J Korean Surg Soc.
2009 Apr;76(4):262-265. 10.4174/jkss.2009.76.4.262.
Pancreas-Sparing Total Duodenectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunkim@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1465066
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2009.76.4.262
Abstract
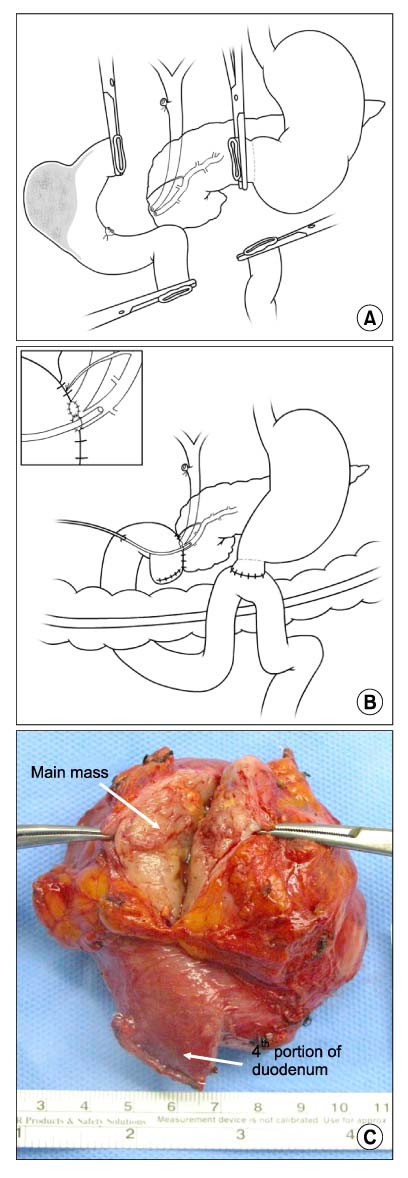
- Pancreas-sparing total duodenectomy (PSTD), which allows preservation of the pancreas in its entirety is a promising procedure for benign or premalignant lesions at duodenum without invading the pancreas. We report two cases of tubular adenoma of Ampulla of Vater and a GIST of duodenum, which were resected by PSTD. The proximal duodenum was transected at 2 cm distal of pylorus and the distal end was cut in the distal portion of the Treitz ligament. The proximal jejunal limb was used for biliary-pancreatic duct systems reconstruction with end-to-side anastomosis and distal jejunum was anastomosed to duodenal bulb with an end-to-side anastomosis. Although a pancreatic fistula occurred in one patient, it was improved by conservative management. PSTD is a challenging surgical technique and requires excellent knowledge of anatomy. If performed for appropriate indications, PSTD is a useful alternative to formal pancreatoduodenecotmy and can be done safely with gastrointestinal function maintained.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung RS, Church JM, vanStolk R. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy: indications, surgical technique, and results. Surgery. 1995. 117:254–259.2. Konishi M, Kinoshita T, Nakagohri T, Takahashi S, Gotohda N, Ryu M. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for duodenal neoplasms including malignancies. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007. 54:753–757.3. Mackey R, Walsh RM, Chung R, Brown N, Smith A, Church J, et al. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy is effective management for familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2005. 9:1088–1093.4. Kimura Y, Mukaiya M, Honma T, Okuya K, Akizuki E, Kihara C, et al. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for a recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma: report of a case. Surg Today. 2005. 35:91–93.5. Eisenberger CF, Knoefel WT, Peiper M, Yekebas EF, Hosch SB, Busch C, et al. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy in duodenal pathology: indications and results. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. 51:727–731.6. Lundell L, Hyltander A, Liedman B. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy: technique and indications. Eur J Surg. 2002. 168:74–77.7. Sarmiento JM, Thompson GB, Nagorney DM, Donohue JH, Farnell MB. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for duodenal polyposis. Arch Surg. 2002. 137:557–562.8. Suzuki H, Yasui A. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy for a huge leiomyosarcoma in the third portion of the duodenum. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999. 6:414–417.9. Kalady MF, Clary BM, Tyler DS, Pappas TN. Pancreas-preserving duodenectomy in the management of duodenal familial adenomatous polyposis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002. 6:82–87.10. Lee SE, Yang SH, Jang JY, Kim SW. Pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a comparison between the two pancreaticojejunostomy methods for approximating the pancreatic parenchyma to the jejunal seromuscular layer: interrupted vs continuous stitches. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. 13:5351–5356.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic pancreas-preserving near total duodenectomy for large villous adenoma in patients with total colectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis
- Pancreatic Head Resection with Segmental Duodenectomy
- Lymphoepithelial Cyst of the Pancreas: A Case Report
- Pancreas transplantation
- Agenesis of the Dorsal Pancreas: An autopsy case