J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2013 Sep;15(3):145-151. 10.7461/jcen.2013.15.3.145.
The Anatomy of the Superficial Temporal Artery in Adult Koreans Using 3-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Angiogram: Clinical Research
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Yeungnam University, College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bychoi@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1491431
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2013.15.3.145
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The increased use of bypass surgery in the treatment of ischemic cerebrovascular diseases requires a better understanding of the superficial temporal artery (STA) anatomy. This study is to describe the gross anatomy of STA in adult Korean population with respect to cranial surgery and to provide basic anatomic data for bypass surgery.
METHODS
The study evaluated retrospectively 35 patients who visited the neurosurgery department at a single institution. For each patient, both the left and right STA (70 vessels) were evaluated by a 3-dimensional computed tomographic angiogramfor diameter and anatomic relationships to external landmarks.
RESULTS
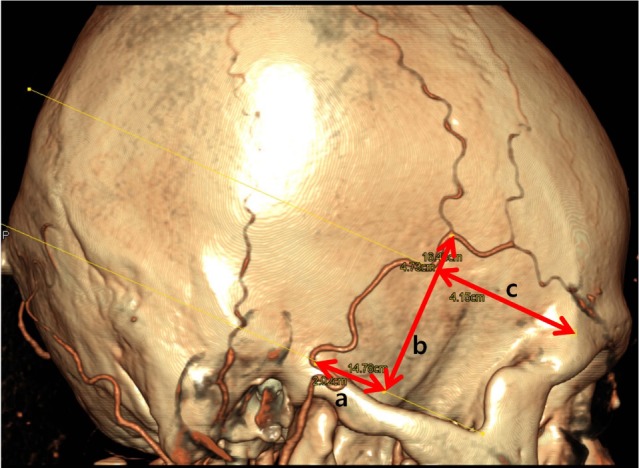
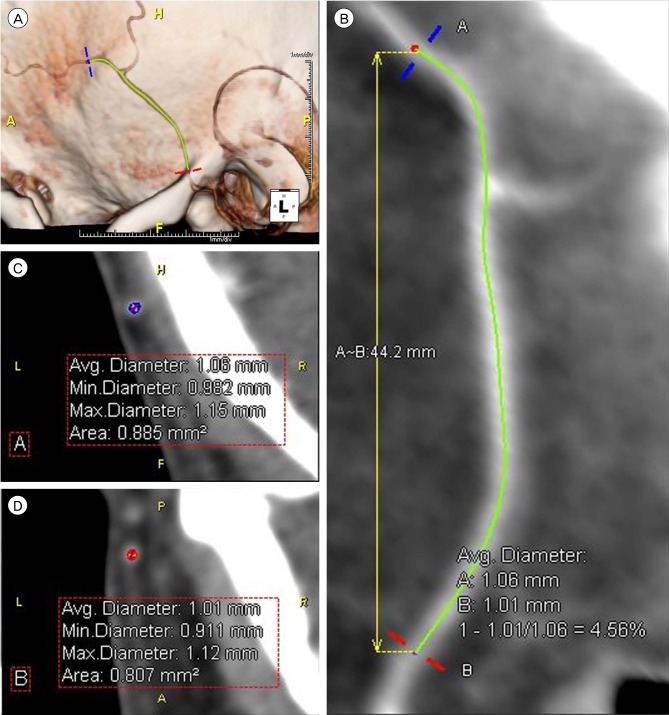
Of 70 STAs, 69 had a bifurcation. Among these, 57 (82.6%) were above the superior margin of the zygomatic arch. The STA bifurcation was 53.2 +/- 5.9 mm posterior to the keyhole, 9.5 +/- 5.3 mm anterior to the posterior margin of condylar process of the mandible, and 21.7 +/- 15.8 mm superior to the superior margin of the zygomatic arch. The inner diameter of the STA was 1.8 +/- 0.5 mm at the superior margin of the zygomatic arch, and 1.4 +/- 0.4 mm and 1.4 +/- 0.5 mm for frontal and parietal branches, respectively. The 75.7% of frontal and 66.7% of parietal branches were suitable for microvascular anastomosis.
CONCLUSION
This present study demonstrated the STA in Korean adults, which may benefit the clinician in dealing with the surgical procedures related to this STA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Superficial Temporal Artery-Sparing Mini-Pterional Approach for Cerebral Aneurysm Surgery
Jun-Young Ahn, Sung-Tae Kim, Ki-Chang Yi, Won-Hee Lee, Sung Hwa Paeng, Young-Gyun Jeong
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(1):8-14. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.0707.004.
Reference
-
1. Abul-Hassan HS, von Drasek Ascher G, Acland RD. Surgical anatomy and blood supply of the fascial layers of the temporal region. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1986; 1. 77(1):17–28. PMID: 3941846.2. Chen TH, Chen CH, Shyu JF, Wu CW, Lui WY, Liu JC. Distribution of the superficial temporal artery in the Chinese adult. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999; 10. 104(5):1276–1279. PMID: 10513906.
Article3. Marano SR, Fischer DW, Gaines C, Sonntag VK. Anatomical study of the superficial temporal artery. Neurosurgery. 1985; 6. 16(6):786–790. PMID: 4010900.
Article4. Mwachaka P, Sinkeet S, Ogeng'o J. Superficial temporal artery among Kenyans: Pattern of branching and its relation to pericranial structures. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2010; 2. 69(1):51–53. PMID: 20235051.5. Pinar YA, Govsa F. Anatomy of the superficial temporal artery and its branches: Its importance for surgery. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006; 6. 28(3):248–253. PMID: 16568216.
Article6. Sinna R, Hajji H, Qassemyar Q, Perignon D, Benhaim T, Havet E. Anatomical background of the perforator flap based on the deep branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery (SCIP Flap): A cadaveric study. Eplasty. 2010; 1. 10:e11. PMID: 20090859.7. Stock AL, Collins HP, Davidson TM. Anatomy of the superficial temporal artery. Head Neck Surg. 1980; Jul-Aug. 2(6):466–469. PMID: 7390853.
Article8. Tayfur V, Edizer M, Magden O. Anatomic bases of superficial temporal artery and temporal branch of facial nerve. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 11. 21(6):1945–1947. PMID: 21119463.
Article9. Yonenaga K, Tohnai I, Mitsudo K, Mori Y, Saijo H, Iwai T, et al. Anatomical study of the external carotid artery and its branches for administration of superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy via the superficial temporal artery. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011; 12. 16(6):654–659. PMID: 21537883.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Topographical Relationship of the Superficial Temporal Vessels and the Auriculotemporal Nerve
- Aneurysms of the superficial temporal artery
- Traumatic Pseudoaneurysm of the Superficial Temporal Artery Diagnosed by 3-dimensional CT Angiography
- Computed Tomographic Angiogram of an Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm Causing Acute Retrobulbar Optic Neuropathy: A Case Report
- Anatomical variants of the superficial temporal artery in patients with microtia: a pilot descriptive study