J Vet Sci.
2010 Mar;11(1):9-13. 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.1.9.
Multidetector row computed tomography evaluation of the micropig kidney as a potential renal donor
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Biotherapy Human Resources Center (BK21), Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea. hjhan@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju 501-757, Korea.
- 3College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- KMID: 1106151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.1.9
Abstract
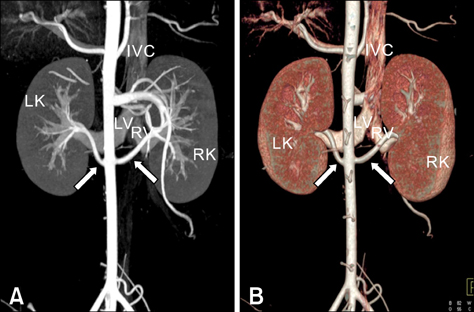
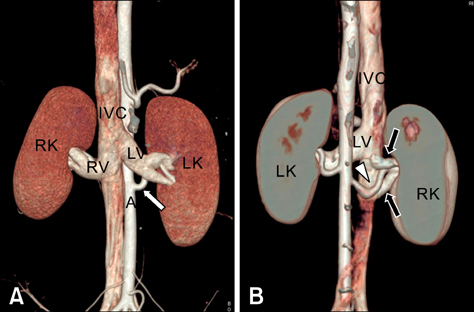
- Multidetector row computed tomography (MDCT) provides anatomical information about the kidney and other internal organs. Presently, the suitability of 64-channel MDCT to assess the kidney of healthy micropigs was evaluated. Morphological evaluations of the kidney and the major renal vessels of six healthy micropigs were carried out using MDCT, recording kidney volume and the diameter and length of renal arteries and veins. The mean diameters and lengths of the renal artery were 0.44 +/- 0.05 and 4.51 +/- 0.55 cm on the right side and 0.46 +/- 0.06 and 3.36 +/- 0.27 cm on the left side, respectively. The mean diameters and lengths of the renal vein were 1.44 +/- 0.52 and 4.22 +/- 1.29 cm on the right side and 1.38 +/- 0.17 and 5.15 +/- 0.87 cm on the left side, respectively. The mean volume of the right kidney was 79.3 +/- 14.5 mL and of the left kidney was 78.0 +/- 13.9 mL. The data presented in this study suggest that the MDCT offers a noninvasive, rapid, and accurate method for the evaluation of the renal anatomy in living kidney donors. It also provides sufficient information about extra-renal anatomy important for donor surgery and determination of organ suitability.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dooldeniya MD, Warrens AN. Xenotransplantation: where are we today? J R Soc Med. 2003. 96:111–117.
Article2. Foley WD. Special focus session: multidetector CT: abdominal visceral imaging. Radiographics. 2002. 22:701–719.3. Grude M, Juergens KU, Wichter T, Paul M, Fallenberg EM, Muller JG, Heindel W, Breithardt G, Fischbach R. Evaluation of global left ventricular myocardial function with electrocardiogram-gated multidetector computed tomography: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol. 2003. 38:653–661.
Article4. Hosenpud JD, Bennett LE, Keck BM, Fiol B, Boucek MM, Novick RJ. The registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: fifteenth official report-1998. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1998. 17:656–668.
Article5. Janschek EC, Rothe AU, Hölzenbein TJ, Langer F, Brugger PC, Pokorny H, Domenig CM, Rasoul-Rockenschaub S, Mühlbacher F. Anatomic basis of right renal vein extension for cadaveric kidney transplantation. Urology. 2004. 63:660–664.
Article6. Juergens KU, Maintz D, Grude M, Boese JM, Heimes B, Fallenberg EM, Heindel W, Fischbach R. Multi-detector row computed tomography of the heart: does a multi-segment reconstruction algorithm improve left ventricular volume measurements? Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:111–117.
Article7. Kalender WA, Polacin A. Physical performance characteristics of spiral CT scanning. Med Phys. 1991. 18:910–915.
Article8. Kawamoto S, Montgomery RA, Lawler LP, Horton KM, Fishman EK. Multidetector CT angiography for preoperative evaluation of living laparoscopic kidney donors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:1633–1638.
Article9. Kim T, Murakami T, Takahashi S, Hori M, Takahara S, Ichimaru N, Okuyama A, Narumi Y, Nakamura H. Evaluation of renal arteries in living renal donors: comparison between MDCT angiography and gadolinium-enhanced 3D MR angiography. Radiat Med. 2006. 24:617–624.
Article10. Newman SJ, Confer AW, Panciera RJ. McGavin MD, Zachary JF, editors. Urinary system. Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease. 2006. 4th ed. St. Louis: Elsvier;613–691.11. Prokop M. General principles of MDCT. Eur J Radiol. 2003. 45:Suppl 1. S4–S10.
Article12. Saldarriaga B, Pérez AF, Ballesteros LE. A direct anatomical study of additional renal arteries in a Colombian mestizo population. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2008. 67:129–134.13. Shin HS, Chung BH, Lee SE, Kim WJ, Ha HI, Yang CW. Measurement of kidney volume with multi-detector computed tomography scanning in young Korean. Yonsei Med J. 2009. 50:262–265.
Article14. Smith PA, Ratner LE, Lynch FC, Corl FM, Fishman EK. Role of CT angiography in the preoperative evaluation for laparoscopic nephrectomy. Radiographics. 1998. 18:589–601.
Article15. Tunaci A, Yekeler E. Multidetector row CT of the kidneys. Eur J Radiol. 2004. 52:56–66.
Article16. Turba UC, Uflacker R, Bozlar U, Hagspiel KD. Normal renal arterial anatomy assessed by multidetector CT angiography: are there differences between men and women? Clin Anat. 2009. 22:236–242.
Article17. Valastro M, Veroux M, Macarone M, Cappello D, Vizcarra D, Gagliano M, Di Mare M, Spataro M, Giuffrida G, Tallarita T, Magnano San Lio V, Veroux P. Multi-detector row CT scanner angiography in the evaluation of living kidney donors. Chir Ital. 2007. 59:337–341.18. Wilmut I, Schnieke AE, McWhir J, Kind AJ, Campbell KH. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature. 1997. 385:810–813.
Article19. Wintersperger BJ, Herzog P, Jakobs T, Reiser MF, Becker CR. Initial experience with the clinical use of a 16 detector row CT system. Crit Rev Comput Tomogr. 2002. 43:283–316.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multidetector computed tomographic angiography evaluation of micropig major systemic vessels for xenotransplantation
- Sacroiliitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Comparison with Multidetector Row CT and Plain Radiography
- Multidetector-Row CT Findings of Gastric Cystic Lymphangioma: A Case Report
- Preoperative Radiologic Evaluation of Cholangiocarcinoma
- Multidetector Row CT Findings of a Sternal Variation