J Korean Med Sci.
2008 Dec;23(6):1102-1104. 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.6.1102.
Serial Magnetic Resonance Imagings of Multiple Brain Abscesses in a Patient with Pneumococcal Meningoencephalitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. dacda@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1107539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.6.1102
Abstract
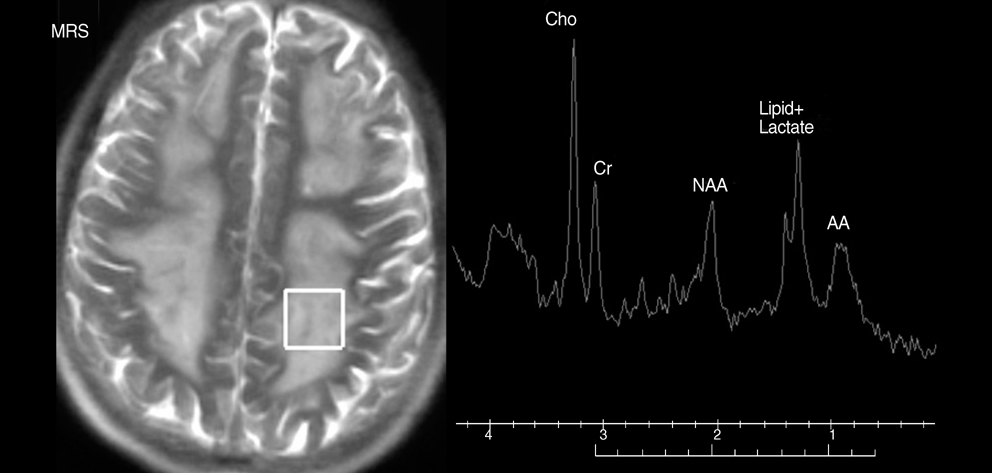
- We report a 43-yr-old man manifesting bacterial meningoencephalitis and multiple abscesses by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Serial magnetic resonance (MR) imagings and MR spectroscopy showed the evolution of multiple brain abscesses over 4 weeks: the enhanced rings became thicker and the dimension of whole lesions larger despite shrinkage of the ring-enhanced regions. These findings may be evidence of active inflammation working to sequestrate the lesion and protect the surrounding normal brain parenchyma from additional damage, even in the final stage of the brain abscess.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kastenbauer S, Pfister HW. Pneumococcal meningitis in adults: spectrum of complications and prognostic factors in a series of 87 cases. Brain. 2003. 126:1015–1025.
Article2. Weisfelt M, de Gans J, van der Poll T, van de Beek D. Pneumococcal meningitis in adults: new approaches to management and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2006. 5:332–342.
Article3. Carpenter J, Stapleton S, Holliman R. Retrospective analysis of 49 cases of brain abscess and review of the literature. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007. 26:1–11.
Article4. Singhal AB, Topcuoglu MA, Buonanno FS. Acute ischemic stroke patterns in infective and nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis: a diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging study. Stroke. 2002. 33:1267–1273.5. Kielian T. Immunopathogenesis of brain abscess. J Neuroinflammation. 2004. 1:16.6. Erdogan C, Hakyemez B, Yildirim N, Parlak M. Brain abscess and cystic brain tumor: discrimination with dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion-weighted MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2005. 29:663–667.7. Lai PH, Ho JT, Chen WL, Hsu SS, Wang JS, Pan HB, Yang CF. Brain abscess and necrotic brain tumor: discrimination with proton MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 23:1369–1377.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple, Diffuse Brain Abscesses due to Listeria Monocytogenes
- A case of fatal pneumococcal 19A meningoencephalitis despite administration of seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
- Recurrent Streptococcus Pneumoniae Meningoencephalitis in a Patient With a Transethmoidal eningoencephalocele
- Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Complicated by Meningoencephalitis and Radiologic findings: a Rare Case Report
- Meningoencephalitis associated with Parvovirus B19 Infection in an Immunocompetent Patient