Korean J Radiol.
2013 Apr;14(2):321-323. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.321.
Pure Intrasellar Meningioma Located Under the Pituitary Gland: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Guri Hospital, Guri 471-701, Korea. dwpark@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul 133-792, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Guri Hospital, Guri 471-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1482794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.2.321
Abstract
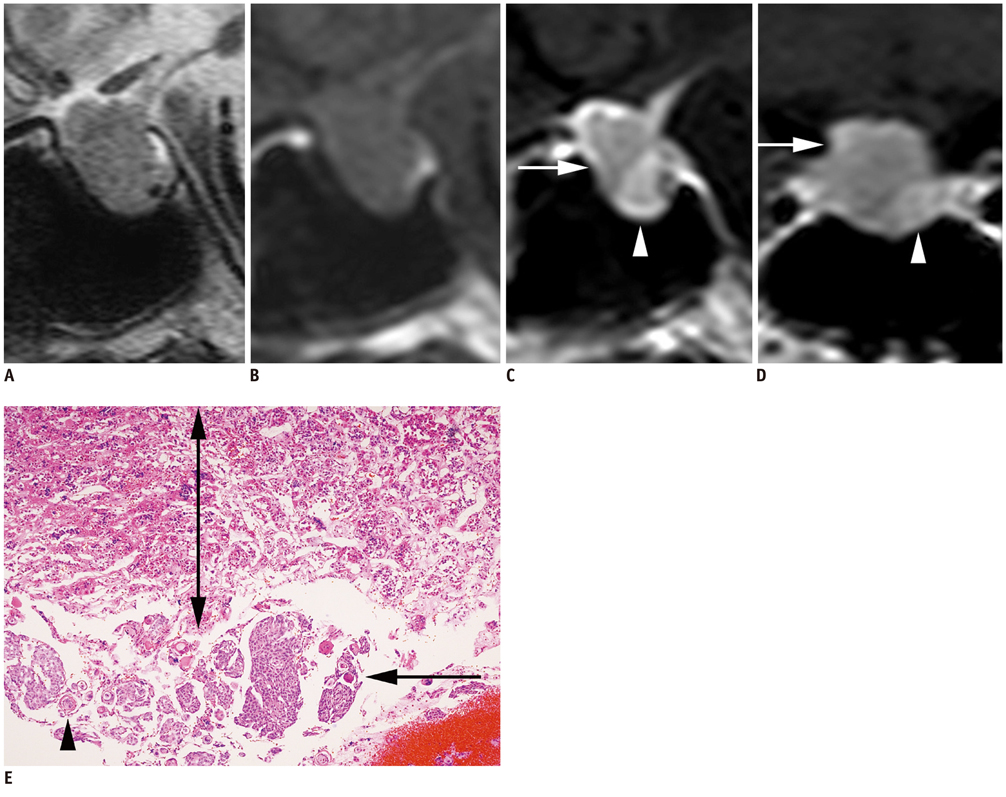
- Most intrasellar meningiomas are located in the subdiaphragmatic and supraglandular region because they originate from the diaphragma sellae. Subglandular meningiomas located under the pituitary gland are extremely rare. Intrasellar meningiomas in the subdiaphragmatic and subglandular region probably originate from the dura in the sellar floor. We report a case of a subglandular meningioma along with a review of the literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nozaki K, Nagata I, Yoshida K, Kikuchi H. Intrasellar meningioma: case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 1997. 47:447–452. discussion 452-454.2. Kudo H, Takaishi Y, Minami H, Takamoto T, Kitazawa S, Maeda S, et al. Intrasellar meningioma mimicking pituitary apoplexy: case report. Surg Neurol. 1997. 48:374–381.3. Peker S, Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Kiliç T, Pamir MN. Microsurgical anatomy of the lateral walls of the pituitary fossa. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005. 147:641–648. discussion 649.4. Hardy J, Robert F. [A meningioma of the sella turcica, subdiaphragmatic variety. Exeresis through the transsphenoidal route]. Neurochirurgie. 1969. 15:535–543.5. Al-Mefty O, Holoubi A, Rifai A, Fox JL. Microsurgical removal of suprasellar meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1985. 16:364–372.6. Kinjo T, al-Mefty O, Ciric I. Diaphragma sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1995. 36:1082–1092.7. Cappabianca P, Cirillo S, Alfieri A, D'Amico A, Maiuri F, Mariniello G, et al. Pituitary macroadenoma and diaphragma sellae meningioma: differential diagnosis on MRI. Neuroradiology. 1999. 41:22–26.8. Civit T, Marchal JC, Pinelli C, Auque J, Hepner H. [Meningiomas of the sellar diaphragm. Apropos of 4 cases]. Neurochirurgie. 1997. 43:21–26. discussion 26-27.