J Korean Med Sci.
2009 Aug;24(4):614-620. 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.614.
Interleukin-13 and Its Receptors in Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia: Clinical Implications for Lung Function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Genome Research Center for Allergy and Respiratory Disease, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. mdcspark@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1779192
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.614
Abstract
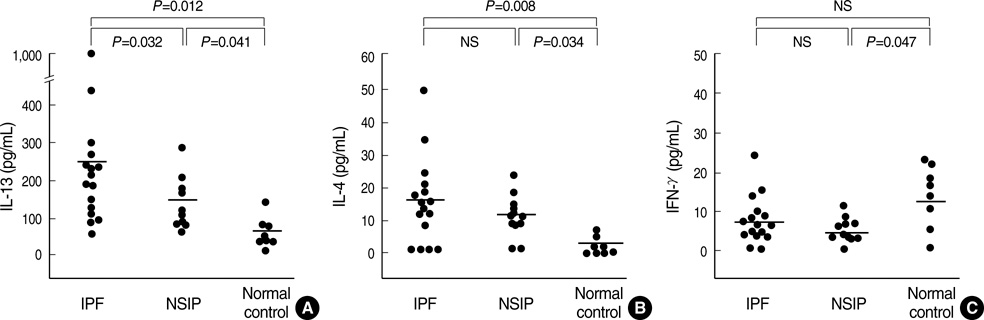
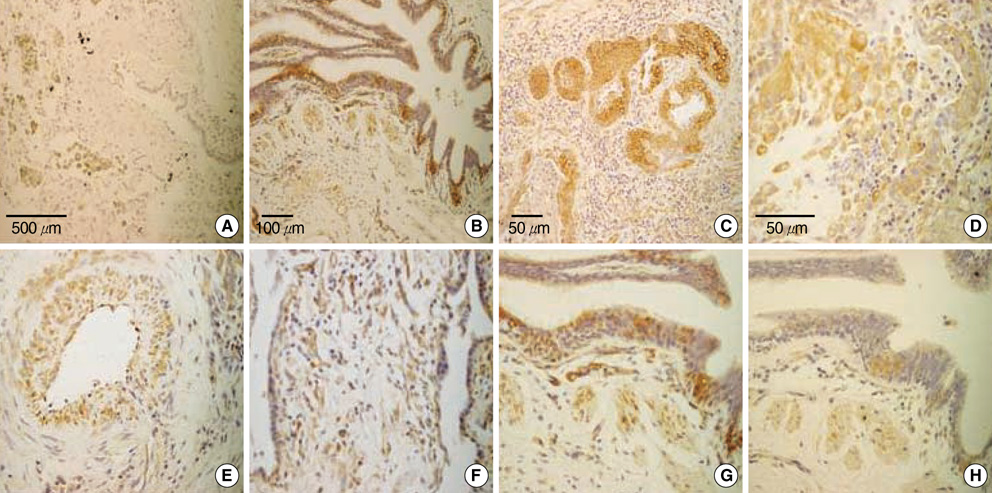
- Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP) is characterized by varying degrees of interstitial fibrosis. IL-13 and IL-4 are strong inducers of tissue fibrosis, whereas IFN-gamma has antifibrotic potential. However, the roles of these substances in IIP remain unknown. IL-13, IL-4, and IFN-gamma were measured in the BAL fluid of 16 idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) patients, 10 nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) patients, and 8 normal controls. The expression of IL-13 and IL-13Ralpha1/alpha2 in lung tissues was analyzed using ELISA and immunohistochemistry. IL-13 levels were significantly higher in IPF patients than the others (P<0.05). IL-4 levels were higher in both IPF and NSIP patients than in normal controls (P<0.05), and IFN-gamma levels were lower in NSIP patients than in normal controls (P=0.047). IL-13 levels correlated inversely with FVC% (r=-0.47, P=0.043) and DLCO% (r=-0.58, P=0.014) in IPF and NSIP patients. IL-13 was strongly expressed in the smooth muscle, bronchial epithelium, alveolar macrophages and endothelium of IPF patients. IL-13Ralpha1, rather than IL-13Ralpha2, was strongly expressed in the smooth muscle, bronchial epithelium, and endothelium of IPF patients. IL-13 and its receptors may contribute to the pathogenesis of fibrosis in IIP and appear to be related to the severity of the disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Female
Humans
Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias/diagnosis/*metabolism
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis/diagnosis/*metabolism
Interferon-gamma/analysis
Interleukin-13/*analysis
Interleukin-13 Receptor alpha1 Subunit/*metabolism
Interleukin-13 Receptor alpha2 Subunit/*metabolism
Interleukin-4/analysis
Lung/physiopathology
Male
Middle Aged
Figure
Reference
-
1. Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:1301–1315.2. Wallace WA, Ramage EA, Lamb D, Howie SE. A type 2 (Th2-like) pattern of immune response predominates in the pulmonary interstitium of patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA). Clin Exp Immunol. 1995. 101:436–441.
