Yonsei Med J.
2012 Mar;53(2):363-368. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.363.
Application of a New Spirometric Reference Equation and Its Impact on the Staging of Korean Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary, Allergy and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Medical Center, Anyang, Korea. pulmoks@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 1120204
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.363
Abstract
- PURPOSE
A new spirometric reference equation was recently developed from the first national chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) survey in Korea. However, Morris' equation has been preferred for evaluating spirometric values instead. The objective of this study was to evaluate changes in severity staging in Korean COPD patients by adopting the newly developed Korean equation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We evaluated the spirometric data of 441 COPD patients. The presence of airflow limitation was defined as an observed post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) less than 0.7, and the severity of airflow limitation was assessed according to GOLD stages. Spirometric values were reassessed using the new Korean equation, Morris' equation and other reference equations.
RESULTS
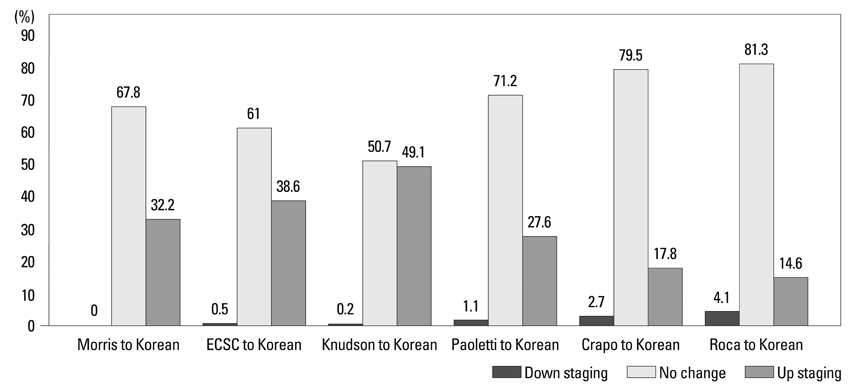
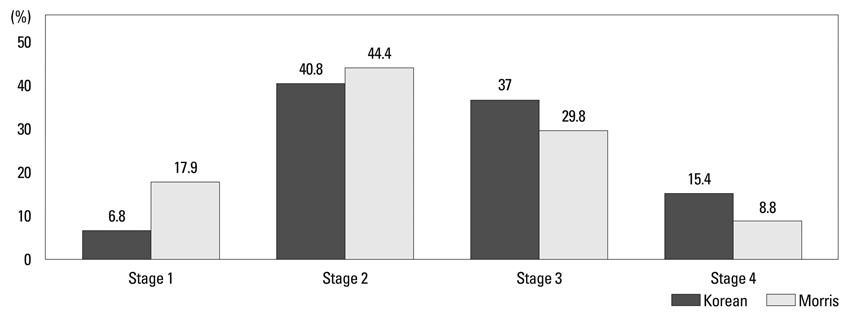
The severity of airflow limitation was differently graded in 143 (32.4%) patients after application of the new Korean equation when compared with Morris' equation. All 143 patients were reallocated into more severe stages (49 at mild stage, 65 at moderate stage, and 29 at severe stage were changed to moderate, severe and very severe stages, respectively). Stages according to other reference equations were changed in 18.6-49.4% of the patients.
CONCLUSION
These results indicate that equations from different ethnic groups do not sufficiently reflect the airflow limitation of Korean COPD patients. The Korean reference equation should be used for Korean COPD patients in order to administer proper treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fromer L, Cooper CB. A review of the GOLD guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. Int J Clin Pract. 2008. 62:1219–1236.
Article2. Fabbri LM, Hurd SS. GOLD Scientific Committee. Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD: 2003 update. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:1–2.
Article3. Celli BR, MacNee W. ATS/ERS Task Force. Standards for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD: a summary of the ATS/ERS position paper. Eur Respir J. 2004. 23:932–946.
Article4. Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J. 2005. 26:948–968.
Article5. Morris JF, Koski A, Johnson LC. Spirometric standards for healthy nonsmoking adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971. 103:57–67.
Article6. Choi JK, Paek D, Lee JO. Normal predictive values of spirometry in Korean population. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2005. 58:230–242.
Article7. American Thoracic Society. Standardization of Spirometry, 1994 Update. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995. 152:1107–1136.8. Roca J, Sanchis J, Agusti-Vidal A, Segarra F, Navajas D, Rodriguez-Roisin R, et al. Spirometric reference values from a Mediterranean population. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986. 22:217–224.9. Paoletti P, Pistelli G, Fazzi P, Viegi G, Di Pede F, Giuliano G, et al. Reference values for vital capacity and flow-volume curves from a general population study. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986. 22:451–459.10. Standardized lung function testing. Report working party. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1983. 19:Suppl 5. 1–95.11. Knudson RJ, Lebowitz MD, Holberg CJ, Burrows B. Changes in the normal maximal expiratory flow-volume curve with growth and aging. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983. 127:725–734.12. Crapo RO, Morris AH, Gardner RM. Reference spirometric values using techniques and equipment that meet ATS recommendations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981. 123:659–664.13. Roca J, Burgos F, Sunyer J, Saez M, Chinn S, Antó JM, et al. Group of the European Community Respiratory Health Survey. References values for forced spirometry. Eur Respir J. 1998. 11:1354–1362.
Article14. Korotzer B, Ong S, Hansen JE. Ethnic differences in pulmonary function in healthy nonsmoking Asian-Americans and European-Americans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 161:1101–1108.
Article15. Aelony Y. Ethnic norms for pulmonary function tests. Chest. 1991. 99:1051.
Article16. Oh YM, Hong SB, Shim TS, Lim CM, Koh Y, Kim WS, et al. Effect of a new spirometric reference equation on the interpretation of spirometric patterns and disease severity. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006. 60:215–220.
Article17. Hardie JA, Buist AS, Vollmer WM, Ellingsen I, Bakke PS, Mørkve O. Risk of over-diagnosis of COPD in asymptomatic elderly never-smokers. Eur Respir J. 2002. 20:1117–1122.
Article18. Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB. Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 159:179–187.
Article19. Enright PL, Kronmal RA, Higgins M, Schenker M, Haponik EF. Spirometry reference values for women and men 65 to 85 years of age. Cardiovascular health study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993. 147:125–133.
Article20. Ra SW, Oh JS, Hong SB, Shim TS, Lim CM, Koh YS, et al. Effect of the changing the lower limits of normal and the interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2006. 61:129–136.
Article21. Celli BR, Halbert RJ, Isonaka S, Schau B. Population impact of different definitions of airway obstruction. Eur Respir J. 2003. 22:268–273.
Article22. Hwang YI, Kim CH, Kang HR, Shin T, Park SM, Jang SH, et al. Comparison of the prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease diagnosed by lower limit of normal and fixed ratio criteria. J Korean Med Sci. 2009. 24:621–626.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of a New Spirometric Reference Equation on the Interpretation of Spirometric Patterns and Disease Severity
- Cor Pulmonale with Particular Reference to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Phenotype of asthma-chronic obstructive pulmonary disease overlap syndrome
- Spirometric Interpretation and Clinical Relevance According to Different Reference Equations
- Management of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease