J Vet Sci.
2014 Jun;15(2):297-307. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.297.
Evaluation of endoscopically obtained duodenal biopsy samples from cats and dogs in an adapter-modified Ussing chamber
- Affiliations
-
- 1Gastrointestinal Laboratory, Department of Small Animal Clinical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843-4474, USA. iruhnke@une.edu.au
- 2Department of Biomedical and Diagnostic Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996-4542, USA.
- 3Department of Medicine, Section of Gastroenterology, College of Medicine, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA.
- KMID: 1784652
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.2.297
Abstract
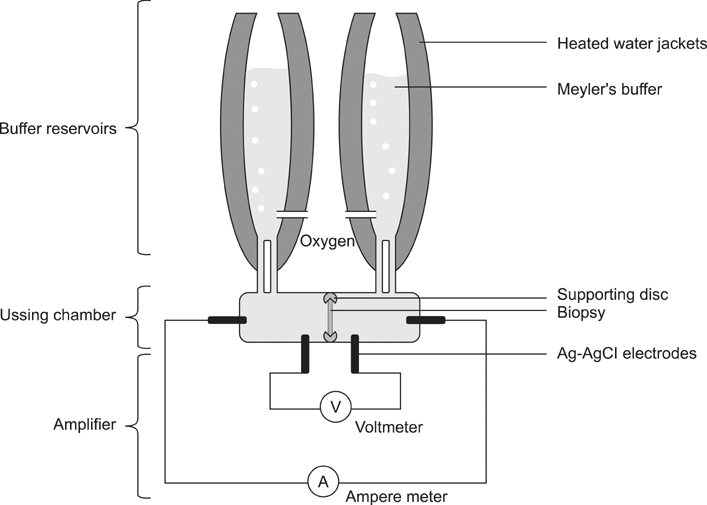
- This study was conducted to evaluate an adapter-modified Ussing chamber for assessment of transport physiology in endoscopically obtained duodenal biopsies from healthy cats and dogs, as well as dogs with chronic enteropathies. 17 duodenal biopsies from five cats and 51 duodenal biopsies from 13 dogs were obtained. Samples were transferred into an adapter-modified Ussing chamber and sequentially exposed to various absorbagogues and secretagogues. Overall, 78.6% of duodenal samples obtained from cats responded to at least one compound. In duodenal biopsies obtained from dogs, the rate of overall response ranged from 87.5% (healthy individuals; n = 8), to 63.6% (animals exhibiting clinical signs of gastrointestinal disease and histopathological unremarkable duodenum; n = 15), and 32.1% (animals exhibiting clinical signs of gastrointestinal diseases and moderate to severe histopathological lesions; n = 28). Detailed information regarding the magnitude and duration of the response are provided. The adapter-modified Ussing chamber enables investigation of the absorptive and secretory capacity of endoscopically obtained duodenal biopsies from cats and dogs and has the potential to become a valuable research tool. The response of samples was correlated with histopathological findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Allenspach K, Wieland B, Gröne A, Gaschen F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J Vet Intern Med. 2007; 21:700–708.
Article2. Bastl CP. Regulation of cation transport by low doses of glucocorticoids in in vivo adrenalectomized rat colon. J Clin Invest. 1987; 80:348–356.
Article3. Batt RM, Scott J. Response of the small intestinal mucosa to oral glucocorticoids. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1982; 74:75–88.4. Bijlsma PB, Backhaus B, Weidenhiller M, Donhauser N, Hahn EG, Raithel M. Food allergy diagnosis by detection of antigen-induced electrophysiological changes and histamine release in human intestinal biopsies during mucosa-oxygenation. Inflamm Res. 2004; 53:Suppl 1. S29–S30.
Article5. Binder HJ, Turnamian SG. Differential effects of corticosteroids on active electrolyte transport in the mammalian distal colon. Acta Vet Scand Suppl. 1989; 86:174–180.6. Bukhave K, Rask-Madsen J, Hogan DL, Koss MA, Isenberg JI. Proximal duodenal prostaglandin E2 release and mucosal bicarbonate secretion are altered in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1990; 99:951–955.
Article7. Cohen-Cymberknoh M, Yaakov Y, Shoseyov D, Shteyer E, Schachar E, Rivlin J, Bentur L, Picard E, Aviram M, Israeli E, Kerem E, Wilschanski M. Evaluation of the intestinal current measurement method as a diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013; 48:229–235.
Article8. Craven M, Simpson JW, Ridyard AE, Chandler ML. Canine inflammatory bowel disease: retrospectice analysis of diagnosis and outcome in 80 cases (1995-2002). J Small Anim Pract. 2004; 45:336–342.
Article9. Day MJ, Bilzer T, Mansell J, Wilcock B, Hall EJ, Jergens A, Minami T, Willard M, Washabau R. Histopathological standards for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal inflammation in endoscopic biopsy samples from the dog and cat: a report from the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization group. J Comp Pathol. 2008; 138:Suppl 1. S1–S43.
Article10. Donowitz M, Charney AN, Heffernan JM. Effect of serotonin treatment on intestinal transport in the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1977; 232:E85–E94.
Article11. Ferraris RP, Diamond JM. Use of phlorizin binding to demonstrate induction of intestinal glucose transporters. J Membr Biol. 1986; 94:77–82.
Article12. Freeman HJ, Quamme GA. Age-related changes in sodium-dependent glucose transport in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1986; 251:G208–G217.
Article13. Frizzell RA, Turnheim K. Ion transport by rabbit colon: II. Unidirectional sodium influx and the effects of amphotericin B and amiloride. J Membr Biol. 1978; 40:193–211.
Article14. Greig ER, Mathialahan T, Boot-Handford RP, Sandle GI. Molecular and functional studies of electrogenic Na+ transport in the distal colon and rectum of young and elderly subjects. Gut. 2003; 52:1607–1615.
