J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Feb;28(2):213-219. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.213.
Feasibility and Efficacy of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer-C Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea. mskim@kcch.re.kr
- 2CyberKnife Center, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1429183
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.213
Abstract
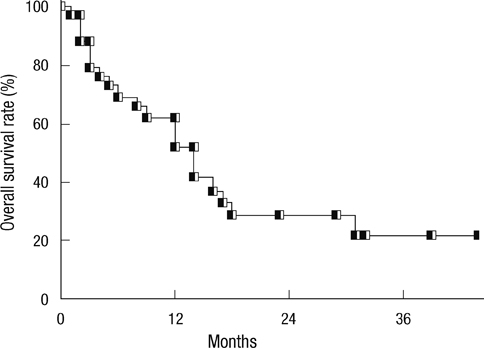
- The purpose of this study was to assess the feasibility and efficacy of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for liver tumor in patients with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC)-C stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 35 patients between 2003 and 2011. Vascular invasion was diagnosed in 32 patients, extrahepatic metastases in 11 and both in 8. Thirty-two patients were categorized under Child-Pugh (CP) class A and 3 patients with CP class B. The median SABR dose was 45 Gy (range, 30-60 Gy) in 3-5 fractions. The median survival time was 14 months. The 1- and 3-yr overall survival (OS) rate was 52% and 21%, respectively. On univariate analysis, CP class A and biologically equivalent dose > or = 80 Gy10 were significant determinants of better OS. Severe toxicity above grade 3, requiring prompt therapeutic intervention, was observed in 5 patients. In conclusion, SABR for BCLC-C stage HCC showed 1-yr OS rate of 52% but treatment related toxicity was moderate. We suggest that patients with CP class A are the best candidate and at least SABR dose of 80 Gy10 is required for BCLC-C stage.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/mortality/*radiotherapy
Feasibility Studies
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Liver Failure/etiology
Liver Neoplasms/mortality/*radiotherapy
Male
Middle Aged
Myelitis/etiology
Neoplasm Staging
Prognosis
Radiation Dosage
Retrospective Studies
Severity of Illness Index
Stereotaxic Techniques
Survival Rate
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Does It Have a Role in Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
Seo Hee Choi, Jinsil Seong
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(8):912-922. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.8.912.2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association–National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
,
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(7):1042-1113. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0140.2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
J Liver Cancer. 2023;23(1):1-120. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2022.11.07.Current perspectives on radiotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma management: a comprehensive review
Dowook Kim, Jun-Sang Kim
J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):33-46. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2024.02.26.
Reference
-
1. Kudo M, Han KH, Kokudo N, Cheng AL, Choi BI, Furuse J, Izumi N, Park JW, Poon RT, Sakamoto M. Liver cancer working group report. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010. 40:i19–i27.2. Han KH, Kudo M, Ye SL, Choi JY, Poon RT, Seong J, Park JW, Ichida T, Chung JW, Chow P, et al. Asian consensus workshop report: expert consensus guideline for the management of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Oncology. 2011. 81:158–164.3. Korean Liver Cancer Study Group and National Cancer Center, Korea. Practice guidelines for management of hepatocellular carcinoma 2009. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. 15:391–423.4. Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ, Lin SM, Yoshida H, Kudo M, Lee JM, Choi BI, Poon RT, et al. Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2010. 4:439–474.5. Marrero JA, Kudo M, Bronowicki JP. The challenge of prognosis and staging for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 2010. 15:23–33.6. Marrero JA, Fontana RJ, Barrat A, Askari F, Conjeevaram HS, Su GL, Lok AS. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of 7 staging systems in an american cohort. Hepatology. 2005. 41:707–716.7. Cillo U, Bassanello M, Vitale A, Grigoletto FA, Burra P, Fagiuoli S, D'Amico F, Ciarleglio FA, Boccagni P, Brolese A, et al. The critical issue of hepatocellular carcinoma prognostic classification: which is the best tool available? J Hepatol. 2004. 40:124–131.8. Cillo U, Vitale A, Grigoletto F, Farinati F, Brolese A, Zanus G, Neri D, Boccagni P, Srsen N, D'Amico F, et al. Prospective validation of the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging System. J Hepatol. 