Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Hospitalized Children with Acute Respiratory Disease in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Sanggyepaik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. imswk@sanggyepaik.ac.kr
- 2Diagnostic Laboratory Medicine, Sanggyepaik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1781902
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.5.838
Abstract
- Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a recently isolated virus, mostly associated with acute lower respiratory infection in children, of which symptoms are similar to those of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. The aim of our study was to determine the frequency of hMPV in hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract disease in Korea. Nasal aspirates from hospitalized children with respiratory infections under 15 yr old between December 2003 and February 2005 were included in the study. Each sample was analyzed for RSV, adenovirus, influenza virus A and B, and parainfluenza virus by indirect fluorescent assay (IFA). F-gene sequences were used for PCR for the detection and sequencing of hMPV. In total 381 samples, negative samples in which any viral pathogen could not be identified by IFA were 231 cases. hMPV was detected using reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR) in 28 of 231 (12.1%) children who were not infected with another respiratory viruses. The hMPV-infected children were diagnosed as having pneumonia, bronchiolitis, bronchial asthma exacerbation, croup, and upper respiratory tract infection. Most of the RT-PCR positive samples for hMPV were collected in winter season. These results suggest that hMPV may be a responsible pathogen causing acute respiratory tract infection in Korean children.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
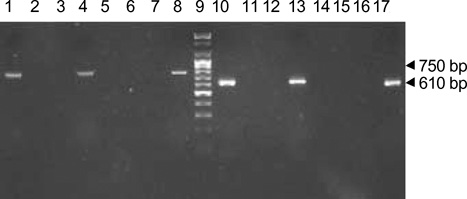
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
Clinical and Epidemiological Comparison of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Seoul, Korea, 2003-2008
Chang Keun Kim, Jungi Choi, Zak Callaway, Hyo Bin Kim, Ju Young Chung, Young-Yull Koh, Bo Moon Shin
J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25(3):342-347. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.3.342.Clinical Manifestations of Respiratory Viruses in Hospitalized Children with Acute Viral Lower Respiratory Tract Infections from 2010 to 2011 in Busan and Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea
Hye-Young Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Seong Heon Kim, Seung Kook Son, Hee Ju Park
Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2012;22(3):265-272. doi: 10.7581/pard.2012.22.3.265.Study on Causes of Respiratory Disease to the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-negative Subjects
Su-Jeong Hwang, Dong-Ju Park, Hee-Soo Koo, Ho-Cheol Yun, Pyeung-Tae Gu, Mi-Ok Lee, Sung-Hyun Jin
J Bacteriol Virol. 2017;47(3):156-164. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2017.47.3.156.Viral Infections and Associated Factors That Promote Acute Exacerbations of Asthma
Chang-Keun Kim, Zak Callaway, James E. Gern
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(1):12-17. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.12.The epidemiology and clinical manifestation of human metapneumovirus infection in children during 2011–2014
Myeong Sun Jang, Meeyong Shin
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(5):269-273. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.5.269.Literature review and future strategies of childhood respiratory diseases in Korea
Man Yong Han, Hai Lee Chung, Young Min Ahn, Jung Yeon Shim
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2018;6(Suppl 1):S66-S76. doi: 10.4168/aard.2018.6.S1.S66.Detection of 12 Respiratory Viruses with Two-set Multiplex Reverse Transcriptase-PCR Assay Using a Dual Priming Oligonucleotide System
Soo Jin Yoo, Eun-Young Kuak, Bo-Moon Shin
Korean J Lab Med. 2007;27(6):420-427. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2007.27.6.420.
Reference
-
1. van den Hoogen BG, de Jong JC, Groen J, Kuiken T, de Groot R, Fouchier RA, Osterhaus AD. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nat Med. 2001. 7:719–724.
Article2. van den Hoogen BG, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Analysis of the genomic sequence of a human metapneumovirus. Virology. 2002. 295:119–132.
Article3. Peret TC, Boivin G, Li Y, Couillard M, Humphrey C, Osterhaus AD, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Characterization of human metapneumovirus isolated from patients in North America. J Infect Dis. 2002. 185:1660–1663.4. Boivin G, De Serres G, Cote S, Gilca R, Abed Y, Rochette L, Bergeron MG, Dery P. Human metapneumovirus infections in hospitalized children. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:634–640.
Article5. Esper F, Boucher D, Weibel C, Martinello RA, Kahn JS. Human metapneumovirus infection in the United States: clinical manifestations associated with a newly emerging respiratory infection in children. Pediatrics. 2003. 111:1407–1410.
Article6. Freymouth F, Vabret A, Legrand L, Eterradossi N, Lafay-Delaire F, Brouard J, Guillois B. Presence of the new human metapneumovirus in French children with bronchiolitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003. 22:92–94.7. Maggi F, Pifferi M, Vatteroni M, Fornai C, Tempestini E, Anzilotti S, Lanini L, Andreoli E, Ragazzo V, Pistello M, Specter S, Bendinelli M. Human metapneumovirus associated with respiratory tract infections in a 3-year study of nasal swabs from infants in Italy. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:2987–2991.
