Clin Orthop Surg.
2013 Sep;5(3):235-242. 10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.235.
How to Calculate Sample Size and Why
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Sacred Heart General Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kjhnav@naver.com
- KMID: 1705551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.3.235
Abstract
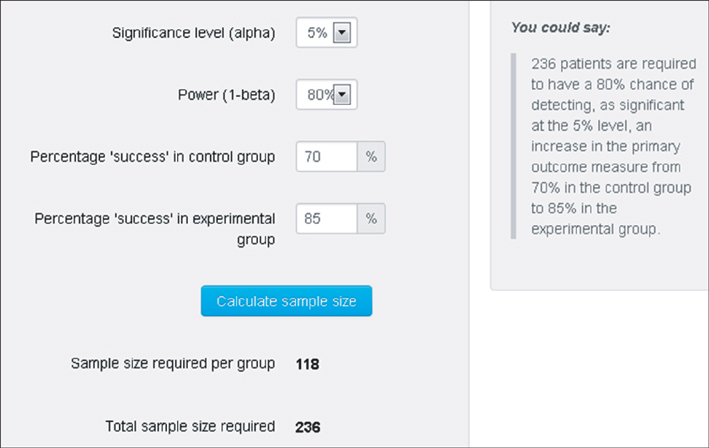
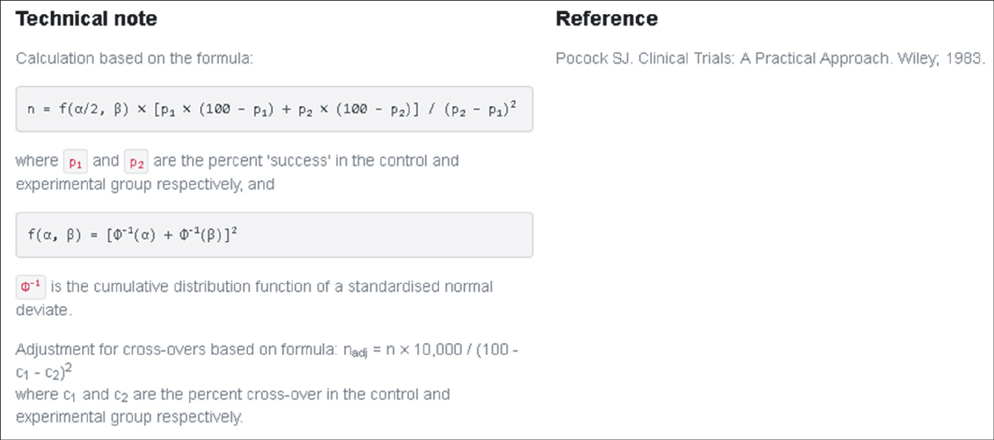
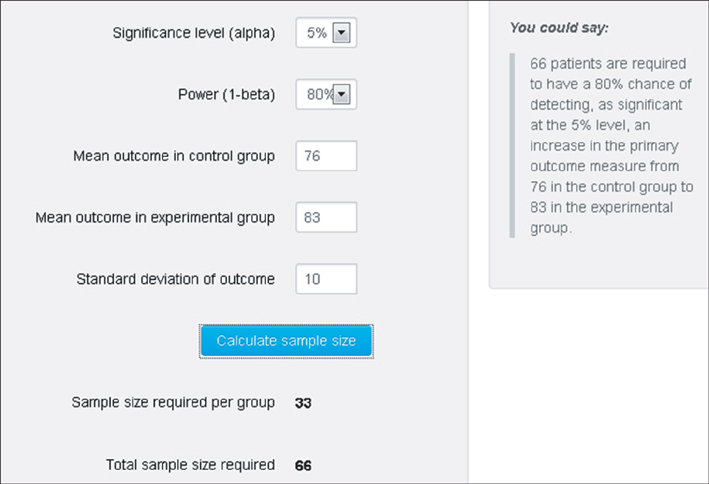
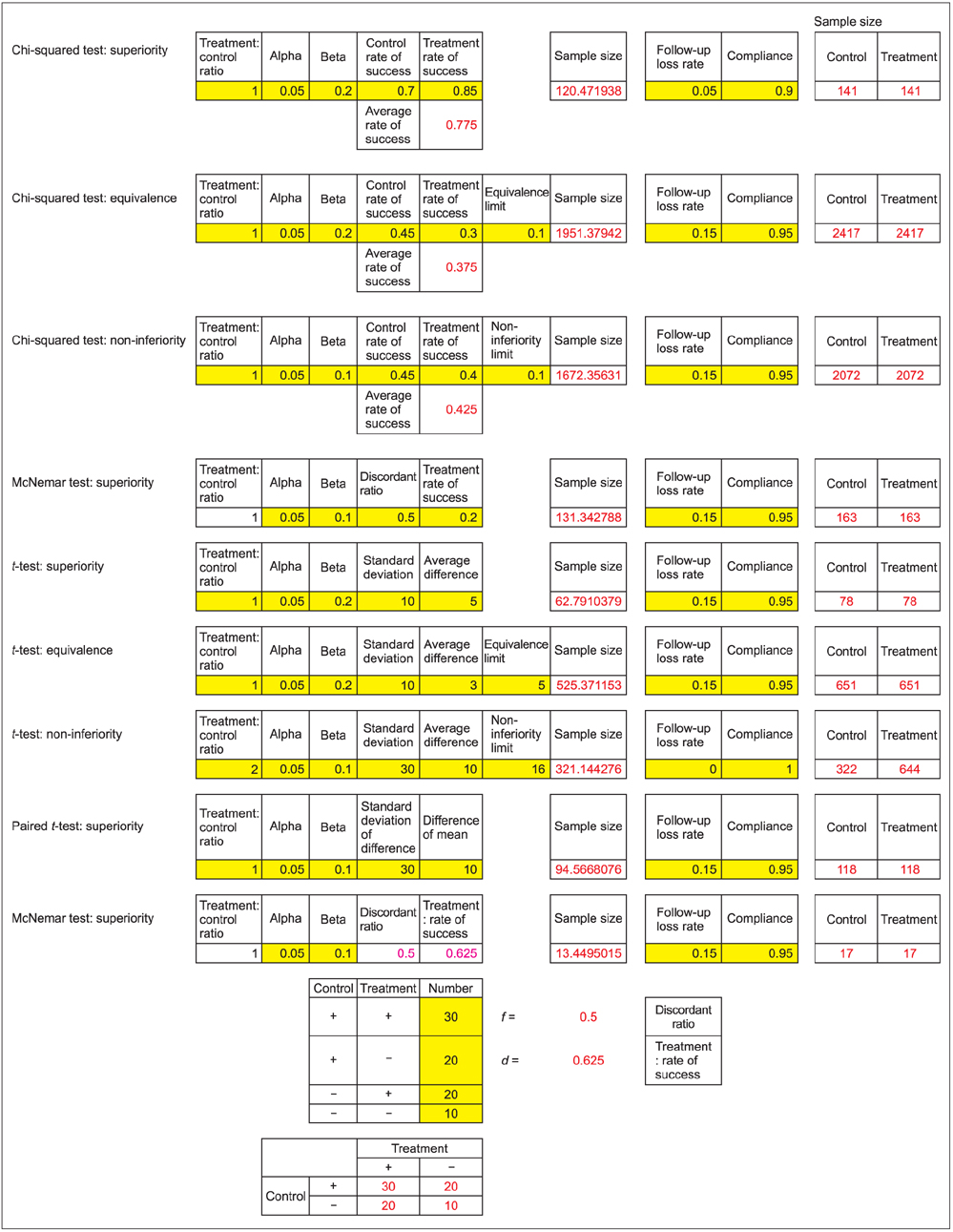
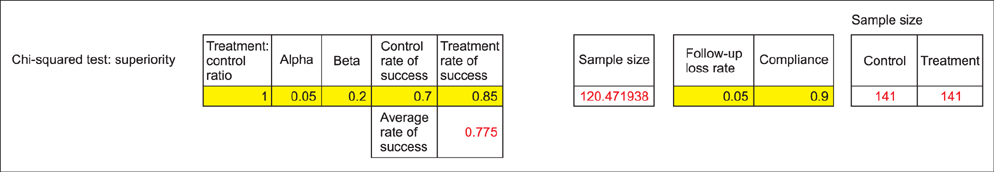
- WHY: Calculating the sample size is essential to reduce the cost of a study and to prove the hypothesis effectively. HOW: Referring to pilot studies and previous research studies, we can choose a proper hypothesis and simplify the studies by using a website or Microsoft Excel sheet that contains formulas for calculating sample size in the beginning stage of the study. MORE: There are numerous formulas for calculating the sample size for complicated statistics and studies, but most studies can use basic calculating methods for sample size calculation.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Pharmacologic treatment of osteoarthritis
Seung-Hoon Baek, Shin-Yoon Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2013;56(12):1123-1131. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2013.56.12.1123.Long-Term Efficacy of Mirabegron Add-On Therapy to Antimuscarinic Agents in Patients With Spinal Cord Injury
Seok-Hee Han, In Kyoung Cho, Joo Hwan Jung, Seong Ho Jang, Bum-Suk Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2019;43(1):54-61. doi: 10.5535/arm.2019.43.1.54.
Reference
-
1. Altman DG, Bland JM. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence. BMJ. 1995; 311(7003):485.
Article2. Petrie A. Statistics in orthopaedic papers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88(9):1121–1136.
Article3. Sexton SA, Ferguson N, Pearce C, Ricketts DM. The misuse of 'no significant difference' in British orthopaedic literature. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008; 90(1):58–61.
Article4. Wikipedia. Effect size [Internet]. Wikipedia;2013. cited 2013 May 22. Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Effect_size&oldid=554920483.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Considerations when calculating the sample size for an inequality test
- Sample size determination and power analysis using the G*Power software
- Sample size determination for repeated measures design using G Power software
- Calculation of Sample Size in Clinical Trials
- Sample size calculation in clinical trial using R