Article3. Majumdar S, Li D, Ansari T, Pantelidis P, Black CM, Gizycki M, du Bois RM, Jeffery PK. Different cytokine profiles in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and fibrosing alveolitis associated with systemic sclerosis: a quantitative study of open lung biopsies. Eur Respir J. 1999. 14:251–257.
Article4. Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Kunkel SL, Evanoff H, Martinez FJ, Puri RK, Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Colby TV, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Travis WD, Hogaboam CM. Augmented pulmonary IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. J Clin Pathol. 2004. 57:477–486.
Article5. Rottoli P, Magi B, Perari MG, Liberatori S, Nikiforakis N, Bargagli E, Cianti R, Bini L, Pallini V. Cytokine profile and proteome analysis in bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with sarcoidosis, pulmonary fibrosis associated with systemic sclerosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proteomics. 2005. 5:1423–1430.
Article6. Gharaee-Kermani M, Nozaki Y, Hatano K, Phan SH. Lung interleukin-4 gene expression in a murine model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cytokine. 2001. 15:138–147.
Article7. Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen Q, Geba GP, Wang J, Zhang Y, Elias JA. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest. 1999. 103:779–788.
Article8. Hilton DJ, Zhang JG, Metcalf D, Alexander WS, Nicola NA, Willson TA. Cloning and characterization of a binding subunit of the interleukin 13 receptor that is also a component of the interleukin 4 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996. 93:497–501.
Article9. Andrews R, Rosa L, Daines M, Khurana Hershey G. Reconstitution of a functional human type II IL-4/IL-13 receptor in mouse B cells: demonstration of species specificity. J Immunol. 2001. 166:1716–1722.
Article10. Murata T, Obiri NI, Puri RK. Structure of and signal transduction through interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 receptors. Int J Mol Med. 1998. 1:551–557.11. Donaldson DD, Whitters MJ, Fitz LJ, Neben TY, Finnerty H, Henderson SL, O'Hara RM Jr, Beier DR, Turner KJ, Wood CR, Collins M. The murine IL-13 receptor alpha 2: molecular cloning, characterization, and comparison with murine IL-13 receptor alpha 1. J Immunol. 1998. 161:2317–2324.12. Chiaramonte MG, Mentink-Kane M, Jacobson BA, Cheever AW, Whitters MJ, Goad ME, Wong A, Collins M, Donaldson DD, Grusby MJ, Wynn TA. Regulation and function of the interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 during a T helper cell type 2-dominant immune response. J Exp Med. 2003. 197:687–701.13. Elliot TL, Lynch DA, Newell JD Jr, Cool C, Tuder R, Markopoulou K, Veve R, Brown KK. High-Resolution computed tomography features of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2005. 29:339–345.
Article14. Flaherty KR, Travis WD, Colby TV, Toews GB, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Jain A, Strawderman RL, Flint A, Lynch JP, Martinez FJ. Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 164:1722–1727.
Article15. Jegal Y, Kim DS, Shim TS, Lim CM, Do Lee S, Koh Y, Kim WS, Kim WD, Lee JS, Travis WD, Kitaichi M, Colby TV. Physiology is a stronger predictor of survival than pathology in fibrotic interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005. 171:639–644.