Article15. Hall EJ, Rutgers HC, Scholes SFE, Middleton DJ, Tennant BJ, King NM, Kelley DF. Histiocytic ulcerative colitis in boxer dogs in the UK. J Small Anim Pract. 1994; 35:509–515.
Article16. Hogan DL, Yao B, Barrett KE, Isenberg JI. Histamine inhibits prostaglandin E2-stimulated rabbit duodenal bicarbonate secretion via H2 receptors and enteric nerves. Gastroenterology. 1995; 108:1676–1682.
Article17. Jergens AE, Crandell JM, Evans R, Ackermann M, Miles KG, Wang C. A clinical index for disease activity in cats with chronic enteropathy. J Vet Intern Med. 2010; 24:1027–1033.
Article18. Jergens AE, Moore FM, Haynes JS, Miles KG. Idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease in dogs and cats: 84 cases (1987-1990). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1992; 201:1603–1608.19. Jergens AE, Schreiner CA, Frank DE, Niyo Y, Ahrens FE, Eckersall PD, Benson TJ, Evans R. A scoring index for disease activity in canine inflammatory bowel disease. J Vet Intern Med. 2003; 17:291–297.
Article20. Kosik-Bogacka D, Tyrakowski T. Ion transport in rabbit caecum at 12 and 36 months of age. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004; 55:Suppl 2. 117–128.21. Larsen R, Mertz-Nielsen A, Hansen MB, Poulsen SS, Bindslev N. Novel modified Ussing chamber for the study of absorption and secretion in human endoscopic biopsies. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001; 173:213–222.
Article22. Littman MP, Dambach DM, Vaden SL, Giger U. Familial protein-losing enteropathy and protein-losing nephropathy in Soft Coated Wheaten Terriers: 222 cases (1983-1997). J Vet Intern Med. 2000; 14:68–80.
Article23. Meddings JB, Swain MG. Environmental stress-induced gastrointestinal permeability is mediated by endogenous glucocorticoids in the rat. Gastroenterology. 2000; 119:1019–1028.
Article24. Neirinckx E, Vervaet C, Michiels J, De Smet S, Van den Broeck W, Remon JP, De Backer P, Croubels S. Feasibility of the Ussing chamber technique for the determination of in vitro jejunal permeability of passively absorbed compounds in different animal species. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 34:290–297.
Article25. Polentarutti BI, Peterson AL, Sjöberg AK, Anderberg EK, Utter LM, Ungell AL. Evaluation of viability of excised rat intestinal segments in the Ussing chamber: investigation of morphology, electrical parameters, and permeability characteristics. Pharm Res. 1999; 16:446–454.26. Powell DW. Barrier function of epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1981; 241:G275–G288.
Article27. Pratha VS, Thompson SM, Hogan DL, Paulus P, Dreilinger A, Barrett KE, Isenberg JI. Utility of endoscopic biopsy samples to quantitate human duodenal ion transport. J Lab Clin Med. 1998; 132:512–518.
Article28. Pressley TA. Structure and function of the Na, K pump: ten years of molecular biology. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996; 22:264–271.29. Rangachari PK, McWade D. Epithelial and mucosal preparations of canine proximal colon in Ussing chambers: comparison of responses. Life Sci. 1986; 38:1641–1652.
Article30. Rocha F, Musch MW, Lishanskiy L, Bookstein C, Sugi K, Xie Y, Chang EB. IFN-γ downregulates expression of Na+/H+ exchangers NHE2 and NHE3 in rat intestine and human Caco-2/bbe cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2001; 280:C1224–C1232.31. Ruhnke I, DeBiasio JV, Suchodolski JS, Newman SJ, Musch MW, Steiner JM. Adapter-modified Ussing chamber enables evaluation of endoscopically-obtained biopsy samples from cats and dogs. Res Vet Sci. 2012; 93:1454–1461.
Article32. Saunders PR, Kosecka U, McKay DM, Perdue MH. Acute stressors stimulate ion secretion and increase epithelial permeability in rat intestine. Am J Physiol. 1994; 267:G794–G799.
Article33. Söderholm JD, Hedman L, Arthursson P, Franzén L, Larsson J, Pantzar N, Permert J, Olaison G. Integrity and metabolism of human ileal mucosa in vitro in the Ussing chamber. Acta Physiol Scand. 1998; 162:47–56.34. Söderholm JD, Perdue MH. Stress and gastrointestinal tract. II. Stress and intestinal barrier function. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001; 280:G7–G13.35. Stevens CE. Transport of sodium and chloride by the isolated rumen epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1964; 206:1099–1105.
Article36. Sugi K, Musch MW, Field M, Chang EB. Inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase by interferon γ down-regulates intestinal epithelial transport and barrier function. Gastroenterology. 2001; 120:1393–1403.
Article37. Takeyoshi I, Zhang S, Nomoto M, Zhu Y, Kokudo Y, Suzuki T, Hamada N, Nemoto A, Starzl TE, Todo S. Mucosal damage and recovery of the intestine after prolonged preservation and transplantation in dogs. Transplantation. 2001; 71:1–7.
Article38. Venkatasubramanian J, Sahi J, Rao MC. Ion transport during growth and differentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000; 915:357–372.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Isolation Rates and Carrier State of Dermatophytes, Nondermatophyte Molds, Malassezia Species, and Candida Species in Indoor Dogs and Cats in Daegu
- Guidelines for vaccination of dogs and cats in Korea
- Rabies neutralizing antibody titers in Korean dogs and cats intended for overseas travel
- Isolation Rates of Dermatophytes and Fungi from Dogs and Cats in an Animal Shelter in Daegu
- Prevalence of Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae in cats and dogs in Korea