Sentinel Lymph Node Radiolocalization with 99mTc Filtered Tin Colloid in Clinically Node-Negative Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Cavity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chbaek@smc.samsung.co kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781907
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.5.865
Abstract
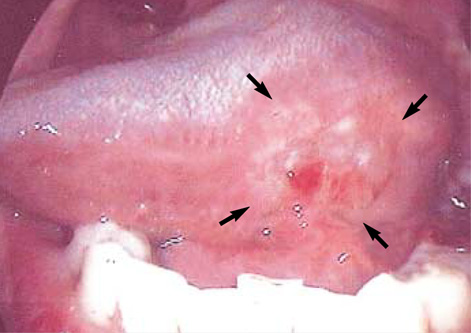
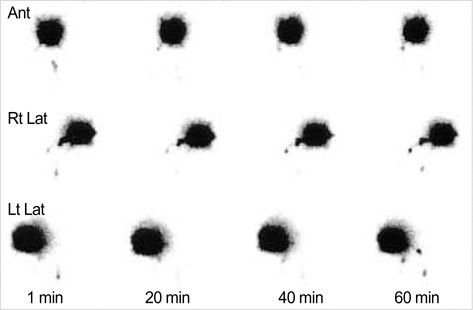
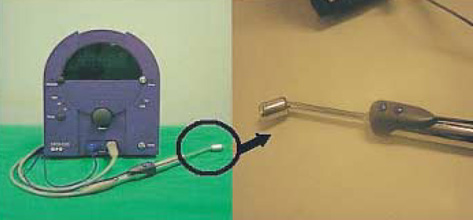
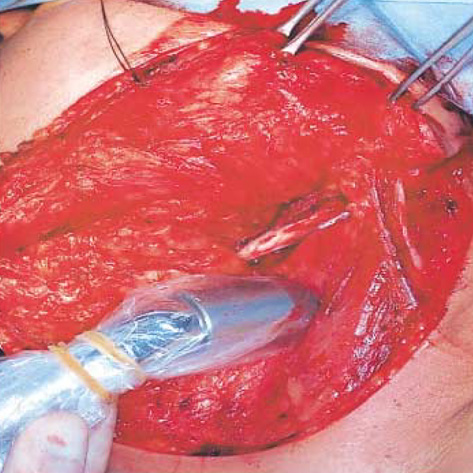
- The objective of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of sentinel lymph node biopsy by using a radiotracer lymphatic mapping technique in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, and the diagnostic value of this technique. We studied twenty patients with previously untreated squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity and N0 necks. After the peritumoral injection of 99mTc filtered tin colloid preop-eratively, lymphoscintigraphy and intraoperative mapping using a gamma detector were performed to localize sentinel nodes. An open biopsy of the sentinel node was followed by complete neck dissection. We identified the sentinel nodes in 19 of 20 patients (95.0%) by lymphoscintigraphy and in all (100%) by intraoperative gamma detector. In all cases, the status of the sentinel node accurately predicted the pathologic status of the neck with the false negative rate being 0%. The negative predictive value for the absence of cervical metastases was 100%. In conclusion, our radio-localization technique of sentinel nodes using 99mTc filtered tin colloid in N0 squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity is technically feasible and appears to accurately predict the presence of the occult metastatic disease.
MeSH Terms
-
Tin Compounds/*diagnostic use
Technetium Compounds/*diagnostic use
*Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Radiopharmaceuticals/*diagnostic use
Mouth Neoplasms/*pathology/*radionuclide imaging
Middle Aged
Male
Lymphatic Metastasis
Lymph Nodes/*radionuclide imaging
Humans
Female
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell/*pathology/*radionuclide imaging
Aged
Adult
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in the Oral Cavity Cancer
Chung-Hwan Baek
Hanyang Med Rev. 2009;29(3):255-264. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2009.29.3.255.The Feasibility of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy with a Multidisciplinary Cooperative Team Approach for the Management of Koreans with Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma
Seok-Jong Lee, Hyun Jung Lim, Ho Youn Kim, Chang Hyun Song, Byung Soo Kim, Weon Ju Lee, Do Won Kim, Jin Hyang Jung, Ho Yong Park, Sang Gul Kim, Ghil Suk Yoon, Jae Tae Lee
Ann Dermatol. 2010;22(1):26-34. doi: 10.5021/ad.2010.22.1.26.Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Versus Elective Neck Dissection: Long-Term Oncologic Outcomes in Clinically Node-Negative Tongue Cancer
Woori Park, Hokyung Jin, Yujin Heo, Han-Sin Jeong, Young-Ik Son, Man Ki Chung, Chung-Hwan Baek
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;15(1):107-114. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2020.02411.
Reference
-
1. Don DM, Anzai Y, Lufkin RB, Fu YS, Calcaterra TC. Evaluation of cervical lymph node metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 1995. 105:669–674.
Article2. Friedman M, Mafee MF, Pacella BL Jr, Strorigl TL, Dew LL, Toriumi DM. Rationale for elective neck dissection in 1990. Laryngoscope. 1990. 100:54–59.
