J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Feb;25(2):324-326. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.324.
The First Korean Case of KCNQ2 Mutation in a Family with Benign Familial Neonatal Convulsions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tsko@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1779270
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.2.324
Abstract
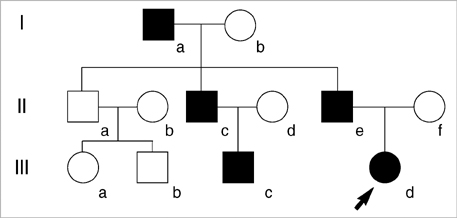
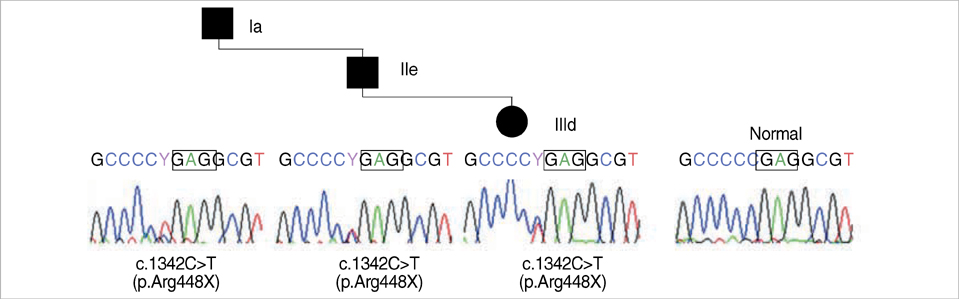
- Neonatal seizures represent a heterogeneous group of disorders with vastly different etiologies and outcomes. Benign familial neonatal convulsions (BFNC) are a distinctive epileptic syndrome of autosomal dominant inheritance with a favorable prognosis, characterized by the occurrence of unprovoked partial or generalized clonic seizures in the neonatal period or early infancy. Recently, mutations in two potassium channel genes, KCNQ2 and KCNQ3, have been described in this disorder. In this report, we describe a family with BFNC due to a KCNQ2 mutation, the first such family to be described in the Korean population. The diagnosis of BFNC can be made based on clinical suspicion and careful history taking with special emphasis on the familial nature of the disorder. KCNQ2 mutations may be associated with BFNC in a number of different races, as has been reported in other ethnic groups.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ronen GM, Rosales TO, Connolly M, Anderson VE, Leppert M. Seizure characteristics in chromosome 20 benign familial neonatal convulsions. Neurology. 1993. 43:1355–1360.
Article2. Plouin P, Anderson V. Roger J, Bureau M, Dravet C, Genton PT, C.A. , Wolf P, editors. Benign familial and Non-familial neonatal seizures. Epilepic syndromes in Infancy, Childhood and Adolescence. 2005. 4th ed. Montrouge, France: John Libbey Eurotext;3–15.3. Wang HS, Pan Z, Shi W, Brown BS, Wymore RS, Cohen IS, Dixon JE, McKinnon D. KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel subunits: molecular correlates of the M-channel. Science. 1998. 282:1890–1893.
Article4. Borgatti R, Zucca C, Cavallini A, Ferrario M, Panzeri C, Castaldo P, Soldovieri MV, Baschirotto C, Bresolin N, Dalla Bernardina B, Taglialatela M, Bassi MT. A novel mutation in KCNQ2 associated with BFNC, drug resistant epilepsy, and mental retardation. Neurology. 2004. 63:57–65.
Article5. Zonana J, Silvey K, Strimling B. Familial neonatal and infantile seizures: an autosomal-dominant disorder. Am J Med Genet. 1984. 18:455–459.
Article6. Singh NA, Westenskow P, Charlier C, Pappas C, Leslie J, Dillon J, Anderson VE, Sanguinetti MC, Leppert MF. KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 potassium channel genes in benign familial neonatal convulsions: expansion of the functional and mutation spectrum. Brain. 2003. 126:2726–2737.
Article7. Kanaumi T, Takashima S, Iwasaki H, Itoh M, Mitsudome A, Hirose S. Developmental changes in KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 expression in human brain: possible contribution to the age-dependent etiology of benign familial neonatal convulsions. Brain Dev. 2008. 30:362–369.
Article8. Ryan SG, Wiznitzer M, Hollman C, Torres MC, Szekeresova M, Schneider S. Benign familial neonatal convulsions: evidence for clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Ann Neurol. 1991. 29:469–473.
Article9. Maihara T, Tsuji M, Higuchi Y, Hattori H. Benign familial neonatal convulsions followed by benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes in two siblings. Epilepsia. 1999. 40:110–113.
Article10. Coppola G, Castaldo P, Miraglia del, Bellini G, Galasso F, Soldovieri MV, Anzalone L, Sferro C, Annunziato L, Pascotto A, Taglialatela M. A novel KCNQ2 K+ channel mutation in benign neonatal convulsions and centrotemporal spikes. Neurology. 2003. 61:131–134.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- KCNQ2 Encephalopathy Showing a Distinct Ictal Amplitude-Integrated Electroencephalographic Pattern
- Two Cases of Benign Non - Familial Neonatal Convulsion
- A novel frameshift mutation of PRRT2 in a family with infantile convulsions and choreoathetosis syndrome: c.640delinsCC (p.Ala214ProfsTer11)
- Novel Mutation in KCNQ2 Causing Ohtahara Syndrome
- A Case Report of Familial Benign Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia: A Mutation in the Calcium-Sensing Receptor Gene