECOG performance status improved from 4 to 2. However, the thoracotomy tube was not removed due to subsequent iatrogenic pneumothorax. Pleural effusion did not recur for the 4 weeks leading up to her death.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Thoracic Society. Management of malignant pleural effusions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1987–2001.2. Rusch VW, Figlin R, Godwin D, Piantadosi S. Intrapleural cisplatin and cytarabine in the management of malignant pleural effusions: a Lung Cancer Study Group trial. J Clin Oncol. 1991. 9:313–319.3. Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V, Jaques D, Budach V, et al. CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003. 13:176–181.4. Masuno T, Kishimoto S, Ogura T, Honma T, Niitani H, Fukuoka M, et al. A comparative trial of LC9018 plus doxorubicin and doxorubicin alone for the treatment of malignant pleural effusion secondary to lung cancer. Cancer. 1991. 68:1495–1500.5. Aasebø U, Norum J, Sager G, Slørdal L. Intrapleurally instilled mitoxantrone in metastatic pleural effusions: a phase II study. J Chemother. 1997. 9:106–111.6. Perng RP, Chen YM, Wu MF, Chou KC, Lin WC, Liu JM, et al. Phase II trial of intrapleural paclitaxel injection for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with malignant pleural effusions. Respir Med. 1998. 92:473–479.7. Markman M, Cleary S, King ME, Howell SB. Cisplatin and cytarabine administered intrapleurally as treatment of malignant pleural effusions. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1985. 13:191–193.8. Aitini E, Cavazzini G, Pasquini E, Rabbi C, Colombo F, Cantore M, et al. Treatment of primary or metastatic pleural effusion with intracavitary cytosine arabinoside and cisplatin. A phase II study. Acta Oncol. 1994. 33:191–194.9. Markman M, Cleary S, Pfeifle C, Howell SB. Cisplatin administered by the intracavitary route as treatment for malignant mesothelioma. Cancer. 1986. 58:18–21.10. Vadi H, Drewinko B. Kinetics and mechanism of the 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine-induced potentiation of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1986. 46:1105–1109.11. Markman M. Intracavitary chemotherapy. Curr Probl Cancer. 1986. 10:401–437.12. Howell SB, Pfeifle CE, Wung WE, Olshen RA. Intraperitoneal cis-diamminedichloroplatinum with systemic thiosulfate protection. Cancer Res. 1983. 43:1426–1431.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intrapleural chemotherapy with cisplatin and cytarabine in the management of malignant pleural effusion
- Intrapleural chemotherapy with cisplatin and cytarabine in the management of malignant pleural effusion
- Intrapleural Paclitaxel Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Breast Cancer-Related Metastatic Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Intrapleural Chemotherapy with Cisplatin and Cytarabine in the Management of Malignant Pleural Effusion
- Malignant Mesothelioma Causing Bloody Pleural Effusion