Article8. Ebihara T, Endo R, Kikuta H, Ishiguro N, Ishiko H, Hara M, Takahashi Y, Kobayashi K. Human metapneumovirus infection in Japanese children. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:126–132.
Article9. Biovin G, Abed Y, Pelletier G, Ruel L, Moisan D, Cote S, Peret TC, Erdman DD, Anderson LJ. Virological features and clinical manifestations associated with the human metapneumovirus, a new paramyxovirus responsible for acute respiratory tract infections in all age groups. J Infect Dis. 2002. 186:1330–1334.10. Stockton J, Stephenson I, Fleming D, Zambon M. Human metapneumovirus as a cause of community acquired respiratory illness. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002. 8:897–901.11. MacKay IM, Jacob KC, Woolhouse D, Waller K, Syrmis MW, Whiley DM, Siebert DJ, Nissen M, Sloots TP. Molecular assay for detection of human metapneumovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:100–105.12. Peiris JS, Tang WH, Chan KH, Khong PL, Guan Y, Lau YL, Chiu SS. Children with respiratory disease associated with metapneumovirus in Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:628–633.
Article13. van den Hoogen BG, Herfst S, Sprong L, Cane PA, Forleo-Neto E, de Swart RL, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Antigenic and genetic variability of human metapneumoviruses. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. 10:658–666.
Article14. Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA 3: Integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignments. Bioinformatics. 2004. 5:150–163.15. von Linstow ML, Henrik Larsen H, Eugen-Olsen J, Koch A, Nordmann Winther T, Meyer AM, Westh H, Lundgren B, Melbye M, Hogh B. Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial in hospitalized Danish children with acute respiratory tract infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 2004. 36:578–584.16. Galiano M, Videla C, Puch SS, Martinez A, Echavarria M, Carballal G. Evidence of human metapneumovirus in children in Argentina. J Med Virol. 2004. 72:299–303.
Article17. Dollner H, Risnes K, Radtke A, Nordbo SA. Outbreak of human metapneumovirus infection in Norwegian children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004. 23:436–440.18. Gerna G, Campanini G, Rovida F, Sarasini A, Lilleri D, Paolucci S, Marchi A, Baldanti F, Revello MG. Changing circulation rate of human metapneumovirus strains and types among hospitalized pediatric patients during three consecutive winter-spring seasons. Arch Virol. 2005. 150:2365–2375.
Article19. Williams JV, Harris PA, Tollefson SJ, Halburnt-Rush LL, Pingsterhaus JM, Edwards KM, Wright PF, Crowe JE Jr. Human metapneumovirus and lower respiratory tract disease in otherwise healthy infants and children. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:443–450.
Article20. Robinson JL, Lee BE, Bastien N, Li Y. Seasonality and clinical features of human metapneumovirus infection in children in Northern Alberta. J Med Virol. 2005. 76:98–105.
Article21. Jartti T, van den Hoogen B, Garofalo RP, Osterhaus AD, Ruuskanen O. Metapneumovirus and acute wheezing in children. Lancet. 2002. 360:1393–1394.
Article22. Rawlinson WD, Waliuzzaman Z, Carter JW, Belessis YC, Gilbert KM, Morton JR. Asthma exacerbation in children associated with rhinovirus but not human metapneumovirus infection. J Infect Dis. 2003. 187:1314–1318.23. Viazov S, Ratjen F, Scheidhauer R, Fielder M, Roggendorf M. High prevalence of human metapneumovirus infection in young children and genetic heterogeneity of the viral isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:3043–3045.
Article24. Bouscambert-Duchamp M, Lina B, Trompette A, Moret H, Motte J, Andreoletti L. Detection of human metapneumovirus RNA sequences in nasopharyngeal aspirates of young French children with acute bronchiolitis by real time reverse transcriptase PCR and phylogenetic analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. 43:1411–1414.25. Cuevas LE, Nasser AM, Dove W, Gurgel RQ, Greensill J, Hart CA. Human metapneumovirus and respiratory syncytial virus, Brazil. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003. 9:1626–1628.
Article26. Konig B, Konig W, Arnold R, Werchau H, Ihorst G, Forster J. Prospective study of human metapneumovirus infection in children less than 3 years of age. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:4632–4635.
Article27. Falsey AR, Erdman D, Anderson LJ, Walsh EE. Human metapneumovirus infections in young and elderly adults. J Infect Dis. 2003. 187:785–790.
Article28. Carr MJ, McCormack GP, Crowley B. Human metapneumovirus associated respiratory tract infections in the Republic of Ireland during the influenza season of 2003-4. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2005. 11:366–371.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Manifestation of Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Korean Children
- Clinical Features of Human Metapneumovirus and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Hospitalized Children
- Clinical Manifestation of Human Metapneumovirus Infection in Korean Children
- Prevalence of respiratory viral infection in children hospitalized for acute lower respiratory tract diseases, and association of rhinovirus and influenza virus with asthma exacerbations
- The epidemiology and clinical manifestation of human metapneumovirus infection in children during 2011–2014