Article3. Werner JA, Dunne AA, Ramaswamy A, Dalchow C, Behr T, Moll R, Folz BJ, Davis RK. The sentinel node concept in head and neck cancer: solution for the controversies in the N0 neck? Head Neck. 2004. 26:603–611.
Article4. Alex JC. The application of sentinel node radiolocalization to solid tumors of the head and neck: a 10-year experience. Laryngoscope. 2004. 114:2–19.5. Morton DL, Thompson JF, Essner R, Elashoff R, Stern SL, Nieweg OE, Roses DF, Karakousis CP, Mozzillo N, Reintgen D, Wang HJ, Glass EC, Cochran AJ. Validation of the accuracy of intraoperative lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for early-stage melanoma: a multicenter trial. Multicenter Selective Lymphadenectomy Trial Group. Ann Surg. 1999. 230:453–463.6. Wiseman SM, Loree TR, Hicks WL Jr, Rigual NR. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in SCC of the head and neck: a major advance in staging the N0 neck. Ear Nose Throat J. 2002. 81:156–160. 1637. Taylor RJ, Wahl RL, Sharma PK, Bradford CR, Terrell JE, Teknos TN, Heard EM, Wolf GT, Chepeha DB. Sentinel node localization in oral cavity and oropharynx squamous cell cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001. 127:970–974.
Article8. Shoaib T, Soutar DS, Prosser JE, Dunaway DJ, Gray HW, McCurrach GM, Bessent RG, Robertson AG, Oliver R, MacDonald DG. A suggested method for sentinel node biopsy in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 1999. 21:728–733.
Article9. Alex JC, Sasaki CT, Krag DN, Wenig B, Pyle PB. Sentinel lymph node radiolocalization in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2000. 110:198–203.
Article10. Mozzillo N, Chiesa F, Botti G, Caraco C, Lastoria S, Giugliano G, Mazzarol G, Paganelli G, Ionna F. Sentinel node biopsy in head and neck cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001. 8:103S–105S.11. Ross GL, Shoaib T, Soutar DS, MacDonald DG, Camilleri IG, Bessent RG, Gray HW. The first international conference on sentinel node biopsy in mucosal head and neck cancer and adoption of a multicenter trial protocol. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002. 9:406–410.
Article12. Higashi H, Natsugoe S, Uenosono Y, Ehi K, Arigami T, Nakabeppu Y, Nakajo M, Aikou T. Particle size of tin and phytate colloid in sentinel node identification. J Surg Res. 2004. 121:1–4.13. Jinno H, Ikeda T, Matsui A, Kitagawa Y, Kitajima M, Fujii H, Nakamura K, Kubo A. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer using technetium-99m tin colloids of different sizes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2002. 56:Suppl 1. 213s–216s.14. Byers RM, Weber RS, Andrews T, McGill D, Kare R, Wolf P. Frequency and therapeutic implications of "skip metastases" in the neck from squamous carcinoma of the oral tongue. Head Neck. 1997. 19:14–19.
Article15. Norman J, Cruse CW, Espinosa C, Cox C, Berman C, Clark R, Saba H, Wells K, Reintgen D. Redefinition of cutaneous lymphatic drainage with the use of lymphoscintigraphy for malignant melanoma. Am J Surg. 1991. 162:432–437.
Article16. Stoeckli SJ, Pfaltz M, Ross GL, Steinert HC, MacDonald DG, Wittekind C, Soutar DS. The second international conference on sentinel node biopsy in mucosal head and neck cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2005. 12:919–924.
Article17. Paleri V, Rees G, Arullendran P, Shoaib T, Krishman S. Sentinel node biopsy in squamous cell cancer of the oral cavity and oral pharynx: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2005. 27:739–747.
Article18. Gallegos-Hernandez JF, Hernandez-Hernandez DM, Flores-Diaz R, Sierra-Santiesteban I, Pichardo-Romero P, Arias-Ceballos H, Minauro-Munoz G, Alvarado-Cabrero I. The number of sentinel nodes identified as prognostic factor in oral epidermoid cancer. Oral Oncol. 2005. 41:947–952.19. Terada A, Hasegawa Y, Goto M, Sato E, Hyodo I, Ogawa T, Nakashima T, Yatabe Y. Sentinel lymph node radiolocalization in clinically negative neck oral cancer. Head Neck. 2006. 28:114–120.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in the Oral Cavity Cancer
- Comparison of the Results for Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in the Breast Cancer Patients using 99mTc-Antimony Trisulfide Colloid, 99mTc-Tin Colloid, and 99mTc-Human Serum Albumin
- Size Control of 99mTc-tin Colloid Using PVP and Buffer Solution for Sentinel Lymph Node Detection
- Camparison of the Efficiency for Tc-99m Tin-colloid and Tc-99m Phytate in Sentinel Node Detection in Breast Cancer Patients
- Optimized Criteria for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node Negative Breast Cancer