J Korean Med Sci.
2004 Apr;19(2):283-288. 10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.283.
Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure and Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. nikim@khmc.or.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1733490
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2004.19.2.283
Abstract
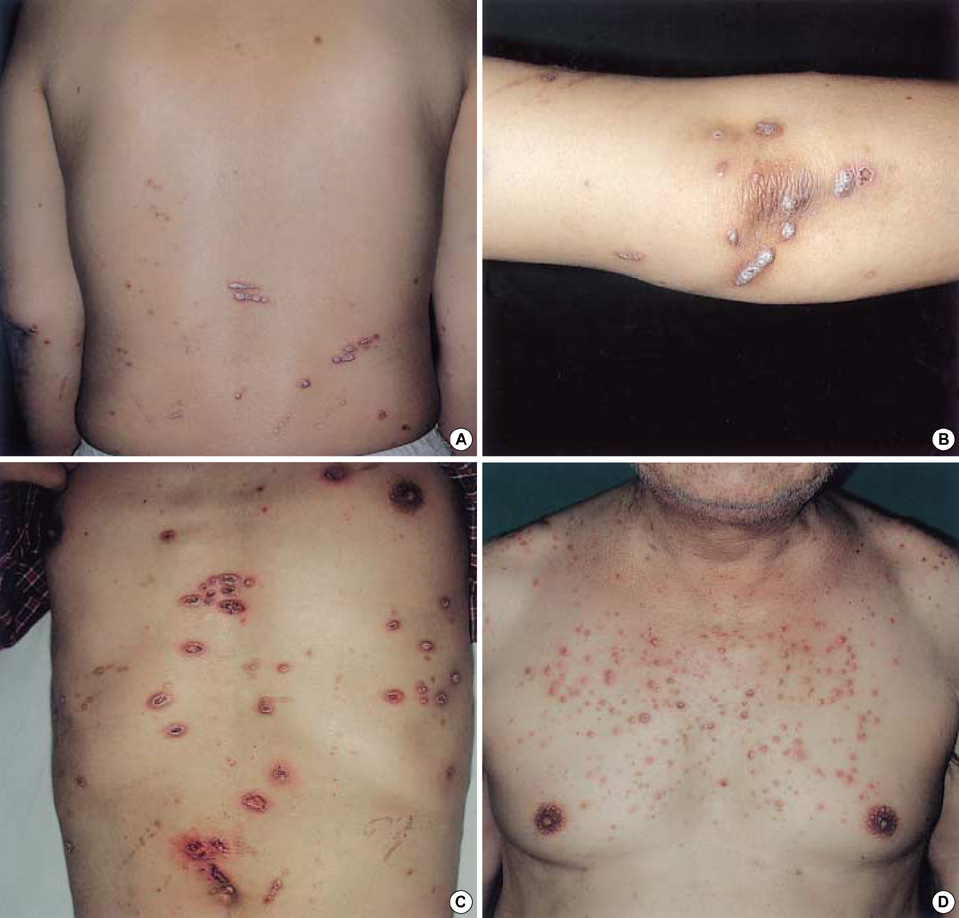
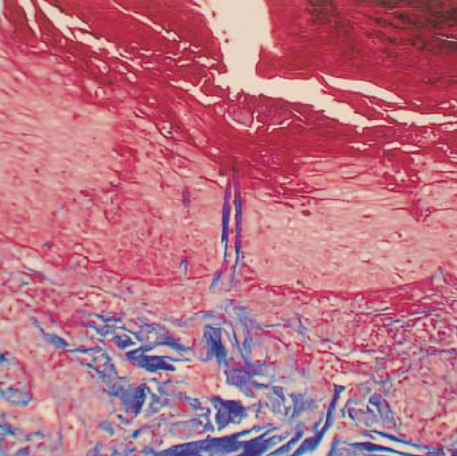
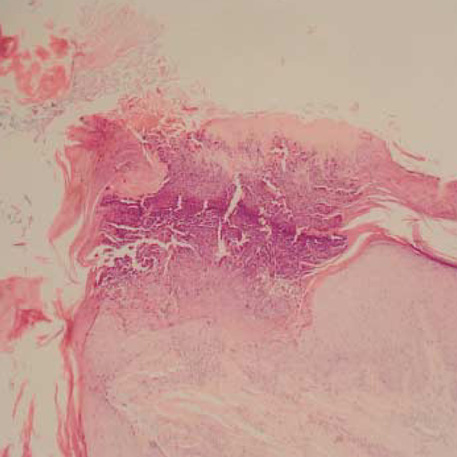
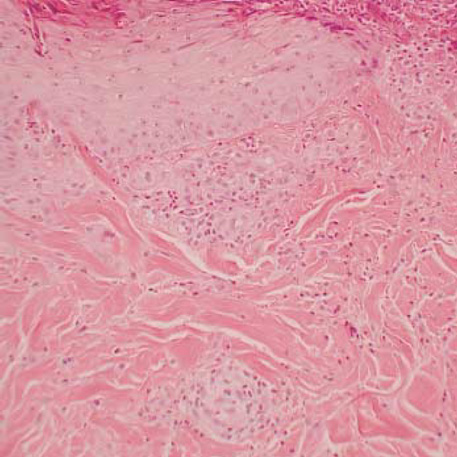
- Acquired perforating dermatosis (APD) is a skin disorder occurring in the patients with chronic renal failure (CRF), diabetes mellitus (DM) or both. The purpose of this study was to clarify the clinical and histopathological features of APD, and evaluate role of scratching in the pathogenesis of APD. Twelves patients with APD associated with CRF and DM were enrolled in the study. In six patients who required hemodialysis, the lesions appeared 2-5 yr (mean 3 yr) after the initiation of dialysis, 18-22 yr (mean 19.3 yr) after the occurrence of DM. The other patients who did not receive hemodialysis noted the lesions 4-17 yr (mean 9.5 yr) after the onset of DM. All patients had an eruption of generally pruritic keratotic papules and nodules, primarily on the extensor surface of the extremities and the trunk. The histologic features of our cases showed a crateriform invagination of the epidermis filled by a parakeratotic plug and basophilic cellular debris. The period of treatment for patients who suffered from severe (7 cases) or very severe (3 cases) on the pruritus intensity was longer than that of patients who had mild pruritus (2 cases). These data showed that scratching appear to play a critical part in the pathogenesis of APD.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Diabetes Mellitus, Type I/*complications
Diabetes Mellitus, Type II/*complications
Female
Histamine H1 Antagonists/therapeutic use
Human
Kidney Failure, Chronic/*complications
Male
Middle Aged
Phototherapy
Pruritus/drug therapy/etiology
Skin Diseases/drug therapy/*etiology/pathology
Tranquilizing Agents/therapeutic use
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Clinicopathologic Study of Thirty Cases of Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in Korea
Seo Wan Kim, Mi Sun Kim, June Hyunkyung Lee, Sook-Ja Son, Kui Young Park, Kapsok Li, Seong Jun Seo, Tae Young Han
Ann Dermatol. 2014;26(2):162-171. doi: 10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.162.