Article16. Park CS, Jeon JW, Park SW, Lim GI, Jeong SH, Uh ST, Park JS, Choi DL, Jin SY, Kang CH. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis: clinical manifestations, histologic and radiologic features. Korean J Intern Med. 1996. 11:122–132.
Article17. Park CS, Chung SW, Ki SY, Lim GI, Uh ST, Kim YH, Choi DI, Park JS, Lee DW, Kitaichi M. Increased levels of interleukin-6 are associated with lymphocytosis in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:1162–1168.
Article18. Ishii H, Mukae H, Kadota J, Fujii T, Abe K, Ashitani J, Kohno S. Increased levels of interleukin-18 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Respiration. 2005. 72:39–45.
Article19. Yoshioka S, Mukae H, Sugiyama K, Kakugawa T, Sakamoto N, Nakayama S, Abe K, Fujii T, Kadota J, Kohno S. High-BAL fluid concentrations of RANTES in nonspecific interstitial pneumonia compared with usual interstitial pneumonia. Respir Med. 2004. 98:945–951.
Article20. Nakayama S, Mukae H, Ishii H, Kakugawa T, Sugiyama K, Sakamoto N, Fujii T, Kadota J, Kohno S. Comparison of BALF concentrations of ENA-78 and IP10 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Respir Med. 2005. 99:1145–1151.
Article21. American Thoracic Society (ATS) and European Respiratory Society (ERS). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society, and the European Respiratory Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:646–664.22. Belperio JA, Dy M, Burdick MD, Xue YY, Li K, Elias JA, Keane MP. Interaction of IL-13 and C10 in the pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002. 27:419–427.
Article23. Kolodsick JE, Toews GB, Jakubzick C, Hogaboam C, Moore TA, Mckenzie A, Wilke CA, Chrisman CJ, Moore BB. Protection from fluorescein isothiocyanate-induced fibrosis in IL-13-deficient, but not IL-4-deficient, mice results from impaired collagen synthesis by fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2004. 172:4068–4076.
Article24. Jakubzick C, Kunkel SL, Puri RK, Hogaboam CM. Therapeutic targeting of IL-4- and IL-13-responsive cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Immunol Res. 2004. 30:339–349.
Article25. Chiaramonte MG, Donaldson DD, Cheever AW, Wynn TA. An IL-13 inhibitor blocks the development of hepatic fibrosis during a T-helper type 2-dominated inflammatory response. J Clin Invest. 1999. 104:777–785.
Article26. Lee CG, Homer RJ, Zhu Z, Lanone S, Wang X, Koteliansky V, Shipley JM, Gotwals P, Noble P, Chen Q, Senior RM, Elias JA. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J Exp Med. 2001. 194:809–821.27. Lanone S, Zheng T, Zhu Z, Liu W, Lee CG, Ma B, Chen Q, Homer RJ, Wang J, Rabach LA, Rabach ME, Shipley JM, Shapiro SD, Senior RM, Elias JA. Overlapping and enzyme-specific contributions of matrix metalloproteinases-9 and -12 in IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling. J Clin Invest. 2002. 110:463–474.
Article28. Akaiwa M, Yu B, Umeshita-Suyama R, Terada N, Suto H, Koga T, Arima K, Matsushita S, Saito H, Ogawa H, Furue M, Hamasaki N, Ohshima K, Izuhara K. Localization of human interleukin 13 receptor in non-haematopoietic cells. Cytokine. 2001. 13:75–84.
Article29. Zheng T, Zhu Z, Liu W, Lee CG, Chen Q, Homer RJ, Elias JA. Cytokine regulation of IL-13Ralpha2 and IL-13Ralpha1 in vivo and in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. 111:720–728.30. Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K, Puri RK, Kitani A. IL-13 signaling through the IL-13 alpha(2) receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta(1) production and fibrosis. Nat Med. 2006. 12:99–106.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Radiologic Findings
- Clinical Year in Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Focused on Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia
- A Case of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia with Clinical Course of Rapid Aggravation
- Radiologic Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases
- A Case Report of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia after Treatment of Bronchopneumonia