J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Sep;22(Suppl):S79-S85. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S79.
Clinicopathological Aspects of 542 Cases of Pancreatic Cancer: a Special Emphasis on Small Pancreatic Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. mhkim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1785793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.S.S79
Abstract
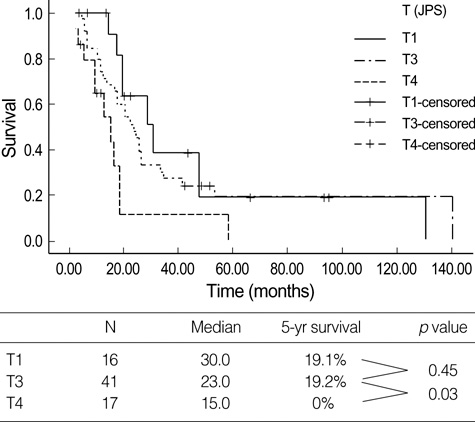
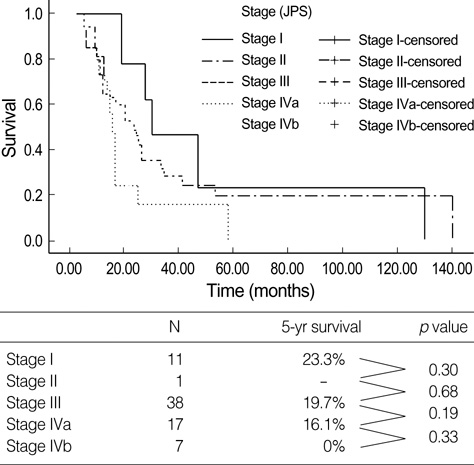
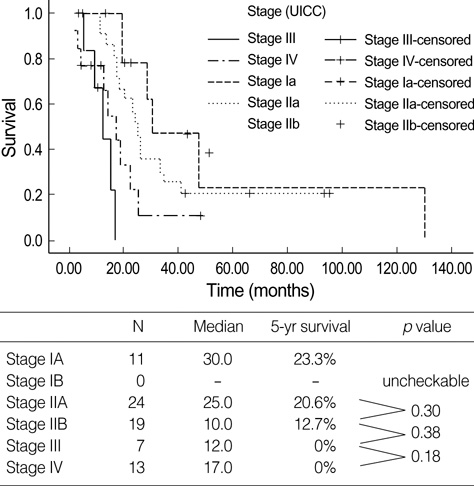
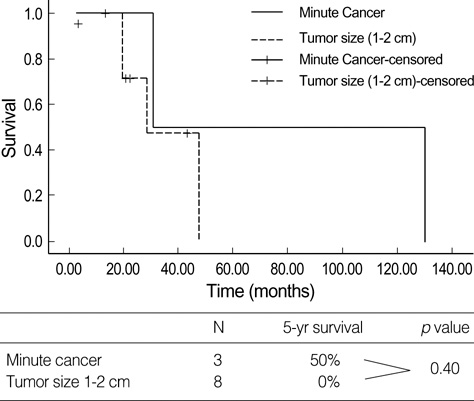
- Small pancreatic cancers (longest diameter < or =2 cm) have been regarded as preliminary to early pancreatic cancer, which was thought to be highly curable. During our experience since 1989, we evaluated 542 cases of pancreatic cancer. Among them we found 74 cases of tumors < or =2 cm in diameter, small pancreatic cancer (TS1 pancreatic cancer). Well-differentiated adenocarcinomas (18.9%) and absence of symptoms (8.1%) were more frequent in patients with TS1 than in those with larger pancreatic tumors. Only 16 of the 74 patients (21.6%) with small pancreatic cancers had T1 tumors. According to the International Union Against Cancer (UICC) staging, only 11 patients (14.9%) were stage IA: their 5-yr survival rate was 23.3% and their median survival was 30.0 months. Among these 11 patients, 3 had tumors <1 cm; their median survival time was 30.0 months and their 5-yr survival rate was 50.0%. These findings may indicate that 'small' pancreatic cancer is not equivalent to 'early' pancreatic cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma/pathology
Adenocarcinoma, Mucinous/pathology
Adenocarcinoma, Papillary/pathology
Adult
Aged
CA-19-9 Antigen/metabolism
Carcinoembryonic Antigen/metabolism
Carcinoma/pathology
Carcinoma, Adenosquamous/pathology
Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal/pathology
Female
Humans
Korea/epidemiology
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Staging
Pancreatic Neoplasms/immunology/mortality/*pathology
Prognosis
Survival Rate
Tumor Burden
Figure
Reference
-
1. Monge JJ, Dockerty MB, Wollaeger EE, Waugh JM, Priestley JT. Clinicopathologic observations on radical pancreatoduodenal resection for peripapillary carcinoma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1964. 118:275–283.2. Tsuchiya R, Noda T, Harada N, Miyamoto T, Tomioka T, Yamamoto K, Yamaguchi T, Izawa K, Tsunoda T, Yoshino R, Eto T. Collective review of small carcinomas of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 1986. 203:77–81.