Reference
-
1. Maurice PD. Acquired perforating dermatosis in renal patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1997. 12:2774–2775.
Article2. Kawakami T, Saito R. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis associated with diabetes mellitus: eight cases that meet Faver's criteria. Br J Dermatol. 1999. 140:521–524.
Article3. Poliak SC, Lebwohl MG, Parris A, Prioleau PG. Reactive perforating collagenosis associated with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1982. 306:81–84.
Article4. Cochran RJ, Tucker SB, Wilkin JK. Reactive perforating collagenosis of diabetes mellitus and renal failure. Cutis. 1983. 31:55–58.5. Rapini RP, Herbert AA, Drucker CR. Acquired perforating dermatosis. Evidence for combined transepidermal elimination of both collagen and elastic fibers. Arch Dermatol. 1989. 125:1074–1078.
Article6. Heilman ER, Friedman RJ. Elder D, editor. Lever's Histopathology of the Skin. 1997. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;341–351.7. Lee MW, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, Koh JK. Acquired perforating dermatosis in renal failure. Korean J Dermatol. 2000. 38:1157–1161.8. Bang SW, Bu TS, Hyun C, Whang KU, Kim YK. Four cases of acquired perforating disease in patients with chronic renal failure. Korean J Dermatol. 1997. 35:333–338.9. Morton CA, Henderson IS, Jones MC, Lowe JG. Acquired perforating dermatosis in a British dialysis population. Br J Dermatol. 1996. 135:671–677.
Article10. Faver IR, Daoud MS, Su WP. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: report of six cases and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994. 30:575–580.11. Pedragosa R, Knobel HJ, Huguet P, Oristrell J, Valdes M, Bosch JA. Reactive perforating collagenosis with Hodgkin's disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987. 9:41–44.12. Mehregan AH. Elastosis perforans serpiginosa: a review of the literature and report of 11 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1968. 97:381–393.
Article13. Yuzuk S, Trau H, Stempler D, Sofer E, Levy A, Schewach-Millet M. Reactive perforating collagenosis. Int J Dermatol. 1985. 24:584–586.
Article14. Denman ST. A review of pruritus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986. 14:375–392.
Article15. Cohen RW, Auerbach R. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 20:287–289.
Article16. Ponticelli C, Bencini PL. Uremic pruritus: a review. Nephron. 1992. 60:1–5.
Article17. Bayoumi AH, Gaskell S, Marks R. Development of a model for transepidermal elimination. Br J Dermatol. 1978. 99:611–620.
Article18. Patterson JW, Brown PC. Ultrastructural changes in acquired perforating dermatosis. Int J Dermatol. 1992. 31:201–205.
Article19. Hood A, Hardegen GL, Zarate AR, Nigra TP, Gelfand MC. Kyrle's disease in patients with chronic renal failure. Arch Dermatol. 1982. 118:85–88.
Article20. Bank DE, Cohen PR, Kohn SR. Reactive perforating collagenosis in a setting of double disaster: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and end-stage renal disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989. 21:371–374.
Article21. Stone RA. Kyrle-like lesions in two patients with renal failure undergoing dialysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981. 5:707–709.
Article22. Blanchley JD, Blankenship M, Menter A. Uremic pruritus: skin divalent ion content and response to ultraviolet therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985. 5:237–241.23. Haftek M, Euvrard S, Kanitakis J, Delawari E, Schmitt D. Acquired perforating dermatosis of diabetes mellitus and renal failure: further ultrastructural clues to its pathogenesis. J Cutan Pathol. 1993. 20:350–355.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in Chronic Renal Failure with Allopurinol
- A Giant Variant of Acquired Perforating Collagenosis in Chronic Renal Failure
- Acquired Perforating Dermatosis in Renal Failure
- Four Cases of Acquired Perforating Disease in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure
- A Case of Reactive Perforating Collagenosis Associated With Diabetes Mellitus