2006. 44:723–731.9. Wang JH, Changchien CS, Hu TH, Lee CM, Kee KM, Lin CY, Chen CL, Chen TY, Huang YJ, Lu SN. The efficacy of treatment schedules according to Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging for hepatocellular carcinoma - survival analysis of 3892 patients. Eur J Cancer. 2008. 44:1000–1006.10. Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:378–390.11. Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009. 10:25–34.12. Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, Coia L, Goitein M, Munzenrider JE, Shank B, Solin LJ, Wesson M. Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991. 21:109–122.13. Kim JY, Chung SM, Choi BO, Kay CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: improved treatment outcomes with external beam radiation therapy. Hepatol Res. 2011. 41:813–824.14. Seo YS, Kim MS, Yoo SY, Cho CK, Choi CW, Kim JH, Han CJ, Park SC, Lee BH, Kim YH, et al. Preliminary result of stereotactic body radiotherapy as a local salvage treatment for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010. 102:209–214.15. Kang JK, Kim MS, Cho CK, Yang KM, Yoo HJ, Kim JH, Bae SH, Jung DH, Kim KB, Lee DH, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma as a local salvage treatment after incomplete transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer. 2012. 118:5424–5431.16. Vitale A, Morales RR, Zanus G, Farinati F, Burra P, Angeli P, Frigo AC, Del Poggio P, Rapaccini G, Di Nolfo MA, et al. Barcelona clinic liver cancer staging and transplant survival benefit for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2011. 12:654–662.17. Yang T, Lin C, Zhai J, Shi S, Zhu M, Zhu N, Lu JH, Yang GS, Wu MC. Surgical resection for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma according to Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) Staging. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. 138:1121–1129.18. Kim TH, Kim DY, Park JW, Kim YI, Kim SH, Park HS, Lee WJ, Park SJ, Hong EK, Kim CM. Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients for whom transcatheter arterial chemoembolization was ineffective or unsuitable. Am J Clin Oncol. 2006. 29:568–575.19. Yoon SM, Lim YS, Won HJ, Kim JH, Kim KM, Lee HC, Chung YH, Lee YS, Lee SG, Park JH, et al. Radiotherapy plus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma invading the portal vein: long-term patient outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. 82:2004–2011.20. Choi BO, Choi IB, Jang HS, Kang YN, Jang JS, Bae SH, Yoon SK, Chai GY, Kang KM. Stereotactic body radiation therapy with or without transarterial chemoembolization for patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma: preliminary analysis. BMC Cancer. 2008. 8:351.21. Llovet JM. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005. 40:225–235.22. Groupe d'etude et de traitement du carcinome hepatocellulaire. A comparison of lipiodol chemoembolization and conservative treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1995. 332:1256–1261.23. Kwon JH, Bae SH, Kim JY, Choi BO, Jang HS, Jang JW, Choi JY, Yoon SK, Chung KW. Long-term effect of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma ineligible for local ablation therapy or surgical resection. Stereotactic radiotherapy for liver cancer. BMC Cancer. 2010. 10:475.24. Andolino DL, Johnson CS, Maluccio M, Kwo P, Tector AJ, Zook J, Johnstone PA, Cardenes HR. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. 81:e447–e453.25. Bae SH, Kim MS, Cho CK, Kang JK, Lee SY, Lee KN, Lee DH, Han CJ, Yang KY, Kim SB. Predictor of severe gastroduodenal toxicity after stereotactic body radiotherapy for abdomino-pelvic malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. 84:e469–e474.26. Noh G, Han C, Kim Y, Yang K, Park S, Kim J, Kim Y, Kim M. A case of paraplegia after successful treatment of cyberknife for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011. 11:165–171.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent developments in radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma
- Evaluation of the Outcome after Transarterial Chemoembolization; Refinement of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage-B from Eastern Point of View
- The Optimal Selection of Radiotherapy Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Long-term survival after multimodal treatment involving radiotherapy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma with oligometastasis: a case report
- Subclassification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Intermediate Stage