Article3. Ariyama J, Suyama M, Satoh K, Sai J. Imaging of small pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 1998. 3:396–401.
Article4. Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Imaoka S, Nakaizumi A, Uehara H, Kitamura T, Kuroda C. Minute carcinoma of the pancreas measuring 1cm or less in diameter--collective review of Japanese case reports. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. 46:8–15.5. Albert MB, Steinberg WM, Henry JP. Elevated serum levels of tumor marker CA19-9 in acute cholangitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1988. 33:1223–1225.
Article6. Tsunoda T, Yamamoto Y, Kimoto M, Imai H, Iwamoto S, Kawasaki S, Kawashima K, Tadaoka Y, Majima T, Onuma E, Iki K, Kubozoe T, Eto T. Staging and treatment for patients with pancreatic cancer. How small is an early pancreatic cancer? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1998. 5:128–132.
Article7. Tsuchiya R, Tajima Y, Matsuzaki S, Onizuka S, Kanematsu T. Early pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2001. 1:597–603.
Article8. Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Compton C, Garrett ES, Goodman SN, Kern SE, Klimstra DS, Klöppel G, Longnecker DS, Lüttges J, Offerhaus GJ. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001. 25:579–586.9. Birk D, Fortnagel G, Formentini A, Beger HG. Small carcinoma of the pancreas. Factors of prognostic relevance. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1998. 5:450–454.
Article10. Pantalone D, Ragionieri I, Nesi G. Improved survival in small pancreatic cancer. Dig Surg. 2001. 18:41–46.
Article11. Kimura W. How many millimeters do atypical epithelia of the pancreas spread intraductally before beginning to infiltrate? Hepatogastroenterology. 2003. 50:2218–2224.12. Kimura W. Pancreatic carcinoma in the early stage and limited dilated lesions of the pancreatic ductuli. Nippon Rinsho. 2006. 64:Suppl 1. 165–169.13. Egawa S, Takeda K, Fukuyama S, Motoi F, Sunamura M, Matsuno S. Clinicopathological aspects of small pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2004. 28:235–240.
Article14. Fernandez-del Castillo C, Jimenez RE. Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, editors. Pancreatic cancer, cystic pancreatic neoplasms, and other nonendocrine pancreatic tumors. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 2006. 8th ed. 1309–1330.15. Isaji S, Kawarada Y, Uemoto S. Classification of pancreatic cancer: comparison of Japanese and UICC classifications. Pancreas. 2004. 28:231–234.16. Sawabu N, Watanabe H, Yamaguchi Y, Ohtsubo K, Motoo Y. Serum tumor markers and molecular biological diagnosis in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 2004. 28:263–267.
Article17. Gattani AM, Mandeli J, Bruckner HW. Tumor markers in patients with pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1996. 78:57–62.
Article18. Kim HJ, Kim MH, Myung SJ, Lim BC, Park ET, Yoo KS, Seo DW, Lee SK, Min YI. A new strategy for the application of CA19-9 in the differentiation of pancreaticobiliary cancer: analysis using a receiver operating characteristic curve. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. 94:1941–1946.
Article19. Steinberg W. The clinical utility of the CA 19-9 tumor-associated antigen. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990. 85:350–355.20. Wang TH, Lin JT, Chen DS, Sheu JC, Sung JL. Noninvasive diagnosis of advanced pancreatic cancer by real-time ultrasonography, carcinoembryonic antigen, and carbohydrate antigen 19-9. Pancreas. 1986. 1:219–223.
Article21. DelMaschio A, Vanzulli A, Sironi S, Castrucci M, Staudacher C, Carlucci M, Zerbi A, Parolini D, Faravelli A. Pancreatic cancer versus chronic pancreatitis: diagnosis with CA 19-9 assessment, US, CT, and CT-guided fine-needle biopsy. Radiology. 1991. 178:95–99.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Updates of Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Adjuvant Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer
- Pancreas club international joint symposium on pancreatic cancer 2012, Kyoto: down staging chemo+/-radiotherapy for borderline resectable pancreatic cancer
- Prophylaxis of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
- Updates of Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer