Oral Muscle Relaxant May Induce Immediate Allergic Reactions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 1716891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.4.863
Abstract
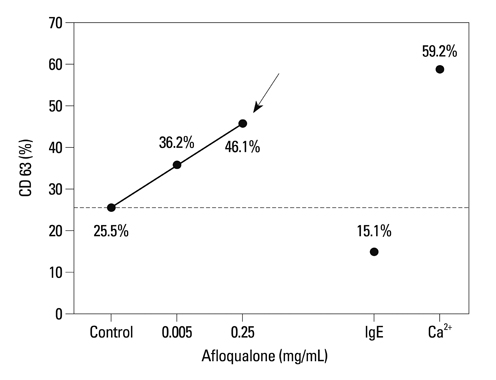
- Eperisone and afloqualone act by relaxing both skeletal and vascular smooth muscles to improve circulation and suppress pain reflex. These drugs are typically prescribed with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) as painkillers. However, there have been no reports on serious adverse reactions to oral muscle relaxants; and this is the first report to describe three allergic reactions caused by eperisone and afloqualone. All three patients had histories of allergic reactions after oral intake of multiple painkillers, including oral muscle relaxants and NSAIDs, for chronic muscle pain. An open-label oral challenge test was performed with each drug to confirm which drugs caused the systemic reactions. All patients experienced the same reactions within one hour after oral intake of eperisone or afloqualone. The severity of these reactions ranged from laryngeal edema to hypotension. To confirm that the systemic reaction was caused by eperisone or afloqualone, skin prick testing and intradermal skin tests were performed with eperisone or afloqualone extract in vivo, and basophil activity tests were performed after stimulation with these drugs in vitro. In one patient with laryngeal edema, the intradermal test with afloqualone extract had a positive result, and CD63 expression levels on basophils increased in a dose-dependent manner by stimulation with afloqualone. We report three allergic reactions caused by oral muscle relaxants that might be mediated by non-immunoglobulin E-mediated responses. Since oral muscle relaxants such as eperisone and afloqualone are commonly prescribed for chronic muscle pain and can induce severe allergic reactions, we should prescribe them carefully.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Eperisone-Induced Anaphylaxis: Pharmacovigilance Data and Results of Allergy Testing
Kyung Hee Park, Sang Chul Lee, Ji Eun Yuk, Sung-Ryeol Kim, Jae-Hyun Lee, Jung-Won Park
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(2):231-240. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.231.Anaphylaxis caused by muscle relaxant (eperisone hydrochloride)
Sung Hyun Kim, Jaechun Lee, Su Hee Kim, Hyun Woo Kim, Young Uck Kim, Younghyup Lim, Shinhang Moon, Jaecheol Moon, Dahee Heo
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2013;1(2):172-175. doi: 10.4168/aard.2013.1.2.172.Recent applications of basophil activation tests in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity
Woo-Jung Song, Yoon-Seok Chang
Asia Pac Allergy. 2013;3(4):266-280. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2013.3.4.266.A case series of eperisone-induced immediate hypersensitivity
Dong Yoon Kang, Jin Lee, young-Hee Sohn, Sung Yoon Kang, Yoon Sook Cho, Hye-Ryun Kang
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(4):228-231. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.4.228.KAAACI Standardization Committee Report on the procedures and applications of the diagnostic tests for drug allergy
Min-Suk Yang, Ga-Young Ban, Min-Hye Kim, Kyung-Hwan Lim, Hyouk-Soo Kwon, Woo-Jung Song, Jae-Woo Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Dong In Suh, Jae-Woo Kwon, Sae-Hoon Kim, Yoo Seob Shin, Hye-Ryun Kang, Tae-Bum Kim, Byung-Jae Lee, Ai-Young Lee, Hae-Sim Park, Sang-Heon Cho
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2017;5(5):239-247. doi: 10.4168/aard.2017.5.5.239.
Reference
-
1. Matsunaga M, Uemura Y, Yonemoto Y, Kanai K, Etoh H, Tanaka S, et al. Long-lasting muscle relaxant activity of eperisone hydrochloride after percutaneous administration in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1997. 73:215–220.
Article2. Ochiai T, Ishida R. Pharmacological studies on 6-amino-2-fluoromethyl-3-(O-tolyl)-4(3H)-quinazolinone (afloqualone), a new centrally acting muscle relaxant. (II) Effects on the spinal reflex potential and the rigidity. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1982. 32:427–438.
Article3. Inoue S, Bian K, Okamura T, Okunishi H, Toda N. Mechanisms of action of eperisone on isolated dog saphenous arteries and veins. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1989. 50:271–282.
Article4. Iwase S, Mano T, Saito M, Ishida G. Effect of a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, eperisone hydrochloride, on muscle sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Funct Neurol. 1992. 7:459–470.5. Choonhakarn C. Non-pigmenting fixed drug eruption: a new case due to eperisone hydrochloride. Br J Dermatol. 2001. 144:1288–1289.
Article6. Ueno T, Kawana S. [A case of eperisone hydrochloride (myonal)--induced drug eruption leading to erythema and angioedema]. Arerugi. 2007. 56:709–713.7. Ribi C, Vermeulen C, Hauser C. Anaphylactic reactions to tolperisone (Mydocalm). Swiss Med Wkly. 2003. 133:369–371.8. Demitsu T, Tomita Y. Fixed drug eruption due to afloqualone: the first reported case. J Dermatol. 1998. 25:136.
Article9. Webb LM, Lieberman P. Anaphylaxis: a review of 601 cases. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. 97:39–43.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anesthetic Management in a Patient with Cross-Sensitivity to Muscle Relaxants: A case report
- General and Spinal Anesthetic Experiences in a Patient Suspected with a History of Anaphylactic Reaction to Muscle Relaxants: A case report
- Management of Insect Sting Hypersensitivity: An Update
- Allergic contact dermatitis to hydroquinone in bleaching cream
- Repeat oral food challenges in peanut and tree nut allergic children with a history of mild/moderate reactions